Abstract
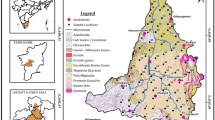
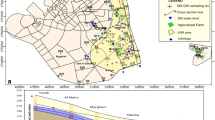
The main objective of the present study is to evaluate the hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater and its suitability for drinking water supply in Kangayam taluk, Tirupur district, Tamil Nadu, India. To achieve this objective, seventy-eight groundwater samples were collected from the wells spread over the study area during December 2016. The collected groundwater samples were tested in the laboratory for various hydrogeochemical parameters such as hydrogen ion concentration (pH), electrical conductivity, total dissolved solids, total hardness, calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium, chloride, bicarbonate, carbonate, nitrate, sulphate and fluoride. The analytical results were compared with WHO drinking water standards to assess the suitability of groundwater for drinking purposes. To understand the spatial variation of hydrogeochemical parameters over the study area, choropleth (zonation) maps were prepared using geographical information system (GIS). Overall groundwater quality zones were demarcated by overlaying and integrating all the spatial plots using GIS. Three groundwater quality zones such as (1) most desirable, (2) maximum allowable and (3) not permissible were demarcated based on the limits prescribed by the WHO for drinking purposes. This study indicates that 49% of the study area does not possess potable groundwater. About 21% of the area represents “most desirable” category, and the remaining 30% area represents “maximum allowable” category for drinking purposes. The Piper’s trilinear diagram indicates that groundwater of this region is Mixed CaMgCl type. As the groundwater quality is poor nearly 49% of the total area, it is necessary to go for treatment before drinking water supply. It is also essential to recharge the aquifer artificially to improve the quantity and quality of groundwater.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abboud, I. A. (2018). Statistical analysis of the hydro-geochemical evolution of groundwater in the aquifers of the Yarmouk basin, North Jordan. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11, 111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3448-z.
Al-Abadi, A. (2015). Modeling of groundwater productivity in north-eastern Wasit Governorate, Iraq by using frequency ratio and Shannon’s entropy models. Applied Water Science, 7(2), 699–716. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0283-1.
Alaya, M. B., Saidi, S., Zemni, T., & Zargouni, F. (2014). Suitability assessment of deep groundwater for drinking and irrigation use in the Djeffara aquifers (Northern Gabes, south-eastern Tunisia). Environmental Earth Sciences, 71, 3387–3421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2729-9.
Annapoorna, H., & Janardhanab, M. R. (2015). Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking purpose in rural areas surrounding a defunct copper mine. Aquatic Procedia, 4, 685–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqpro.02.088.
APHA. (1999). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington DC: American Public Health Association.
Ashwani, K. S., & Abhay, K. T. (2014). Hydrogeochemical investigation and groundwater quality assessment of Pratapgarh District, Uttar Pradesh. Journal Geological Society of India, 83, 329–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-014-0045-y.
Barbieri, M., Nigro, A., & Petitta, M. (2017). Groundwater mixing in the discharge area of San Vittorino Plain (Central Italy): Geochemical characterization and implication for drinking uses. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76, 393.
Behera, B., & Das, M. (2018). Application of multivariate statistical techniques for the characterization of groundwater quality of Bacheli and Kirandul Area, Dantewada District, Chattisgarh. Journal Geological Society of India, 91, 76–80.
Bertolo, R. H., Hirata, O., & Sracek, O. (2006). Geochemistry and geochemical modeling of unsaturated zones in a tropical region in Urania, Sao Paulo state, Brazil. Journal of Hydrology, 329(1–2), 49–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.02.001.
Bocanegra, E., Londono, O. M. Q., Martinez, D. E., & Romanelli, A. (2013). Quantification of the water balance and hydrogeological processes of groundwater-lake interactions in the Pampa Plain, Argentina. Environmental Earth Sciences, 68, 2347–2357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1916-4.
Bouderbala, A., Remini, B., SaaedHamoudi, A., & Pulido-Bosch, A. (2016). Assessment of groundwater vulnerability and quality in coastal aquifers: A case study (Tipaza, North Algeria). Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9, 181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2151-6.
Chandrasekar, N., Selvakumar, S., Srinivas, Y., Wilson, J. J., Peter, T. S., & Magesh, N. (2014). Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater quality along the coastal aquifers of southern Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71, 4739–4750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2864-3.
Choubisa, K., Sompuria, D. K., Choubisa, H., Pandya, S. K., Bhatt, S. K., & Parmar, L. (1995). Fluoride content in domestic water sources of Dungarpur district of Rajasthan. Indian Journal of Environmental Health, 37, 154–160.
