Abstract
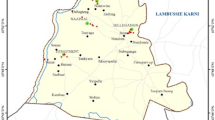
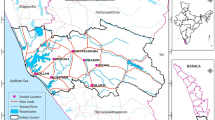
The aim of this study was to investigate the heavy metals concentrations in soils and groundwater within the Ntem watershed in Yaoundé, to prevent the risk on the public health. Soils investigated were sampled in five (05) representative profiles at the surface and the bottom of the unsaturated zone of each profile. Soil samples were air-dried and ground to pass through a 2-mm sieve, and different soil extracts were prepared for chemical analysis (organic matter, cation exchange capacity and pH). By soil digestion method with diacid, total Pb, Cd, Cr and Ni were extracted and determined by atomic absorption spectrophotometry (AAS). Representative groundwater samples were also collected directly from some soil profiles and analysed using AAS instrument after filtration. Average metals concentrations in groundwater were higher than those of the World Health Organisation (WHO) norms. Besides, the geo-accumulation indices (Igeo) were ranged between zero and one (0 < Igeo < 1) for Pb (0.13–0.19), Cr (0.13–0.16) and Ni (0.09–0.11), indicating that the soils are contaminated by these metals, except Cd (Igeo < 0) in the whole watershed. Gleysols (Mollic (Igeo = 0.18) and Plenthic (Igeo = 0.16)) were found more contaminated than Ferralsols (Igeo = 0.15). Regardless of the sampling stations, soils were typified polluted by metals (pollution index (PI) > 1), except Cd (PI < 1). The integrated pollution index (IPI) values were ranged in descending order for soil pollution level as follows: Mollic Gleysols (3.47–4.94) > Plenthic Gleysol (1.89) > Xanthic Ferralsol (1.79) > Rhodic Ferralsol (1.69). The soils and groundwater pollution observed may be a severe threat for the public health in this watershed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul Jameel, A., Sirajudeen, J., & Abdul Vahith, R. (2012). Studies on heavy metal pollution of ground water sources between Tamilnadu and Pondicherry, India. Advances in Applied Science Research, 3(1), 424–429.
Adelekan, B. A., & Abegunde, K. D. (2011). Heavy metals contamination of soil and groundwater at automobile mechanic villages in Ibadan, Nigeria. International Journal of the Physical Sciences, 6(5), 1045–1058.
AL-Jaboobi, M., Adelmajid, Z., M’hamed, T., Abdellah, E., Zakaria, M., Hasna, Y., & Mohammed, B. (2014). Evaluation of heavy metals pollution in groundwater, soil and some vegetables irrigated with wastewater in the Skhirat region “Morocco”. Journal of Materials and Environmental Science, 5(3), 961–966.
Aloueimine, S., Matejka, G., Zurbrugg, C., & Sidi, M. M. (2006). Caractérisation des ordures ménagères à Nouakchott—partie 1: méthode d’échantillonnage. Société Alpine de Publications, 44(16), 4–8.
Amadi, A. N. (2011). Assessing the effects of aladimma dumpsite on soil and groundwater using water quality index and factor analysis. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(11), 763–770.
Amadi, A. N., & Nwankwoala, H. O. (2013). Evaluation of heavy metal in soils from Enyimba Dumpsite in Aba, Southeastern Nigeria using contamination factor and geo-accumulation index. Energy and Environment Research, 3(1), 125–134.
Asaah, V. A., Abimbola, A. F., & Suh, C. E. (2006). Heavy metals concentrations and distribution in surface soils of the Bassa industrial zone 1, Douala, Cameroon. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 31(2), 1–12.
Atiemo, M. S., Ofosu, G. F., Kuranchie-Mensah, H., Tutu, A. O., & Blankson, S. A. (2011). Contamination assessment of heavy metals in road dust from selected roads in Accra, Ghana. Research Journal of Environmental and Earth Sciences, 3(5), 473–480.
