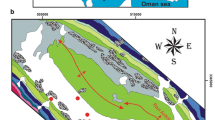
Abstract
Monitoring the groundwater quality situation and identifying the various pollution loads’ sources are a prerequisites to finding solutions. In many areas, nitrate and salinity are one of the prime pollutants in the groundwater. This investigation is carried to present the results of a monitoring study focusing on 20 wells samples collected from the shallow groundwater of Guenniche plain (North Tunisia) during the wet season of May 2016, to present its suitability for drinking purposes with emphasis on the assessment of the presence of nitrate and salinity elements. Nitrate levels’ results show that 55% of the samples exceeded the National Tunisian standard limit (NT) and the World Health Organization standard limit (WHO). The salinity results, measured as total dissolved solids (TDS), show that 95% of the samples exceed the international standard, and 25% exceed the national standard. A total of 20% of the wells exceeded the nitrite standards. The total hardness levels indicate that 90% of the samples present very hard water. The Guenniche shallow groundwater average concentrations are categorized as follows: Na+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > K+ for the cations and Cl− > SO42− > HCO3− > NO3− for the anions. Nitrate and salinity variations during the period 2006–2015 follow the rainfall fluctuation patterns. The assessment of water quality using Water Quality Index revealed that 95% of the wells’ water classes ranged between “poor”, “very poor,” and “unsuitable for drinking purposes”. Therefore, these wells are affected by anthropogenic and/or natural factors and they are inadvisable for drinking purposes, unless the water from these wells undergoes appropriate treatment before use.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abboud, I. A. (2018). Geochemistry and quality of groundwater of the Yarmouk basin aquifer, north Jordan. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 40, 1405–1435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-0064-x.
Akib Jabed, M., Paul, A., & Nath, T. K. (2020). Peoples’ perception of the water salinity impacts on human health: a case study in south-eastern coastal region of Bangladesh. Exposure and Health, 12, 41–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0283-0.
Al Nahian, M., Ahmed, A., Lazar, A. N., Hutton, C. W., Salehin, M., & Streatfield, P. K. (2018). Drinking water salinity associated health crisis in coastal Bangladesh. Elementa-Science of the Anthropocene, 6. https://doi.org/10.1525/elementa.143.
Alderman, M. H. (2000). Salt, blood pressure, and human health. Hypertension, 36, 8903–8893. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.36.5.890.
Ameur, M., Hamzaoui-Azaza, F., & Gueddari, M. (2016). Nitrate contamination of Sminja aquifer groundwater in Zaghouan, northeast Tunisia: WQI and GIS assessments, Desalination and Water Treatment. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1137495.
APHA. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (Vol. 20). Washington: American Public Health Association (APHA).
Bahrami, M., Zarei, A. R., & Rostami, F. (2020). Temporal and spatial assessment of groundwater contamination with nitrate by nitrate pollution index (NPI) and GIS (case study: Fasarud Plain, southern Iran). Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00546-x.
Bartzas, G., Zaharaki, D., & Komnitsas, K. (2015). Assessment of aquifer vulnerability in an agricultural area in Spain using the DRASTIC model. Environmental Forensics, 16(4), 356–373. https://doi.org/10.1080/15275922.2015.1091407.
Béjaoui, B., Armi, Z., Ottaviani, E., Barelli, E., Gargouri-Ellouz, E., Chérif, R., Turki, E., Solidoro, C., & Aleya, L. (2016). Random forest model and TRIX used in combination to assess and diagnose the trophic status of Bizerte Lagoon, southern Mediterranean. Ecological Indicators, 71, 293–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.07.010.
Ben Garali, A., Ouakad, M., & Gueddari, M. (2009). Bilans hydrologiques de la lagune de Bizerte (nord-est de la Tunisie). Revue des Sciences de l'Eau, 22(4), 525–534. https://doi.org/10.7202/038329ar.
Ben Moussa, A., Chandoul, S., Mzali, H., Bel Haj Salem, S., Elmejri, H., Zouari, K., Hafiane, A., & Mrabet, H. (2020). Hydrogeochemistry and evaluation of groundwater suitability for irrigation purpose in the Mornag region, northeastern Tunisia. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00696-z.