Croize, D., Renard, F., & Gratier, J. P. (2013). Compaction and porosity reduction in carbonates: A review of observations, theory, and experiments. Advances in Geophysics, 54, 181–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-380940-7.00003-2.
Davis, J. C. (2002). Statistics and data analysis in geology (pp. 526–540). New York: John Wiley & Sons. (ASIA) Pte Ltd.
Enad. T. H. (2007). Stratigraphic and sedimentologic study of the Mukdadiya formation in Badra area Wasit Provinance. Unpublished M.Sc. thesis, Baghdad University (p. 136).
Ganzhorn, A. C., Trap, P., Arbaret, L., et al. (2016). Impact of gneissic layering and localized incipient melting upon melt flow during experimental deformation of migmatites. Journal of Structural Geology, 85, 68–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2016.02.004.
Geetha, A., Palanisamy, P. N., Sivakumar, P., Ganesh Kumar, P., & Sujatha, M. (2008). Assessment of underground water contamination and effect of textile effluents on Noyyal River basin in and around Tiruppur town, Tamil Nadu. Journal of Chemistry, 5(4), 696–705.
Gnanachandrasamy, G., Ramkumar, T., Venkatramanan, S., Vasudevan, S., Chung, S. Y., & Bagyaraj, M. (2013). Accessing groundwater quality in lower part of Nagapattinam district, Southern India: Using hydrogeochemistry and GIS interpolation techniques. Applied Water Science, 5, 39–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0172-z.
GSI. (1995). Geological and mineral map of Tamil Nadu and Pondicherry. Published by the Director General Geological Survey of India on 1: 500,000 scale.
Gulgundi, M. S., & Shetty, A. (2018). Groundwater quality assessment of urban Bengaluru using multivariate statistical techniques. Applied Water Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0684-z.
Hem, J. D. (1985). Study and interpretation of chemical characteristic of natural water. US Geological Survey. Water supply paper (Vol. 2254, p. 264).
Hu, N. J., Shi, X. F., Liu, J. H., Huang, P., Liu, Y. G., & Liu, Y. (2010). Concentrations and possible sources of PAHs in sediments from Bhai Bay and adjacent shelf. Environmental Earth Sciences, 60(8), 1771–1782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0313-0.
Iranmanesh, A., Locke, R. A., & Wimmer, B. T. (2014). Multivariate statistical evaluation of groundwater compliance data from the Illinois Basin-Decatur Project. Energy Procedia, 63, 3182–3194.
Karunanidhi, D., Vennila, G., Suresh, M., & Subramanian, S. K. (2013). Evaluation of the groundwater quality feasibility zones for irrigational purposes through GIS in Omalur Taluk, Salem District, South India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(10), 7320–7333.
Liu, P., Hoth, N., & Drebenstedt, C. (2017). Hydro-geochemical paths of multi-layer groundwater system in coal mining regions: Using multivariate statistics and geochemical modeling approaches. Science of the Total Environment, 601–602, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.146.
Michael, A. M. (1990). Irrigation; theory and practice (p. 801). New Delhi: Vikas Publishing House Pvt. Ltd.
Nagaraju, A., Kumar, K. S., & Thejaswi, A. (2014). Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation: A case study from Bandalamottu lead mining area, Guntur District, Andhra Pradesh, South India. Applied Water Science, 4, 385–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0154-1.
Narany, T. S., Ramli, M. F., Aris, A. Z., Sulaiman, W. N. A., Juahir, W. H., & Fakharian, K. (2014). Identification of the hydrogeochemical processes in groundwater using classic integrated geochemical methods and geostatistical techniques in Amol-Babol Plain, Iran. The Scientific World Journal. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/419058.
Perrin, J., Ahmed, S., & Hunkeler, D. (2011). The effects of geological heterogeneities and piezometric fluctuations on groundwater flow and chemistry in a hard rock aquifer, southern India. Hydrogeology Journal, 19(6), 1189–1201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-011-0745-y.
Piper, A. M. (1944). A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Transactions, American Geophysical Union, 25, 914–928.
Raju, N. J., Shukla, U. K., & Ram, P. (2011). Hydrogeochemistry for the assessment of groundwater quality in Varanasi: A fast-urbanizing center in Uttar Pradesh, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 173, 279–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1387-6.
Ramesh, K., & Elango, L. (2012). Groundwater quality and its suitability for domestic and agricultural use in Tondiar River basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(6), 3887–3899.
Ranjram, M., Gleeson, T., & Luijendijk, E. (2016). Is the permeability of crystalline rock in the shallow crust related to depth, lithology, or tectonic setting? In T. Gleeson & S. E. Ingebritse (Eds.), Crustal permeability (pp. 123–136). New York: Wiley.