Barbosa, A. E., Fernandes, J. N., & David, L. M. (2012). Key issues for sustainable urban stormwater management. Journal of Water Resources, 46(67), 87–98.
Beata, M., & Mirosław, W. (2014). Trace metals content in soils along the state road 51 (northeastern Poland). Environmental Monitoring Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-013-3562-z.
Bemmo, N., Njine, T., Nola, M., and Ngamga, D. (1998). Techniques utilisées au niveau des quartiers péri-urbains pour l’évaccuation des excrétas humains. Propositions de systèmes appropriés. Programme Solidarité Eau. Rapport final. ENSP, Yaoundé. http://www.pseau.org/epa/epaqppc/rapports/liste_fr.htm#ar4. Accessed 02 February 2012.
Biggan, W., & Linsheng, Y. (2010). A review of heavy metal contamination in urban soils, urban roads, urban dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchemichal Journal, 94, 99–107.
Biney, C., Amuzu, A.T., Calamari, D., Kaba, N., Mbome, I. L., Naeve, H., Ochumba, O., Osibanjo, O., Radegonde, V., and Saad, M. A. H. (2005). Etude des métaux lourds ; Revue de la pollution dans l’environnement aquatique. http://www.fao.org/docrep/005/V3640F/V3640F04.htm. Accessed 01 January 2013.
Brady, M. A., and Sham, S. (1986). Heavy metal pollution problems in Developing Tropical City: case of Kuala Lumpur. Malaysia. Studies in Environmental Science. Elsevier, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0166-1116(08)70931-2.
Chen, X., Xia, X., Zhao, Y., & Zhang, P. (2010). Heavy metal concentrations in roadside soils and correlation with urban traffic in Beijing, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 181(1–3), 640–646.
Cheng, H., Li, M., Zhao, C., Li, K., Peng, M., Qin, A., & Cheng, X. (2014). Overview of trace metals in the urban soil of 31 metropolises in China. Journal of Geochemestry Exploration. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.08.012.
Dejoux, C. (1988). La pollution des eaux continentales africaines: expériences acquises, situation actuelle et perspectives. Paris: ORSTOM.
Delmas-Gadras, C. (2000). Influence des conditions physico-chimiques sur la mobilité du plomb et du zinc dans un sol et un sédiment en domaine routier. Université de Pau et des pays de l’Adour: Thèse en Chimie et Microbiologie de l’eau.
Demanou, J., & Brummett, R. E. (2003). Heavy metal and faecal bacterial contamination of urban lakes in Yaoundé, Cameroon. African Journal of Aquatic Science, 28(1), 49–56.
Djeuda, T. H. B., Tanawa, E., and Ngnikam, E. (2001). L’eau au Cameroun. Tome I. Approvisionnement en Eau Potable. Presses Universitaires de Yaoundé.
Djuikom, E., Temgoua, E., Jugnia, L. B., Nola, M., & Baane, M. (2009). Pollution bactériologique des puits d’eau utilisés par les populations dans la Communauté Urbaine de Douala – Cameroun. International Journal of Biological and Chemical Sciences, 3(6), 622–632.
Duchaufour, P. (2001). Introduction à la science du sol. Paris: 6e édition, DUNOD.
Duong, T. T., & Lee, B. (2011). Determining contamination level of heavy metals in road dust from busy traffic areas with different characteristics. Journal of Environmental Management, 92, 554–562.
Eliot, E. (2002). Land application of sewage sludge and biosolids. A CRC Press Company, Lewis Publisher.
EPA, U. S. (1990). Handbook on in situ treatment of hazardous waste-contaminated soils. Cincinnati: EPA/540/2-90/002.
EPA, U. S. (1993). Clean water act (Sec 503, 58(32)). Washington: U. S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Fifi, U. (2010). Impacts des eaux pluviales urbaines sur les eaux souterraines dans les pays en développement. Mécanismes de tranfert des métaux lourds à travers un sol modèle au Port-au-Prince, Haïti. Thèse de Doctorat/PhD en Cotutelle de l’INSA, France L’Université Quisqueya (Haïti).
