Abstract
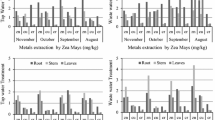
The concentrations of toxic heavy metals—Cd and Pb and micronutrients—Cu, Mn, and Zn were assessed in the surface soil and water of three different stages of paddy (Oryza sativa L.) fields, the stage I—the first stage in the field soon after transplantation of the paddy seedlings, holding adequate amount of water on soil surface, stage II—the middle stage with paddy plants of stem of about 40 cm length, with sufficient amount of water on the soil surface, and stage III—the final stage with fully grown rice plants and very little amount of water in the field at Bahour, a predominantly paddy cultivating area in Puducherry located on the southeast Coast of India. Comparison of the heavy metal and micronutrient concentrations of the soil and water across the three stages of paddy field showed their concentrations were significantly higher in soil compared with that of water (p < 0.05) of the fields probably because of accumulation and adsorption in soil. The elemental concentrations in paddy soil as well as water was in the ranking order of Cd > Mn > Zn > Cu > Pb indicating concentration of Cd was maximum and Pb was minimum. The elemental concentrations in both soil and water across the three stages showed a ranking order of stage II > stage III > stage I. The runoff from the paddy fields has affected the elemental concentrations of the water and sediment of an adjacent receiving rivulet.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway, B. J. (2009). Soil factors associated with zinc deficiency in crops and humans. Environmental Geochemical Health, 31, 537–548.
Anonymous. (2011) Deficiency in soil mars farming, Green Revolution—II. Orissa Post, (Bhubaneswar), 29 Nov 2011.
APHA. (1998). Standard methods for examination of water and waste water (20th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Arao, T., Ishikawa, S., Murakami, M., Abe, K., Maejima, Y., & Makino, T. (2010). Heavy metal contamination of agricultural soil and countermeasures in Japan. Paddy Water and Environment, 8, 247–257.
Awashthi, S. K. (2000). Prevention of Food Adulteration Act No. 37 of 1954. Central and State Rules as Amended for 1999. New Delhi: Ashoka Law House.
Brady, N. C., & Weil, R. R. (2002). The nature and properties of soil (13th ed.). Upper Saddle River: Prentice-Hall.
Cao, R. X., Ma, L. Q., Chen, M., Singh, S. P., & Harissa, W. G. (2004). Mechanisms of lead, copper and Zn retention by phosphate rock. Environmental Pollution, 53, 9–16.
Chaney, R. L. (1983). Fate of toxic substances in sludge applied to cropland. In: Proc. Int. Symp. Land Application of Sewage Sludge, Tokyo, Japan
Chhabra, A., Manjunath, K. R., & Panigrahy, S. (2010). Non-point source pollution in Indian Agriculture: estimation of nitrogen losses from rice crop using remote sensing and GIS. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 12(3), 190–200.
Das, P., Samantaray, S., & Rout, G. R. (1997). Studies on cadmium toxicity in plants: a review. Environmental Pollution, 89, 29–36.
European Union. (2002). Heavy metals in wastes. European Commission on Environment. Available from http://www.ec.europa.eu/environment/waste/studies/pdf/heavymetalsreport.pdf.
Fazeli, M. S., Khosravan, F., Hossini, M., Sathyanarayan, S., & Satish, P. N. (1998). Enrichment of heavy metals in paddy crops irrigated by paper mill effluents near Nanjangud, Mysore district, Karnataka, India. Environmental Geology, 34(4), 297–302.
Garcia, R., & Millán, E. (1998). Assessment of Cd, Pb and Zn contamination in roadside soils and grasses from Gipuzkoa (Spain). Chemosphere, 37(8), 1615–1625.
German Federal Ministry of the Environment. (1992). Novelle zur Verordnung über das Aufringen von Klärschlamm (bundesgesetzblatt).
Goyer, R. A., & Mehlman, M. A. (Eds.). (1977). Toxicology of trace elements. New York: Wiley.
Hang, X., Wang, H., Zhou, J., Ma, C., Du, C., & Chen, X. (2009). Risk assessment of potentially toxic element pollution in soils and rice (Oryza sativa) in a typical area of the Yangtze River Delta. Environmental Pollution, 157, 2542–2549.
Jeng, A. S. (1991). Weathering of some Norwegian alum shales. 1. Laboratory simulations to study acid generation and the release of sulphate and metal cations (Ca, Mg, and K). Acta Agriculturæ Scandinavica Section B, 41, 13–35.
Liu, J., Duan, C. Q., Zhu, Y. N., Zhang, X. H., & Wang, C. X. (2007). Effects of chemical fertilizers on the fractionation of Cu, Cr and Ni in contaminated soil. Environmental Geology, 2, 1601–1606.
