Abstract
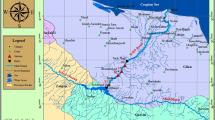
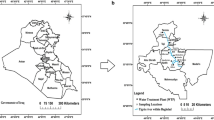
Water quality evaluation is an important step in water environment control and management. The water quality index (WQI) is considered to be an effective method for water quality evaluation. However, when constructing the WQI, the contribution of the lower threshold limits of water quality parameters to water quality has received little attention. The principle of the modified integrated water quality index (IWQI) is that the concentration of any water quality parameter below the lower threshold limits as well as above the upper threshold limits will lead to an increase in the overall index value. Based on the concentration of water quality parameters, the modified IWQI classified water quality into five categories, i.e., bad (> 8), poor (5–8), medium (2–5), good (1–2), and excellent (< 1). Tuo River plays a crucial role in potable and irrigation water sources of Sichuan Province, and the assessment result of modified IWQI reveals that 67.8% of samples were classified as “medium,” 29% “poor,” and 3.2% “bad.” The high concentrations of N and P from agricultural activities and industrial wastewater are the main contributors to the deterioration of water quality in the Tuo River. Additionally, the Tuo River presents the characteristics of worse water quality in the midstream. The evaluation results of the modified IWQI are consistent with that of the conventional WQI, which proves the accuracy of the modified IWQI as a surface water quality evaluation method.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data used to support the findings of this study can be obtained by requesting from the corresponding author.
References
Akkoyunlu, A., & Akiner, M. E. (2012). Pollution evaluation in streams using water quality indices: A case study from Turkey’s Sapanca Lake Basin. Ecological Indicators, 18, 501–511.
Alam, J. B., Hossain, A., Khan, S. K., Banik, B. K., Islam, M. R., Muyen, Z., & Rahman, M. H. (2007). Deterioration of water quality of Surma River. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 134, 233–242.
Amiri, V., Rezaei, M., & Sohrabi, N. (2014). Groundwater quality assessment using entropy weighted water quality index (EWQI) in Lenjanat. Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72(9), 3479–3490.
Avvannavar, S. M., & Shrihari, S. (2008). Evaluation of water quality index for drinking purposes for river Netravathi, Mangalore, South India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 143, 279–290.
Brown, R. M., Mcclelland, N. I., Deininger, R. A., & Tozer, R. G. (1970). A water quality index—Do we dare? Water & Sewage Works, 117, 339–343.
Chandra, A. K., Goswami, H., & Sengupta, P. (2012). Dietary calcium induced cytological and biochemical changes in thyroid. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 34(2), 454–465.
Chen, H. Y., Teng, Y. G., Yue, W. F., & Song, L. T. (2013). Characterization and source apportionment of water pollution in Jinjiang River, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 9639–9650.
Dodds, W. K., & Smith, V. H. (2016). Nitrogen, phosphorus, and eutrophication in streams. Inland Waters, 6, 155–164.
Evans, M. A., Fahnenstiel, G., & Scavia, D. (2011). Incidental oligotrophication of North American Great Lakes. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(8), 3297–3303.
Fu, D., Wu, X. F., Chen, Y. C., & Yi, Z. Y. (2020). Spatial variation and source apportionment of surface water pollution in the Tuo River, China, using multivariate statistical techniques. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 745.
Gao, Q., Li, Y., Cheng, Q. Y., Yu, M. X., Hu, B., Wang, Z. G., & Yu, Z. Q. (2016). Analysis and assessment of the nutrients, biochemical indexes and heavy metals in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China, from 2008 to 2013. Water Research, 92, 262–274.
Gao, Y. Y., Qian, H., Ren, W. H., Wang, H. K., Liu, F. X., & Yang, F. X. (2020). Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater based on integrated-weight water quality index in a concentrated urban area. Journal of Cleaner Production, 260, 121006.
Gharibi, H., Mahvi, A. H., Nabizadeh, R., Arabalibeik, H., Yunesian, M., & Sowlat, M. H. (2012). A novel approach in water quality assessment based on fuzzy logic. Journal of Environmental Management, 112, 87–95.
