Abstract
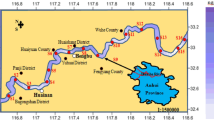
The contamination of organochlorine pesticides hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) and Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) and their eco-environmental assessment in surface sediments from Lake Dongting, the second-largest freshwater lake in China, were studied. Concentrations of ∑HCH (=α-HCH + β-HCH + γ-HCH +δ-HCH) were 0.21--9.59 ng/g dry weight and those of ∑ DDT = p,p'-DDD+p,p'-DDE+o,p'-DDT+p,p'-DDT) ranged from under detectable limit to 10.15 ng/g dry weight. The ratios of α-HCH to γ-HCH were above 7 at most sampling sites while no or a small amount of β-HCH were found at all sites, suggesting the degradation of HCH used in the history and possibly current use of HCH in the region. The low ratios (below 2.0 in most cases) of (p,p'-DDE+p,p'-DDD) to p,p'-DDT and high levels of individual isomers of DDT at some sites also suggested that there have still been fresh inputs of DDT into Lake Dongting. Through the comparison between concentrations of HCH and DDT residues in sediments of Lake Dongting and those from other places in China and also from the results of our eco-environmental assessment, it can be concluded that Lake Dongting is the water body with high contamination of both HCH and DDT in its sediments in comparison with other water bodies in China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai, D. J., Sun, L. J., Ke, J. L. and Tang, G. C.: 1992, “Pesticide usage in China”, Report prepared for Environment Canada, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
FAO Information Divison: 2000, “FAO Pesticide Disposal Series 8, Assessing soil contamination” (A reference manual), Rome.
Feng, K., Yu, B. Y., Ge, D. M., Wong, M. H., Wang, X. C. and Cao, Z. H.: 2003, “Organo-chlorine pesticide (DDT and HCH) residues in the Taihu lake region and its movent in soil-water system I. Field sury of DDT and HCH residues in ecosystem of the region”, Chemosphere 50, 683–687.
Fu, J. M., Mai, B. X., Sheng, G. Y., Zhang, G., Wang, X. M., Peng, P. A., Xiao, X. M., Ran, R., Cheng, F. Z., Peng, X. Z., Wang, Z. S. and Tang, U. W.: 2003, “Persistent organic pollutants in environment of the Pearl River Delta, China: An overview”, Chemosphere 52, 1411–1422.
Hong, H., Chen, W. Q., Xu, L., Wnag, X. H. and Zhang, L. P.: 1999, “Distribution and fate of organochlorine pollutants in the Pearl River estuary”, Mar. Pollut. Bull. 39, 376–382.
Kim, S.-K., Oh, J. R., Shim, W. J., Lee, D. H., Yim, U. H., Hong, S. h., Shin, Y. B. and Lee, D. S.: 2002, “Geographical distribution and accumulation features of organochlorine residues in bivalves from coastal areas of South Korea”, Mar. Pollut. Bull. 45, 268–279.
Li, Y. F., Cai, D. J. and Singh, A., 1998, “Technical Hexachlorocyclohexane use trends in China and their impact on the environment”, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 35, 688–697.
Li, Y. F., Cai, D. J. and Singh, A.: 1999, “Historical DDT use trend in China and usage data gridding with 1/4. by 1/6. longitude/latitude resolution”, Adv. Environ. Res. 2, 497–506.
Li, Y. F., Cai, D. J., Shan, Z. J. and Zhu, Z. L.: 2001, “Gridded usage inventories of technical hexachlorocyclohexane and lindane for China with 1/6° latitude by 1/4° longitude resolution”, Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 41, 261–266.
Lin, Y. S., Gong, R. Z. and Zhu, Z. L.: 2000, Pesticides and Eco-Environmental Protection, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing.
Liu, X. M., Xu, X. R., Zhang, X. T., Zhang, G. G., Li, H. and Zhou, C. G.: 2001, “Organochlorine pesticides and PCBs in Dalian Bay”, Mar. Environ. Sci. 20(4), 40–44 (in Chinese).
Long, E. R., MacDonald, D. D., Smith, S. L. and Calder, F. D.: 1995, “Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments”, Environ. Manage. 19(1), 81–97.
Long, E. R., Field, L. J. and MacDonald, D. D.: 1998, “Predicting toxicity marine sediments with numerical sediment quality guidelines”, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17(4), 714–727.
McCauley, D. J., DeCraeve, G. M. and Linton, T. K.: 2000, “Sediment quality guidelines and assessment: Overview and research needs”, Environ. Sci. Policy 3, 133–144.
Qiu, X. H., Zhu, T., Li, J., Pan, H. S., Li, Q. L., Miao, G. F. and Gong, J. C.: 2004, “Organochlorine pesticides in the air around the Taihu Lake, China”, Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 1368–1374.
Ramesh, A., Tanabe, S., Iwata, H., Tatsukawa, R., Subramanian, A. N., Mohan, D. and Venugopalan, V. K.: 1989, “Seasonal variations of organochlorine insecticide residues in air from Porto Novo, South India”, Environ. Pollut. 62, 213–222.
Richardson, B. J. and Zheng, G. J.: 1999, “Chlorinated hydrocarbon contaminants in Hong Kong surficial sediments”, Chemosphere 39, 913–923.
Strandberg, B., Bandh, C., Bavel, B. V., Bergqvist, P. A., Broman, D., Ishaq, R., Naf, C. and Rappe, C.: 2000, “Organochlorine compounds in the Gulf of Bothnia: Sediment and benthic species”, Chemosphere 40, 1205–1211.
Tu, J. W.: 2001, “Hydrogeological present situation of regional environment in Dongtinghu district”, Hunan Geol. 20(3), 203–205 (in Chinese).
Wu, Y., Zhang, J. and Zhou, Q.: 1999, “Persistent organochlorine residues in sediments from Chinese river/estuary systems”, Environ. Pollut. 105, 143–150.
Xu, S. F., Jiang, X., Feng, J. F., Dong, Y. Y., Sun, C., Wang, L. S.: 2000, “Gas chromatographic method for the determination of organochlorine pesticides in suspended solids and sediments of the Yangtze River”, Acta Environ. Sci. 20(4), 494–498 (in Chinese).
Yuan, X. Y., Wang, Y., Chen, J., Sun, C. and Xu, N. Z.: 2003, “Organochlorine residues of sediments in Taihu lake and its risk evaluation”, Environ. Sci. 24(1), 121–125 (in Chinese).
Zhang, Z. L., Hong, H. S., Zhou, J. L., Huang, J. and Yu, G.: 2003, “Fate and assessment of persistent organic pollutants in water and sediment from Mingjiang river estuary, southeast China”, Chemosphere 52, 1423–1430.
Zhou, J. L., Maskaou, K., Qiu, Y. W., Hong, H. S. and Wang, Z. D.: 2001, “Polychlorinated biphenyl congeners and organochlorine insecticides in the water column and sediments of Daya Bay, China”, Environ. Pollut. 113, 373–384.
Zoumis, T., Schmidt, A., Grigorova, L. and Calmano, W.: 2001, “Contaminants in sediments: Remobilization and demobilization”, Sci. Total Environ. 266(1–3), 195–202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, Y., Zheng, M., Zhang, B. et al. Determination and Assessment of HCHs and DDTs Residues in Sediments from Lake Dongting, China. Environ Monit Assess 116, 157–167 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-7233-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-7233-1