Fonkou, T., Agendia, P., Kengne, I., Amougou, A., Focho, D., Nya, J., & Dongmo, F. (2005). Heavy metal concentrations in some biotic and abiotic components of the Olezoa Wetland Complex (Yaoundé–Cameroon. Central Africa). Water Quality Resources Journal, 4(4), 457–461.
Graig, A. C., and Colvin G. H. (1996). Evaluation of Background Metal Concentrations in Ohio Soils. Ohio Environmental Protection Agency 1800 WaterMark Drive, Columbus, Ohio 43266–0149.
Gruszecka, A. M., & Wdowin, M. (2013). Characteristics and distribution of analyzed metals in soil profiles in the vicinity of a postflotation waste site in the Bukowno region, Poland. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-013-3164-9.
Guala, S., Vega Flora, A., & Covelo Emma, F. (2013). Modeling the plant–soil interaction in presence of heavymetal pollution and acidity variations. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(1), 73–80.
Guo, G., Wu, F., Xie, F., & Zhang, R. (2012). Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in urban soils from southwest China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 24(3), 410–418.
Houba, V. J. G., van der Lee, J. J., Novozamsky, I., & Waling, I. (1989). Soil and plant analysis, part 5. Wageningen Agricultural University, The Netherlands.
IUSS/FAO/ISRIC. (1998). World Reference Base for soil Resources. World soil Resources Report 84, FAO, Rome.
Ji, Y., Feng, Y., Wu, J., Zhu, T., Bai, Z., & Duan, C. (2008). Using geo-accumulation index to study source profiles of soil dust in China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 20(5), 571–578.
Kalla, M. F. (2006). Contribution à l’étude hydrodynamique des aquifères du bassin du NTEM à Yaoundé. Faculté des Sciences. université de Yaoundé 1: Mémoire de DEA en Géologie de l’ingénieur.
Keegan, T. J., Farago, M. E., Thornton, I., Hong, B., Colvile, R. N., Pesh, B., Jakubis, P., & Nieuwen, H. M. J. (2006). Dispersion of As and selected heavy metals around a coal-burning power station in central Slovakia. Science of the Total Environment, 358(4), 61–71.
Kluge, B., & Wessolek, G. (2011). Heavy metal pattern and solute concentration in soils along the oldest highway of the world - the AVUS Autobahn. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(11), 6469–6481.
Kouame, I. K., Gone, D. L., Savane, I., Kouassi, E. A., Koffi, K., Goula, B. T. A., & Diallo, M. (2006). Mobilité relative des métaux lourds issus de la décharge d’Akouédo et risque de contamination de la nappe du Continental Terminal (Abidjan - Côte d’Ivoire). Afrique Science, 2(1), 39–56.
Kouamé, I. K., Kouassi Lazare, K. B. D., Kouamé, M. A., Loan, D. R., Romanescu, G., Issiaka, S., & Sandu, I. (2013). Potential groundwater pollution risks by heavy metals from agricultural soil in Songon area (Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire). Journal of Environmental Protection. doi:10.4236/jep.2013.412165.
Krami, L., Khoda Fazel, A., Alireza, S., Abdul, R. B., Mohamed, S., Tayebeh, T., & Biswajeet, P. (2014). Spatial patterns of heavy metals in soil under different geological structures and land uses for assessing metal enrichments. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-013-3298-9.
Kuzmanoski, M. M., Marija, N., Todorović, M. P., Aničić, U., & Slavica, F. R. (2014). Heavy metal content of soil in urban parks of Belgrade. Hemijska Industrija, 68(5), 643–651.