Rasmussen, P. (1996). Monitoring shallow groundwater quality in agricultural watersheds in Denmark. Environmental Geology, 27(4), 309–319.
Reddy, A. G., & Kumar, K. N. (2010). Identification of the hydrogeochemical processes in groundwater using major ion chemistry: A case study of Penna-Chitravathi river basin in Southern India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 170(1–4), 365–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1239-4.
Richard, W. H. (1945). Estimating groundwater recharge. ISBN-13: 978-0521863964.
Sajil Kumar, P. J., Elango, L., & James, E. J. (2013). Assessment of hydrochemistry and groundwater quality in the coastal area of South Chennai, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0940-3.
Saravanan, K., Srinivasamoorthy, K., Gopinath, S., Prakash, R., Suma, C. S., Vinnarasi, J., et al. (2018). Geochemical evolution of groundwater along flow path in Upper Vellar sub basin, Tamil Nadu, India: An integrated approach using hydrochemistry, modeling and statistical techniques. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 4(2), 647–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0400-2.
Saravanan, K., Srinivasamoorthy, K., Prakash, R., et al. (2015). An evaluation of hydrogeochemistry of groundwater in Upper Vellar sub-basin using mineral stability and solute transport modelling. Aquatic Procedia, 4, 1119–1125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqpro.2015.02.142.
Singh, C. K., Shashtri, S., Rina, K., & Mukherjee, S. (2013). Chemometric analysis to infer hydro-geochemical processes in a semi-arid region of India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 6, 2915–2932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0597-3.
Srinivasamoorthy, K., Nanthakumar, C., Vasanthavigar, M., Vijayaraghavan, K., Rajivgandhi, R., Chidambaram, S., et al. (2011). Groundwater quality assessment from a hard rock terrain, Salem District of Tamil Nadu, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 4, 91–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-009-0076-7.
Studinger, M., Karner, G. D., Bell, R. E., et al. (2003). Geophysical models for the tectonic framework of the Lake Vostok region, East Antarctica. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 216, 663–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00548-X.
Subramani, T, Anandakumar, S, Kannan, R, & Elango, L (2013), Identification of major hydrogeochemical processes in a hard rock terrain by NETPATH modelling. In Book on Earth resources and environment, research publishing, Singapore, Chapter 29 (pp. 365–370).
Subramani, T., Elango, L., & Damodarasamy, S. R. (2005). Groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in Chithar River basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Geology, 47, 1099–1110.
Subramani, T., Elango, L., & Rajmohan, N. (2010). Groundwater geochemistry and identification of hydrogeochemical processes in a hard rock region, Southern India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 162, 123–137.
Subramanian, A. (2011). Ground water quality assessment of Nagercoil Town (Hand pumps). Journal of Environmental and Earth Science, 1(1), 1–5.
Suresh, M., Gurugnanam, B., Vasudevan, S., Dharanirajan, K., & Jawahar Raj, N. (2010). Drinking and irrigational feasibility of groundwater, GIS spatial mapping in Upper Thirumanimuthar sub-basin, Cauvery River, Tamil Nadu. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 75(2010), 518–526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-010-0045-5.
Thilagavathi, N., Subramani, T., Suresh, M., & Karunanidhi, D. (2015). Mapping of groundwater potential zones in Salem Chalk Hills, Tamil Nadu, India, using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 1–17.
Vennila, G., Subramani, T., & Elango, L. (2007). Rainfall variation analysis of vattamalikarai sub-basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Journal of Applied Hydrology, 3, 50–59.
Wanda, E., Monjerezi, M., Mwatseteza, J. F., & Kazembe, L. N. (2011). Hydro-geochemical appraisal of groundwater quality from weathered basement aquifers in Northern Malawi. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 36, 1197–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2011.07.061.
Wayland, K. G., Hyndman, D. W., David, B., Pijanowski, B. C., & Long, D. T. (2002). Modelling the impact of historical land uses on surface-water quality using groundwater flow and solute transport models. Lakes & Reservoirs Reserch & Management, 7(3), 189–199.
WHO. (2011). WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organization.
Zulu, G., Toyoto, M., & Misawa, S. (1996). Characteristics of water reuse and its effect on paddy irrigation system water balance and riceland ecosystem. Agricultural Water Management, 31(3), 269–283.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duraisamy, S., Govindhaswamy, V., Duraisamy, K. et al. Hydrogeochemical characterization and evaluation of groundwater quality in Kangayam taluk, Tirupur district, Tamil Nadu, India, using GIS techniques. Environ Geochem Health 41, 851–873 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0183-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0183-z