Burollet, P.F. (1951). Etude géologique des bassins Mio-Pliocènes du Nord Est de la Tunisie. Ann. Mines et Géol., n° 7, 82 p. + annexes + cartes 1/50.000.
Bussard, T. (2005). Méthodologie de dimensionnement des zones de protection des captages d’eaux souterraines contre les polluants chimiques persistants, Thèse de doctorat, Ecole Polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne.
Chen, J., Wu, H., Qian, H., & Gao, Y. (2017). Assessing nitrate and fluoride contaminants in drinking water and their health risk of rural residents living in a semiarid region of Northwest China. Expo Health, 9, 183–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0231-9.
CRDA of Bizerte (2015). Commissariat Régional de Développement Agricole Rpp. Int, 2007.
CTV (2015). Cellule Territoriale de Vulgarisation (Commissariat Régional de Développement Agricole) El Alia Bizerte.
Debbiche, T. H. (2002). Evaluation de la qualité des eaux (salinité, azote et métaux lourds) sous l’effet de la pollution saline, agricole et industrielle : Application à la basse plaine de Seybouse – Nord-Est algérien. Thèse doc. U.F.R. des Sciences et Techniques de l’Université de Franche-Comté.
Deepanjau, M., & Navindu, C. (2000). Nitrate pollution of groundwater and associated human health disorders. Indian Journal of Environmental Health, 42(1), 28–39 https://www.academia.edu/download/13611774/2000-Nitrate-pollution.pdf.
DGRE (1995). Direction Générale des Ressources en Eau. Rapport d’exploitation des nappes phréatiques de l’année 1995 [Report of Exploitation of the Groundwater of the Year 1995]. Ministry of Agriculture and hydraulic resources, Tunis
DGRE (2006-2015). Direction Générale de Ressources en Eau. Annuaire d’exploitation des nappes en Tunisie, annuaires piézométriques des nappes en Tunisie. Rapport Tunis.
DGRE (2015). Direction Générale des Ressources en Eau (2015). Annuaires de l’exploitation et de la recharge artificielle des nappes.
Elliott, P., Stamler, J., Nichols, R., Dyer, A. R., Stamler, R., Kesteloot, H., & Marmot, M. (1996). Intersalt revisited: further analyses of 24 hour sodium excretion and blood pressure within and across populations. Intersalt Cooperative Research Group BMJ, 312(1996), 1249–1253. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.312.7041.1249.
Ennabli M. (1966). Etude hydrogéologique de la plaine de l’Oued Guéniche. Rapport interne BIRH, 77 pp.
Fallah-Mehdipour, E., Bozorg-Haddad, O., & Loáiciga, H. A. (2020). Climate-environment-water: Integrated and non-integrated approaches to reservoir operation. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-8039-2.
Fusco, F., Allocca, V., Coda, S., Cusano, D., Tufano, R., & De Vita, P. (2020). Quantitative assessment of specific vulnerability to nitrate pollution of shallow alluvial aquifers by process-based and empirical approaches. Water, 12, 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010269.
Gaikwad, S. K., Kadam, A. R., Ramgir, R. R., Kashikar, A. S., Wagh, V. M., Kandekar, A. M., Kamble, K. D., et al. (2020). Assessment of the groundwater geochemistry from a part of west coast of India using statistical methods and water quality index. Hydrology Research, 3, 48–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydres.2020.04.001.
Ghouili, N., Hamzaoui-Azaza, F., Zammouri, M., Zaghrarni, M. F., Horriche, F. J., & de Melo, M. T. C. (2018). Groundwater quality assessment of the Takelsa phreatic aquifer (Northeastern Tunisia) using geochemical and statistical methods: implications for aquifer management and end-users. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 36306–36327.
Gilson, S. (1995). Enquête hydropédologique sur les zones à risque des futurs périmètres irrigués de Menzel Jemil- El Alia. Edition CRDA de Bizerte et AGRAR-UND HYDROTECHNIK GMBH ingénieurs conseils, Essen, Allemagne. 10 pp. + annexes.
Hammami, J. (2017). Etude du fonctionnement hydrodynamique et caractérisation hydrochimique et isotopique des eaux des aquifers de Rs Jbel et Oued Guenniche (Nord-Est Tunisie) : Impact de la recharge artificiel. Thèse Doc. Fac. Sci. Tunis.