Larmet, H. (2007). Mobilisation et transfert de Zn, Cd, Cu et des colloïdes bactériens dans les bassins d’infiltration d’eaux pluviales: influence des conditions hydrodynamiques. Université Joseph Fourrier, Grenoble 1: Thèse de Doctorat en Science.
Liu, Q., Liu, Y., & Zhang, M. (2012). Mercury and cadmium contamination in traffic soil of Beijing, China. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 88, 154–157.
Logan, Terry, J., and Miller, Robert, H. (1983), Background Levels of Heavy Metals in Ohio Farm Soils. The Ohio State University, Ohio Agricultural Research and Development Center, Research Circular 275. 15 pp.
Lu, F., Yang, J., & Li, H. (2014). Risk evaluation of heavy metals in soil in the sewage irrigation area: a case study of Shijiazhuang. Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 6(6), 2353–2357.
Mabou, P. B. (2013). Pouvoir public et aménagement urbain à Yaoundé. Université de Yaoundé 1: Thèse de Doctorat/Ph.D en Géographie.
Malizia, D., Giuliano, A., Giancarlo, O., and Masotti, A. (2012). Common plants as alternative analytical tools to monitor heavy metals in soil. 6(Suppl 2):S6. http://journal.chemistrycentral.com/content/6/S2/S6.
Massas, I., Kalivas, D., Ehaliotis, C., & Gasparatos, D. (2013). Total and available heavy metal concentrations in soils of the Thriassio plain (Greece) and assessment of soil pollution indexes. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(8), 6751–6766.
Matcheubou, A., Yamba, J., and Tamo Tatietse, T. (2009). Impact du parc automobile sur la congestion du trafic et la pollution de l’air dans la ville de Yaoundé. Colloque international Environnement et transports dans des contextes différents,Ghardaïa, Algérie, 16–18 fév.2009. Actes, ENP ed., Alger, p. 245–252.
Mpakam, H. G. (2008). Etude de la vulnérabilité à la pollution des ressources en eau dans la ville de Bafoussam (Ouest Cameroun) et indices socio-économiques et sanitaires: modalités d’assainissement. Université de Yaoundé 1: Thèse de Doctorat/PhD en science de l’ingénieur. Option hydrochimie et assainissement.
Muller, G. (1969). Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal, 2(3), 108–118.
Musa, O. K., Shaibu, M. M., & Kudamnya, E. A. (2013). Heavy metal concentration in groundwater around Obajana and its environs. American International Journal of Contemporary Research, 3(8), 170–177.
Nagaraju, A., Sreedhar, Y., Kumar, K. S., Thejaswi, A., & Sharifi, Z. (2014). Assessment of groundwater quality and evolution of hydrochemical facies around Tummalapalle area, Cuddapah District, Andhra Pradesh, South India. Journal of Environment and Analytic Chemestry. doi:10.4172/JREAC.1000112.
Nagendrappa, G., Bhaskar, C. V., & Kumar, K. (2010). Assessment of heavy metals in water samples of certain locations situated around Tumkur, Karnataka India. E-Journal of Chemistry, 7(2), 349–352.
Nakayama, S. M., Ikenaka, Y., Hamada, K., Muzandu, K., Choongo, K., Teraoka, H., Mizuno, N., & Ishizuka, M. (2011). Metal and metalloid contamination in roadside soil and wild rats around a Pb-Zn mine in Kabwe, Zambia. Environmental Pollution, 159(1), 175–181.
NF ISO. (2006). Qualité des sol, prétraitement pour analyses physico-chimiques. NF X31-412 /NF ISO 11464 décembre 2006. Ed (01/12/2006).
Nola, M., Njine, T., Djuikom, E., & Sikati, F. V. (2000). Bacteria indicators dynamics in well as influenced by well depth and well water column thickness in Yaoundé (Cameroon). Africa Journal of Science and Technology, 1(2), 82–91.
