Abstract
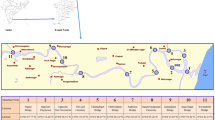
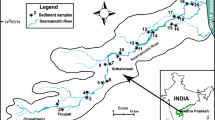
The metal pollution in water and sediment of the River Hindon in western Uttar Pradesh (India) was assessed for Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn. The metal concentrations in water showed wide temporal variation compared with bed sediment because of variability in water discharge and variations in suspended solid loadings. Metal concentrations in bed sediments provided a better evaluation of the degree and the extent of contamination in the aquatic environment, Santagarh and Atali being the most polluted sites of the river. The ratio of heavy metals to conservative elements (Fe, Al, etc.) may reveal the geochemical imbalances due to the elevated metal concentrations normally attributed to anthropogenic sources. Metal/Al ratios for the bed sediments of the river Hindon were used to determine the relative mobility and general trend of relative mobility occurred Fe > Mn > Zn > Cr > Ni > Pb > Cu > Cd.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertin, C. and Bourg, A. C. M.: 1995, ‘Trends in the heavy metal content (Cd, Pb, Zn) of river sediments in the drainage basin of smelting activities’, Water Res. 29(7), 1729–1736.
Combest, K. B.: 1991, ‘Trace metals in sediment: Spatial trends and sorption processes’, Water Resour. Bull. 27(1), 19–28.
Coquery, M. and Welbourn, P. M.: 1995, ‘The relationship between metal concentration and organic matter in sediment and metal concentration in the aquatic macrophyte, Eriocaulon Septangulare’, Water Res. 29(9), 2094–2102.
Drever, J. I.: 1988, The Geochemistry of Natural Waters, 2nd edn., Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N. J.
Dupre, B., Gaillardet, J., Rousseau, D. and Allegre, C. J.: 1996, ‘Major and trace elements of river-borne material: The Congo basin’, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 60(8), 1301–1321.
Erel, Y., Morgan, J. J. and Patterson, C. C.: 1991, ‘Naturals levels of lead and cadmium in a remote mountain stream’, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 55, 707–719.
Forstner, U.: 1981, ‘Metal Transfer between Solid and Aqueous Phases’, in: Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment, Springer, Berlin, pp. 197–269.
Forstner, U.: 1985, ‘Chemical Forms and Reactivities of Metals in Sediments’, in R. Leschber, R. D. Davis and P. L’Hermite (eds.), Chemical Methods for Assessing Bioavailable Metals in Sludges and Soils, Elsevier, London, pp. 1–30.
Forstner, U. and Salomons, W.: 1980, ‘Trace metal analysis on polluted sediments, Part I: Assessment of sources and intensities’, Environ. Technol. Lett. 1, 494–505.
Geesey, G. G., Borstad, L. and Chapman, P. M.: 1984, ‘Influence of flow related events on concentration and phase distribution of metals in the lower Fraser river and a small tributary stream in British Columbia, Canada’, Water Res. 18, 233–238.
Horowitz, A. J., Meybeck, M., Idlafkih, Z. and Biger, E.: 1999, ‘Variations in trace elements geochemistry in the Seine river basin based on floodplain deposits and bed sediments’, Hydrol. Process. 13, 1329–1340.
Jain, C. K. and Ali, I.: 2000, ‘Adsorption of cadmium on riverine sediments: Quantitative treatment of the large particles’, Hydrol. Process. 14, 261–270.
Jain, C. K. and Ram, D.: 1997a, ‘Adsorption of lead and zinc on bed sediments of the river Kali’, Water Res. 31(1), 154–162.
Jain, C. K. and Ram, D.: 1997b, ‘Adsorption of metal ions on bed sediments’, Hydrol. Sci. J. 42(5), 713–723.
Jain, C. K. and Sharma, M. K.: 2001, ‘Distribution of trace metals in the Hindon river system, India’, J. Hydrol. 253, 81–90.
Jain, C. K. and Sharma, M. K.: 2002, ‘Adsorption of cadmium on bed sediments of river Hindon: Adsorption models and kinetics’, Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 137, 1–19.
