Abstract
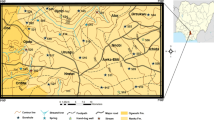
Assessment of the water quality can enhance understanding of the hydrochemical system and effective management of water resources. To this end, an assessment of water quality was conducted in the Messolonghi–Etoliko and Neochorio region. Surface water and groundwater samples have been collected, treated, and subjected to chemical analysis for the following parameters: Br − , Cl − , F − , NO\(_{2}^{-}\), NO\(_{3}^{-}\), PO\(_{4}^{3-}\), SO\(_{4}^{2-}\), Li + , Na + , NH\(_{4}^{+}\), K + , Mg 2+ , Ca 2+ , HCO\(_{3}^{-}\), Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn. A characterization has been carried out using the Piper trilinear diagram, the United States Salinity Laboratory diagram, and the Wilcox diagram. Assessment of water samples by comparing the recorded values of the water quality parameters with the parametric values established by European Community indicated that the 50% of the surface water samples and 67% of the groundwater samples in the study area are chemically suitable for drinking use. Assessment of water samples from calculation of chemical indexes like sodium adsorption ratio, sodium percentage, residual sodium carbonate, and by comparing the values of the water quality parameters with the water quality limits established by Canadian Council of Minister of the Environment indicated that 75% of the surface water and that all the groundwater samples are chemically suitable for irrigation use.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghazadeh, N., & Mogaddam, A. A. (2010). Investigation of hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in the Harzandat aquifer, northwest of Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1575-4.
Alexakis, D. (2008). Geochemistry of stream sediments as a tool for assessing contamination by arsenic, chromium and other toxic elements: East Attica region, Greece. European Water, 21/22, 57–72. (Available online at www.ewra.net).
Alexakis, D., & Tsakiris, G. (2010). Drought impacts on karstic spring annual water potential. Application on Almyros (Heraklion Crete) brackish spring. Desalination and Water Treatment, 16, 1–9. doi:10.5004/dwt.2010.1065.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (2005). Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution (2nd Ed.). Rotterdam: Balkema.
Bathrellos, G. D., Skilodimou, H. D., Kelepertsis, A., Alexakis, D., Chrisanthaki, I., & Archonti, D. (2007). Environmental research of groundwater in the urban and suburban areas of Attica region, Greece. Environmental Geology, 58, 11–18. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-1135-6.
CCME (Canadian Council of Minister of the Environment) (1999). Canadian water quality guidelines for the protection of agricultural water uses. Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines, Pub. No. T/528.
Dar, I. A., Sankar, K., & Dar, M. A. (2010). Spatial assessment of groundwater quality in Mamundiyar basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1702-2.
Davis, S. N., & DeWiest, R. J. (1966). Hydrogeology. New York: Wiley.
EC (European Community) (1998). Council Directive 98/83/EC Directive of the European Parliament on the quality of water intended for human consumption. The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union, Official Journal L 330, 03/11/1998.
Freeze, R. A., & Cherry, J. A. (1979). Groundwater. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall.
Hajizadeh Namaghi, H., Karami, G. H., & Saadat, S. (2011). A study on chemical properties of groundwater and soil in ophiolitic rocks in Firuzabad, east of Shahrood, Iran: With emphasis to heavy metal contamination. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 174 573–583. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1479-3.
Hamzaoui-Azaza, F., Ketata, M., Bouhlila, R., Gueddari, M., & Riberio, L. (2011). Hydrogeochemical characteristics and assessment of drinking water quality in Zeuss–Koutine aquifer, southeastern Tunisia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 174, 283–298. doi:10.1007/s10661-010-1457-9.
IGME (1989). Echinades Sheet. Geological Map 1:50000, Department of Geological Maps. Athens: Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration.
IGME (1991). Evinokhorion Sheet. Geological Map 1:50000, Department of Geological Maps. Athens: Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration.
IGME (1998). Messolonghion Sheet. Geological Map 1:50000, Department of Geological Maps. Athens: Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration.
Karapiperis, L. (1974). Rainfall distribution in Greece. Bulletin of the Geological Society of Greece, 11, 1–27.
Kelepertsis, A., Alexakis, D., & Kita, I. (2001). Environmental geochemistry of soils and waters of Susaki area, Korinthos, Greece. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 23, 117–135. doi:10.1023/A:1010904508981.
Kumar, S. K., Rammohan, V., Sahayam, J., & Jeevanandam, M. (2009). Assessment of groundwater quality and hydrogeochemistry of Manimuktha River basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 159, 341–351. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0633-7.
Lambrakis, N. (2006). Multicomponent heterovalent chromatography in aquifers. Modelling salinization and freshening phenomena in field conditions. Journal of Hydrology, 323, 230–243.
Langmuir, D. (1997). Aqueous environmental geochemistry. New York: Prentice Hall, Inc.
Palma, P., Alvarenga, P., Palma, V., Fernandes, R. M. , Soares, A. M. V. M., & Barbosa, I. R. (2010). Assessment of anthropogenic sources of water pollution using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Alqueva’s reservoir, Portugal. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 165, 539–552. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-0965-y.
Parkhurst, D. L., & Appelo, C. A. J. (1999). User’s guide to PHREEQC (Version 2)—A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 99-4259.
Ragunath, H. M. (1987). Groundwater (2nd Edn). New Delhi: Wiley Eastern Ltd.
Richards, L. A. (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline alkali soils: Agriculture (Vol. 160, Handbook 60). Washinghton DC: U.S. Department of Agriculture.
Saeedi, M., Abessi, O., Sharifi, F., & Meraji, H. (2010). Development of groundwater quality index. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 163, 327–335. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-0837-5.
Sawyer, G. N., McMcartly, D. L., & Parkin, G. F. (2003). Chemistry for environmental engineering and science. New York: McGraw Hill.
Stamatis, G., & Gartzos, E. (1999). The silica supersaturated waters of northern Evia and eastern central Greece. Hydrological Processes, 13, 2833–2845.
Stamatis, G., Lambrakis, N., Alexakis, D., & Zagana, E. (2006). Groundwater quality in eastern Attica (Greece). Hydrological Processes, 20, 2803–2818. doi:10.1012/hyp.6072.
Suthar, S., Sharma, J., Chabukdhara, M., & Nema, A. K. (2010). Water quality assessment of river Hindon at Ghaziabad, India: Impact of industrial and urban wastewater. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 165, 103–112. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-0930-9.
Tank, D. K., & Chandel, C. P. S. (2010). A hydrochemical elucidation of the groundwater composition under domestic and irrigated land in Jaipur City. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 166, 69–77. doi:10.1007/s10661-009-0985-7.
USSL (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of salinity and alkaline soil. USDA Hand Book no. 60, Washington.
Wilcox, L. V. (1955). Classification and use of irrigation water (p. 969). Washington: USDA, Circular.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alexakis, D. Assessment of water quality in the Messolonghi–Etoliko and Neochorio region (West Greece) using hydrochemical and statistical analysis methods. Environ Monit Assess 182, 397–413 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1884-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1884-2