Nola, M., Njine, T., Kemka, N., Zebaze, T. S. H., Servais, P., Messouli, M., Boutin, C. L., Monkiedje, A., & Foto, M. S. (2006). Transfert des bactéries fécales vers une nappe phréatiques à travers une colonne de sol en zone équatoriale. Revue des sciences de l’eau /Journal of Water Science, 19(2), 101–112.
NSW EPA. (1997). Environmental management guidelines for the use and disposal of biosolids products. New South Wales Environmental Protection Authority.
Nwaichi, E. O., Wegwu, M. O., & Nwosu, U. L. (2014). Distribution of selected carcinogenic hydrocarbon and heavy metals in an oil-polluted agriculture zone. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-014-4037-6.
Owamah, H. I. (2013). Heavy Metals Determination and Assessment in a Petroleum Impacted River in the Niger Delta Region of Nigeria. Petroleum and Environmental Biotechnology, http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2157-7463.1000135.
Pacyna, J. M., and Pacyna, E. G. (2001). An assessment of global and regional emissions of trace metals to the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources worldwide. Environmental Reviews, doi: 1139/er-9-4-269.
Pais, I., & Jones, J. B. (1997). The handbook of trace elements. Boca Raton: St. Lucie Press.
Pauwels, J. M., Van Ranst, E., Verloo, M. and Mvondo Ze, A. (1992). Manuel de laboratoire de pédologie. AGC D-INADER: publications agricoles - 28 Bruxelles - Dschang.
Perrono, P. (1999). Les micropolluants métalliques des boues de stations d’épuration urbaine et l’épandage agricole. Amiens: Université de Picardie, Mémoire de D.U.E.S.S., D.E.P.
Phillips, D. J. H. (1994). Macrophytes as biomonitors of trace metals. In K. J. M. Kramer (Ed.), Biomonitoring of coastal waters and estuaries (pp. 85–103). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Pingguo, Y., Miao, Y., Renzhao, M., and Hongbo, S. (2014). Multivariate-Statistical Assessment of Heavy Metals for Agricultural Soils in Northern China. Hindawi Publishing Corporation The Scientific World Journal. doi:10.1155/2014/517020.
Purushotham, D., Mahjoor, A. L., Mehnaz Rashid, A., Narsing, R., & Shakeel, A. (2012). Deciphering heavy metal contamination zones in soils of a granitic terrain of southern India using factor analysis and GIS. Journal of Earth System Science, 121(4), 1059–1070.
Rajmohan, N., Prathapar, S. A., Jayaprakash, M., & Nagarajan, R. (2014). Vertical distribution of heavy metals in soil profile in a seasonally waterlogging agriculture field in Eastern Ganges Basin. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(9), 5411–5427.
Raymond, A. W., & Okieimen, F. E. (2011). Heavy metals in contaminated soils: a review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. International Scholarly Research Network. doi:10.5402/2011/402647.
Rodier, J., Bazin, C., Broutin, J. P., Chambon, P., Champsam, H., & Rodil, L. (2006). L’analyse de l’eau : eau naturelle, eau résiduaire, eau de mer. Paris: Edition Dunod.
Scalenghe, R., & Marsan, F. A. (2009). The anthropogenic sealing of soils in urban areas. Journal of Lanscape and Urban Planning. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2008.10.011.
Service, S. C. (1972). Soil survey laboratory methods and procedures for collecting soil samples (Soil Survey Invest. Rep. no. 1). Wachington: U.S. Government Printing Office.
Sieliechi, J. M., Noumi, G. B., Fadimatou, M., Ali, A., & Kapseu, C. (2013). Speciation of heavy metals in sediments sampled from different pollution sources of Lake Dang, Ngaoundere-Cameroon. International Journal of Environmental Protection, 2(3), 10–19.
Srinivasa, G., Ramakrishna, R. M., & Govil P. K. (2010). Assessment of heavy metals contamination in soils at Jajmaw (Kanpur) and Unnao industrial areas of the Ganga plain, Uttar Praddesh, India. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 174, 113–121.
