Abstract
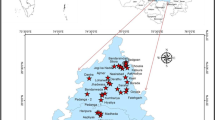
Groundwater resource forms a significant component of the urban water supply. Declining groundwater levels in Bangalore Urban District is generally due to continuous overexploitation during the last two decades or more. There is a tremendous increase in demand in the city for good quality groundwater resource. The present study monitors the groundwater quality using geographic information system (GIS) techniques for a part of Bangalore metropolis. Thematic maps for the study area are prepared by visual interpretation of SOI toposheets on 1:50,000 scale using MapInfo software. Physicochemical analysis data of the groundwater samples collected at predetermined locations form the attribute database for the study, based on which spatial distribution maps of major water quality parameters are prepared using MapInfo GIS software. Water quality index was then calculated by considering the following water quality parameters—pH, total dissolved solids, total hardness, calcium hardness, magnesium hardness, alkalinity, chloride, nitrate and sulphate to find the suitability of water for drinking purpose. The water quality index for these samples ranged from 49 to 502. The high value of water quality index reveals that most of the study area is highly contaminated due to excessive concentration of one or more water quality parameters and that the groundwater needs pretreatment before consumption.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA. (1992). Standard methods for the examination of water and waste waters (18th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Asadi, S. S., Vuppala, P., & Reddy, M. A. (2007). Remote sensing and GIS techniques for evaluation of groundwater quality in municipal corporation of Hyderabad (Zone-V), India. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 4(1), 45–52.
BIS. (1991). Bureau of Indian Standards IS: 10500. New Delhi: Manak Bhavan.
Choi B.-Y., Yu, S.-T., Yu, S.-Y., Lee, P.-K., Park, S.-S., Chae, G.-T., & Mayer, B. (2005). Hydrochemistry of urban groundwater in Seoul, South Korea: effects of land use and pollutant recharge. Environ Geol 48, 979–990.
Horten, R. K. (1965). An index number system for rating water quality. Journal of the Water Pollution Control Federation, 373, 303–306.
Jaiswal, R. K., Mukherjee, S., Krishnamurthy, J., & Saxena, R. (2003). Role of remote sensing and GIS techniques for generation of groundwater prospect zones towards rural development—an approach. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 24(5), 993–1008.
Komnitsas, K., Kontopoulos, A., Lazar, I., & Cambridge, M. (1998). Risk assessment and proposed remedial actions in coastal tailings disposal sites in Romania. Mining Engineering, 11(12), 1179–1190.
Komnitsas, K., & Modis, K. (2006). Soil risk assessment of As and Zn contamination in a coal mining region using geostatistics. Science of the Total Environment, 371, 190–196.
Lakshmikantha, H. (2006). Report on waste dump sites around Bangalore. Waste Management, 26, 640–650.
Lokeshwari, H., & Chandrappa, G. T. (2006). Heavy metals content in water, water hyacinth and sediments of Lalbagh tank, Bangalore, India. Journal of Environmental Science & Engineering, 48, 183–188.
MOWR (2005). 13th National Conference of Water Resources and Irrigation Ministries of State Governments and Union Territories, Ministry of Water Resources, New Delhi.
Pradhan, S. K., Dipika, P., & Rout, S. P. (2001). Water quality index for the groundwater in and around a phosphatic fertilizer plant. Indian Journal of Environmental Protection, 21, 355–358.
Shankar, B. S., Balasubramanya, N., & MarutheshaReddy, M. T. (2008). Impact of Industrialization on groundwater—a case study of Peenya industrial area—Bangalore, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 142, 263–268.
Singh, D. K., & Singh, A. K. (2002). International Journal of Water Resources Development, 18, 563–580.
Skidmore, A. K., Bijer, W., Schmidt, K., & Kumar, L. (1997). Use of remote sensing and GIS for sustainable land management. ITC Journal, 3(4), 302–315.
Tiwari, T. N., & Mishra, M. (1985). A preliminary assignment of water quality index of major Indian rivers. Indian Journal of Environment Protection, 5(4), 276–279.
Tjandra, F. L., Kondhoh, A., & Mohammed, A. M. A. (2003). A conceptual database design for hydrology using GIS (pp. 13–15). Kyoto: Proceedings of Asia Pacific Association of Hydrology and Water Resources.
Wingle, W. L., Poeter, E. P., & McKenna, S. A. (1999). UNCERT: geostatistics, uncertainty analysis and visualization software applied to groundwater flow and contaminant transport modeling. Computers & Geosciences, 25(4), 365–376.
Xenidis, A., Papassiopi, N., & Komnitsas, K. (2003). Carbonate rich mine tailings in Lavrion: risk assessment and proposed rehabilitation schemes. Advances in Environmental Research, 7(2), 207–222.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the University Grants Commission for the fellowship and financial support granted for the accomplishment of this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pius, A., Jerome, C. & Sharma, N. Evaluation of groundwater quality in and around Peenya industrial area of Bangalore, South India using GIS techniques. Environ Monit Assess 184, 4067–4077 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2244-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2244-y