Gikas, G. D., Yiannakopoulou, T., & Tsihrintzis, V. A. (2006). Water quality trends in a coastal lagoon impacted by non-point source pollution after implementation of protective measures. Hydrobiologia, 563, 385–406.
Gu, Y. G., Wang, X. N., Lin, Q., Du, F. Y., Ning, J. J., Wang, L. G., & Li, Y. F. (2016a). Fuzzy comprehensive assessment of heavy metals and Pb isotopic signature in surface sediments from a bay under serious anthropogenic influences: Daya Bay, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 126, 38–44.
Gu, Q., Zhang, Y., Ma, L., Li, J., Wang, K., Zheng, K., Zhang, X., & Sheng, L. (2016b). Assessment of reservoir water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of Qiandao Lake. China Sustainability, 8(3), 243.
Haji, G. M., Melesse, A. M., & Reddi, L. (2016). Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources using APCS-MLR and PMF receptor modeling techniques in three major rivers of South Florida. Science of the Total Environment, 566–567, 1552–1567.
Horton, R. K. (1965). An index number system for rating water quality. Journal of Water Pollution Control Federation, 37(3), 300–306.
Hou, W., Sun, S. H., Wang, M. Q., Li, X., Zhang, N., Xin, X. D., Sun, L., Li, W., & Jia, R. B. (2016). Assessing water quality of five typical reservoirs in lower reaches of Yellow River, China: Using a water quality index method. Ecological Indicators, 61, 309–316.
Huang, F., Wang, X. Q., Lou, L. P., Zhou, Z. Q., & Wu, J. P. (2010). Spatial variation and source apportionment of water Pollution in Qiantang River (China) using statistical techniques. Water Research, 44(5), 1562–1572.
Huang, J., Xu, C. C., Ridoutt, B. G., Wang, X. C., & Ren, P. A. (2017). Nitrogen and phosphorus losses and eutrophication potential associated with fertilizer application to cropland in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 159, 171–179.
Icaga, Y. (2007). Fuzzy evaluation of water quality classification. Ecological Indicators, 7(3), 710–718.
Jahin, H. S., Abuzaid, A. S., & Abdellatif, A. D. (2020). Using multivariate analysis to develop irrigation water quality index for surface water in Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate, Egypt. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 17, 100532.
Jha, D. K., Vinithkumar, N. V., Sahu, B. K., Das, A. K., Dheenan, P. S., Venkateshwaran, P., Begum, M., Ganesh, T., Devi, M. P., & Kirubagaran, R. (2014). Multivariate statistical approach to identify significant sources influencing the physico-chemical variables in Aerial Bay, North Andaman, India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 85, 261–267.
Kamrani, S., Rezaei, M., Amiri, V., & Saberinasr, A. (2016). Investigating the efficiency of information entropy and fuzzy theories to classification of groundwater samples for drinking purposes: Lenjanat Plain. Central Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75, 1370.
Kannel, P. R., Lee, S., & Lee, Y. S. (2008). Assessment of spatial-temporal patterns of surface and ground water qualities and factors influencing management strategy of groundwater system in an urban river corridor of Nepal. Journal of Environmental Management, 86, 595–604.
Klausmeier, C. A., Litchman, E., Daufresne, T., & Levin, S. A. (2004). Optimal nitrogen-tophosphorus stoichiometry of phytoplankton. Nature, 429(6988), 171–174.
Li, T., Li, S., Liang, C., Bush, R. T., Xiong, L., & Jiang, Y. (2018). A comparative assessment of Australia’s Lower Lakes water quality under extreme drought and post-drought conditions using multivariate statistical techniques. Journal of Cleaner Production, 190, 1–11.
Liou, S. M., Lo, S. L., & Wang, S. H. (2004). A generalized water quality index for Taiwan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 96(1–3), 35–52.
Liu, D., & Zou, Z. (2012). Water quality evaluation based on improved fuzzy matter-element method. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 7, 1210–1216.
Liu, D. D., Bai, L., Qiao, Q., Zhang, Y., Li, X. Y., Zhao, R. N., & Liu, J. Y. (2021). Anthropogenic total phosphorus emissions to the Tuojiang River Basin, China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 294, 126325.