Tabue, Y. J. G., Ntamack, D., Feumba, R., Gnikamm, E., Wethem, J., & Tanawa, E. (2009). Vulnérabilité et périmètre de protection dans le bassin versant de la Mingoa (Yaoundé, Cameroun). Erudit Revue de l’université de Moncton, 40(2), 71–96.
Tahra, T. A., & Hameed, S. (2013). Bioconcentration of heavy metals in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) from farm soils around Sohar industrial area in Oman. APCBEE Procedia, 5(2013), 271–278.
Tanawa, E., & Ngnikam, E. (2004). Gestion durable des déchets et de l’assainissement urbain. Comment aller plus loin. ENSTP. Cameroun: Presse universitaire de Yaoundé 1.
Temgoua, E., Ngnikam, E., & Ndongson, B. (2009). Drinking water quality: stakes of control and sanitation in the town of Dschang, Cameroon. International Journal of Biological and Chemical Sciences, 3(3), 441–447.
Temgoua, E., Santiago, H., & Pfeifer, H. R. (2010). Pollution bactériologique de la nappe phréatique et des sols par les latrines proches en zone urbaine pauvre. Cas de la ville de Dschang (Cameroun). International Journal of Advanced Studies and Research in Africa, 1(3), 228–242.
Temgoua, E., Ntangmo Tsafack, H., & Njine, T. (2012). Vegetable production systems of swamps zone in urban environment in west Cameroon: case of Dschang city. Universal Journal of Evironmental Research and Technology, 2(3), 83–92.
Tomasz, C., Grzegorz, K., Poluszyńska, J., & Katarzyna, K. (2014). Pollution of flooded arable soils with heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Water Air Soil Pollution. doi:10.1007/s11270-014-2145-0.
WHO. (2004). Guidelines for drinking water quality. http://www.who.int/. Accessed 05 June 2013.
Yadav, R. N., Dagar, N. K., Yadav, R., and Gupta, P. (2011). Assesment of Ground Water Quality of Adjoining Area of the Bhiwari Industrial Area (Alwar), Rajasthan India. Research Journal of pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Science, 2(4), 258.
Yerima, B.P.K. (1993). Manual for Good Laboratory Practice. Field Document No. 52. National Soil Service Project. ETH/87/010. FAO Addis Ababa.
Yerima, B. P. K., & Van Ranst, E. (2005a). Introduction to soil science: soils of the tropics. Canada: Trafford publishing.
Yerima, B. P. K., & Van Ranst, E. (2005b). Major soil classification systems used in the tropics: soils of Cameroon. Canada: Trafford publishing.
Yerima, B. P. K., Van Ranst, E., Sertsu, S., & Verdoodt, A. (2014). Pedogenic impacts on the distribution of total and available Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb and Co contents of vertisols and vertic inceptisols of the Bale Mountain area of Ethiopia. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 8(44), 5429–5439.
Zogning Moffo, M. O., Tsalefac, M., & Corneliu, I. (2011). Floods risks in the Mfoundi upstream drainage basin in yaounde: a response to climatic modifications or to human impacts? Present Environment and Sustainable Development, 5(2), 33–44.
Acknowledgments
The first author received a research grant from the University of Dschang. The authors would like to thank Late Prof. NONO Alexandre, Mr SIMO KENGNE Robert, Prof. FONKOU Théophile and Dr. NANA Paulin for their scientific support. Moreover, they would like to thank IITA, IRAD and Prof. MVONDO Ze of the Laboratory of Soil and Environment of the Faculty of Agronomy and Agricultural Sciences (FASA) of the University of Dschang for the analysis of the soil and groundwater samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Defo, C., Yerima, B.P.K., Noumsi, I.M.K. et al. Assessment of heavy metals in soils and groundwater in an urban watershed of Yaoundé (Cameroon-West Africa). Environ Monit Assess 187, 77 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4292-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4292-1