Hamza, M. H., Maâlej, A., Ajmi, M., & Added, A. (2010). Validity of the vulnerability methods DRASTIC and SI applied by GIS technique to the study of diffuse agricultural pollution in two phreatic aquifers of a semi-arid region (Northeast of Tunisia). AQUAmundi-Am, 01009, 57–64. https://doi.org/10.4409/Am-006-10-0009.
Hamzaoui-Azaza, F., Ketata, M., Bouhlila, R., Gueddari, M., & Riberio, L. (2011). Hydrogeochemical characteristics and assessment of drinking water quality in Zeuss–Koutine aquifer, southeastern Tunisia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 174, 283–298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1457-9.
Hamzaoui-Azaza, F., Ameur, M., Chaouch, R., Ben Cheikha, L., Gueddari, M., & Carrillo-Rivera, J. (2020). Assessment of groundwater quality based on GIS and geochemical methods: coastal aquifer of Bouficha (North-Eastern Tunisia). Journal of Coastal Conservation, 24, 45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-020-00762-8.
He, F. J., & MacGregor, G. A. (2007). Salt, blood pressure and cardiovascular disease. Current Opinion in Cardiology, 22, 298–305.
INM (2006-2015). Institut de la Météorologie Nationale (2006 – 2015). Tableaux climatologiques mensuels, station de Bizerte-El Alia.
INS (2014). Institut National de la Statistique, Recensement général de la population et du logement.
Intersalt Cooperative Research Group. (1988). An international study of electrolyte excretion and blood pressure. Results for 24hour urinary sodium and potassium excretion. Intersalt Cooperative Research Group., BMJ, 297, 319–328. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.297.6644.319.
Law, M. R., Frost, C. D., & Wald, N. J. (1991). By how much does dietary salt reduction lower blood pressure? I-analysis of observational data among populations. BMJ, 302, 811–815. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.302.6780.811.
Le Floc’h, J. (1959). Etude pédologique de la bordure sud du lac de Bizerte. Edition SOGETHA, 56 pp. + 3 cartes + annexes.
Lee, Y. W., Dahab, M. F., & Bogardi, I. (1991). Nitrate risk management under uncertainty. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 118(2), 151–165.
Liu, J., Gao, Z., Wang, Z., Xu, X., Su, Q., Wang, S., Qu, W., & Xing, T. (2020). Hydrogeochemical processes and suitability assessment of groundwater in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08356-5.
Menció, A., Mas-Pla, J., Otero, N., Regàs, N., Boy-Roura, M., Puig, R., Bach, J., Domènech, C., Zamorano, M., Brusi, D., & Folch, A. (2016). Nitrate pollution of groundwater; all right…, but nothing else? Science of the Total Environment, 539, 241–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.08.151.
Mnassri, S., Dridi, L., Lucas, Y., Schäfer, G., Hachicha, M., & Majdoub, R. (2018). Identifying the origin of groundwater salinisation in the Sidi El Hani basin in central-eastern, Tunisia. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 147, 443–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2018.07.004.
Mountadar, S., Younsi, A., Hayani, A., Siniti, M., & Tahiri, S. (2018). Groundwater salinization process in the coastal aquifer Sidi Abed-Ouled Ghanem (Province of El Jadida, Morocco). Journal of African Earth Sciences, 147, 169–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2018.06.025.
NT (2013). Norme Tunisienne NT 09-14, Relative a la qualite des eaux de boisson.
Rajankar, P. N., Tambekar, D. H., & Wate, S. R. (2011). Groundwater quality and water quality index at Bhandara District. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 179, 619–625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1767-y.
Ritzi, R. W., Wright, S. L., Mann, B., & Chen, M. (1993). Analysis of temporal variability in hydrogeochemical data used for multivariate analyses. Ground Water, 31, 221–229. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1993.tb01814.x.
Rodier, J., Bazin, C., Broutin, J. P., Chambon, P., Champsaur, H., & Rodi, L. (1996). L’analyse de l’eau : eaux naturelles, eaux résiduaires, eau de mer, 8éme édition. Paris: Dunod.
Sebei, A., Slama, T., & Helali, M. A. (2018). Hydrochemical characterization and geospatial analysis of groundwater quality in Cap Bon region, northeastern Tunisia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77, 557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7716-8.