McEldowney, S., Hardman, D. J., & Waite, S. (1993). Pollution, ecology and biotreatment (pp. 48–58). In S. Celdowney, D. J. Hardman, & S. Waite (Eds.), Treatment technologies. Singapore: Longman Singapore Publishers Pvt. Ltd.
Nagajyoti, P. C., Lee, K. D., & Sreekanth, T. V. M. (2010). Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 8, 199–216.
Nouri, J., Mahvi, A. H., Jahed, G. R., & Babaei, A. A. (2008). Regional distribution pattern of groundwater heavy metals resulting from agricultural activities. Environmental Geology, 55, 1337–1343.
Ongley, E. D., Xiaolan, Z., & Tao, Y. (2010). Current status of agricultural and rural non-point source pollution assessment in China. Environmental Pollution, 158, 1159–1168.
Panda, D., Kundu, D. K., Ghosh, A., & Patra, D. D. (2007). Agricultural nitrogen use and its environmental implications. In Y. P. Abrol, N. Raghuram, & M. S. Sachdev (Eds.), Nitrogen use efficiency in rice ecosystems. New Delhi: I.K. International Publishing House Pvt. Ltd.
Parkpian, P., Leong, S. T., Laortanakul, P., & Thunthaisong, N. (2003). Regional monitoring of lead and cadmium contamination in a tropical grazing land site, Thailand. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 85(2), 157–173.
Rai, S., Chopra, A. K., Pathak, C., Sharma, D. K., Sharma, R., & Gupta, P. M. (2011). Comparative study of some physicochemical parameters of soil irrigated with sewage water and canal water of Dehradun city, India. Achieves of Applied Science Research, 3(2), 318–325.
Reddy, M. V. (2005). Restoration and management of tropical eutrophic lakes. Enfield (NH): Science Publishers.
Selene, C. H., Chou, J., & De Rosa, C. T. (2003). Case studies—arsenic. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 206, 381–386.
Shao, G., Chen, M., Wang, D., Xu, C., Mou, R., Cao, Z., & Zhang, X. (2008). Using iron fertilizer to control Cd accumulation in rice plants: a new promising technology. Sci in China Series C: Life Sciences, 51(3), 245–253.
Smuc, N. R. (2010). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in paddy soils from Kočani Field (Republic of Macedonia): part I. Materials and Geoenvironment, 57(4), 511–524.
Suthar, S., Bishnoi, P., Singh, S., Mutiyar, P. K., Nema, A. K., & Patil, N. S. (2009). Nitrate contamination in groundwater of some rural areas of Rajasthan, India. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171(1–3), 189–199.
Taylor, M. D., & Percival, H. J. (2001). Cadmium in soil solutions from a transect of soils away from a fertilizer bin. Environmental Pollution, 113(1), 35–40.
Thorburn, P. J., Biggs, J. S., Weier, K. L., & Keating, B. A. (2003). Nitrate in ground waters of intensive agricultural areas in coastal northeastern Australia. Agriculture Ecosystem and Environment, 94, 49–58.
Tsadilas, C. D., Karaivazoglou, N. A., Tsotsolis, N. C., Stamatiadis, S., & Samaras, V. (2005). Cadmium uptake by tobacco as affected by liming, N form, and year of cultivation. Environmental Pollution, 134, 239–246.
Tu, C., Zheng, C. R., & Chen, H. M. (2000). Effect of applying chemical fertilizers on forms of lead and cadmium in red soil. Chemosphere, 41, 133–138.
Watanabe, M. E. (1997). Phytoremediation on the brink of commercialization. Environmental Science and Technology, 31, 182–186.
WHO/FAO. (2007). Joint FAO/WHO FOOD standard programme codex alimentarius commission 13th session. Report of the thirty eight session of the Codex committee on food hygene. Houston. ALINORM 07/30/13.
Xie, Y., Xiong, Z., Xing, G., Yan, X., Shi, S., Suna, G., & Zhu, Z. (2008). Source of nitrogen in wet deposition to a rice agroecosystem at Tai lake region. Atmospheric Environment, 42, 5182–5192.
Yi, C. Z., Fu, G. P., Zhang, F. S., & Li, H. F. (1996). Effects of potash fertilizer on uptake and accumulation of Cadmium by crops (in chinese). Journal of China Agricultural University, 5, 79–84.
Acknowledgments
The present research was funded through a major research project—MRP/F. No. 40-137/2011 (SR) dated 04–07–2011), funded by UGC (New Delhi). Ms. DS received a project research fellowship from the MRP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, M.V., Satpathy, D. & Dhiviya, K.S. Assessment of heavy metals (Cd and Pb) and micronutrients (Cu, Mn, and Zn) of paddy (Oryza sativa L.) field surface soil and water in a predominantly paddy-cultivated area at Puducherry (Pondicherry, India), and effects of the agricultural runoff on the elemental concentrations of a receiving rivulet. Environ Monit Assess 185, 6693–6704 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-3057-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-3057-3