Jha, P. K., Subramanian, V., Sitasawad, R. and Van Grieken, R.: 1990, ‘Heavy metals in sediments of the Yamuna river (a tributary of the Ganges)’, Sci. Total Environ. 95, 7–27.
Kristensen, P.: 1982, ‘Time dependent variation of mercury in a stream sediment and the effect upon mercury content in Gammarus pulex (L.)’, Water Res. 16, 759–764.
Krumlgalz, B. S.: 1989, ‘Unusual grain size effect on trace metals and organic matter in contaminated sediments’, Mar. Poll. Bull. 20, 608.
Langston, W. J.: 1982, ‘The distribution of mercury in British estuarine sediments and its availability to deposit-feeding bivalves’, J. Mar. Biol. Ass. 62, 667–684, U.K.
Luoma, S. N.: 1990, ‘Processes Affecting Metal Concentrations in Estuarine and Coastal Marine Sediments’, in P. S. Rainbow and R. W. Furness (eds.), Heavy Metals in the Marine Environment, CRC Press, Cleveland, Ohio.
Martin, J. M. and Meybeck, M.: 1979, ‘Elemental mass balance of material carried by major world rivers’, Mar. Chem. 7, 173–206.
Modak, D. P., Singh, K. P., Chandra, H. and Ray, P. K.: 1992, ‘Mobile and bound forms of trace metals in sediments of lower Ganges’, Water Res. 26(11), 1541–1548.
Rada, G. R., Wiener, J. G., Winfrey, M. R. and Powell, D. E.: 1989, ‘Recent increases in atmospheric deposition of mercury to north-central Wisconsin lakes inferred from sediment analyses’, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxic. 18, 175–181.
Rafael Pardo, Enrique Barrado, Lourdes Perez and Marisol Vega: 1990, ‘Determination and speciation of heavy metals in sediments of the Pisuerga river’, Water Res. 24(3), 373–379.
Sabri, A. W., Rasheed, K. A. and Kassim, T. I.: 1993, ‘Heavy metals in the water, suspended solids and sediment of the river Tigris impoundment at Samara’, Water Res. 27(6), 1099–1103.
Sakai, Hiromitsu, Kojima, Y. and Saito, K.: 1986, ‘Distribution of heavy metals in water and sieved sediments in the Toyohira river’, Water Res. 20(5), 559–567.
Salomons, W. and Forstner, U.: 1984, Metals in the Hydrocycle, Springer, Berlin.
Stephenson, M. and Mackie, G. L.: 1988, ‘Total cadmium concentrations in the water and littoral sediments of central Ontario lakes’, Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 38, 121–136.
Thomson, E. A., Luoma, S. N., Johnsson, C. E. and Cain, D. J.: 1984, ‘Comparison of sediments and organisms in identifying sources of biologically available trace metal concentration’, Water Res. 18, 755–765.
Thorne, L. T. and Nickless, G.: 1981, ‘The relation between heavy metals and particle size fractions within the seven estuary (UK) inter-tidal sediments’, Sci. Total Environ. 19, 207–213.
Vertacnik, A., Prohic, E., Kozar, S. and Juracic, M.: 1995, ‘Behaviour of some trace elements in alluvial sediments, Zagreb water well field area, Croatia’, Water Res. 29(1), 237–246.
Viers, J., Dupre, B., Braun, J. J., Deberdt, S., Angeletti, B., Ngoupayou, J. N. and Michard, A.: 2000, ‘Major and trace element abundances, and strontium isotopes in the Nyong basin rivers (Cameroon): Constraints on chemical weathering processes and elements transport mechanisms in humid tropical environments’, Chem. Geol. 169, 211–241.
Wren, C. D., MacCrimmon, H. R. and Loescher, D. R.: 1983, ‘Examination of bioaccumulation and biomagnification of metal in a Precambrian shield lake’, Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 19, 277–291.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, C.K., Singhal, D.C. & Sharma, M.K. Metal Pollution Assessment of Sediment and Water in the River Hindon, India. Environ Monit Assess 105, 193–207 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-3498-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-3498-z