Singh, P., Tiwari, A. K., & Singh, P. K. (2014). Caractéristique hydrochimique et évaluation de la qualité des eaux souterraines de la banlieue de Ranchi, Jharkhand, Inde. Current World Environment: An International Research Journal of Environmental Sciences, 9(3), 804–813.
Su, X. S., Wang, H., & Zhang, Y. L. (2013). Health risk assessment of nitrate contamination in groundwater: a case study of an agricultural area in Northeast China. Water Resources Management, 27, 3025–3034. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-013-0330-3.
Talukder, M. R., Rutherford, S., Huang, C., Phung, D., Islam, M. Z., & Chu, C. (2017). Drinking water salinity and risk of hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Archives of Environmental & Occupational Health, 72, 126–138. https://doi.org/10.1080/19338244.2016.1175413.
Tlili-Zrelli, B., Gueddari, M., & Bouhlila, R. (2018). Spatial and temporal variations of water quality of mateur aquifer (Northeastern Tunisia): suitability for irrigation and drinking purposes. Hindawi,Journal of Chemistry, 2408632, 15 pages. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2408632.
Troudi, N., Hamzaoui, F., Zammouri, M., & Tzoraki, O. (2019). Distribution of trace elements in the shallow aquifer of Guenniche (North Tunisia). Advances in Science, Technology & Innovation, 113–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01572-5_28.
Tsioumas, V., Zorapas, V., Pavlidou, E., Lappas, I., & Voudouris, K. (2011). Groundwater contamination by nitrates and seawater intrusion in Atalanti basin (Fthiotida, Greece). Proceedings of the 9th International Congress of Greek Hydrogeological Society. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-24076-8_37.
Tzoraki, O., Nikolaidis, N. P., Cooper, D., & Kassotaki, E. (2013). Nutrient mitigation in a temporary river basin. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(4), 2243–2257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3533-4.
United Nations (1977). Report of the United Nations water conference. United Nations Publications, New York, Mar del Plara.
Varol, S., & Davraz, A. (2015). Evaluation of the groundwater quality with WQI (water quality index) and multivariate analysis: a case study of the Tefenni plain (Burdur/Turkey). Environment and Earth Science, 73, 1725–1744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3531-z.
Vasanthavigar, M. K., Srinivasamoorthy, K., Vijayaragavan, K., Rajiv Ganthi, R., Chidambaram, S., Anandhan, P., Manivannan, R., & Vasudevan, S. (2010). Application of water quality index for groundwater quality assessment: Thirumanimuttar sub-basin, Tamilnadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 171, 595–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1302-1.
WHO (2011). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, World Health Organization, fourth ed., Geneva, Recommendations, 564.
Wolfe, A. H., & Patz, J. A. (2002). Reactive nitrogen and human health: acute and long-term implications. Ambio, 31(2), 120–125. https://doi.org/10.1579/0044-7447-31.2.120.
Zammouri, M., Jarraya-Horriche, F., Odo, B. O., & Benabdallah, S. (2013). Assessment of the effect of a planned marina on groundwater quality in Enfida plain (Tunisia). Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 7(3), 1187–1203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0814-0.
Zereg, S., Boudoukha, A., & Benaabidate, L. (2018). Impacts of natural conditions and anthropogenic activities on groundwater quality in Tebessa plain, Algeria. Sustainable Environment Research, 28, 340–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.serj.2018.05.003.
Zhang, Q., Xu, P., & Qian, H. (2020). Groundwater quality assessment using improved water quality index (WQI) and human health risk (HHR) evaluation in a semi-arid region of Northwest China. Expo Health., 12, 487–500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-020-00345-w.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Editors and the anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions which have greatly helped us to improve the quality of the manuscript. The authors, also, wish to thank the National Society of Drinking Water in Tunisia (SONEDE “Gdir el Golla”) to provide us the laboratory in order to conduct the analysis of the groundwater. We also wish to thank the Regional Commission for Agricultural Development of Bizerte (CRDA Bizerte) for their assist and provision of the data and the essential materials used during the sampling campaign of groundwater.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Troudi, N., Hamzaoui-Azaza, F., Tzoraki, O. et al. Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking purpose with special emphasis on salinity and nitrate contamination in the shallow aquifer of Guenniche (Northern Tunisia). Environ Monit Assess 192, 641 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08584-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08584-9