Liu, S. G., Lou, S., Kuang, C. P., Huang, W. R., Chen, W. J., Zhang, J. L., & Zhong, G. H. (2011). Water quality assessment by pollution-index method in the coastal waters of Hebei Province in western Bohai Sea. China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(10), 2220–2229.
Liu, L. L., Dong, Y. C., Kong, M., Zhou, J., Zhao, H.B., Tang, Z., Zhang, M., & Wang, Z. P. (2020). Insights into the long-term pollution trends and sources contributions in Lake Taihu, China using multi-statistic analyses models. Chemosphere, 242, 125272.
Ma, Z., Li, H. X., Ye, Z. Y., Wen, J. P., Hu, Y., & Liu, Y. (2020). Application of modified water quality index (WQI) in the assessment of coastal water quality in main aquaculture areas of Dalian, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 157, 111285.
Medeiros, A. C., Faial, K. R. F., Kelson, D. C. F. F., Danielly, D. S. L. I., Marcelo, D. O. L., Guimares, R. M., & Mendonça, N. M. (2017). Quality index of the surface water of Amazonian rivers in industrial areas in Pará, Brazil. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 123, 156–164.
Miyake, Y., Yokoyama, T., Yura, A., Iki, M., & Shimizu, T. (2004). Ecological association of water hardness with prevalence of childhood atopic dermatitis in a Japanese urban area. Environmental Research, 94(1), 33–37.
Mohebbi, M. R., Saeedi, R., Montazeri, A., Azam Vaghefi, K., Labbafi, S., Oktaie, S., Abtahi, M., & Mohagheghian, A. (2013). Assessment of water quality in groundwater resources of Iran using a modified drinking water quality index (DWQI). Ecological Indicators, 30, 28–34.
Mukate, S., Wagh, V., Panaskar, D., Jacobs, J. A., & Sawant, A. (2019). Development of new integrated water quality index (iwqi) model to evaluate the drinking suitability of water. Ecological Indicators, 101, 348–354.
Mwaijengo, G. N., Msigwa, A., Njau, K. N., Brendonck, L., & Vanschoenwinkel, B. (2020). Where does land use matter most? Contrasting land use effects on river quality at different spatial scales. Science of the Total Environment, 715, 134825.
Nong, X. Z., Shao, D. G., Zhong, H., & Liang, J. K. (2020). Evaluation of water quality in the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China using the water quality index (WQI) method. Water Research, 178, 115781.
Pesce, S. F., & Wunderlin, D. A. (2000). Use of water quality indices to verify the impact of Cordoba City (Argentina) on Suquia River. Water Research, 34(11), 2915–2926.
Reid, A. J., Carlson, A. K., Creed, I. F., Eliason, E. J., Gell, P. A., Johnson, P. T., Kidd, K. A., MacCormack, T. J., Olden, J. D., Ormerod, S. J., & Smol, J. P. (2019). Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biological Reviews., 94(3), 849–873.
Salim, I., Sajjad, R. U., Paule-Mercado, M. C., Memon, S. A., Lee, B. Y., Sukhbaatar, C., & Chang, H. L. (2019). Comparison of two receptor models PCA-MLR and PMF for source identification and apportionment of pollution carried by runoff from catchment and sub-watershed areas with mixed land cover in South Korea. Science of the Total Environment, 663, 764–775.
Sener, E., Sener, E., & Davraz, A. (2017). Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (WQI) method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Science of the Total Environment, 584–585, 131–144.
Shen, Z., Chen, L., Ding, X., Hong, Q., & Liu, R. (2013). Long-term variation (1960–2003) and causal factors of non-point-source nitrogen and phosphorus in the upper reach of the Yangtze River. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 45–56.
Su, S. L., Li, D., Zhang, Q., Xiao, R., Huang, F., & Wu, J. P. (2011). Temporal trend and source apportionment of water pollution in different functional zones of Qiantang River. China. Water Research, 45, 1781–1795.
Sun, W., Xia, C. Y., Xu, M. Y., Guo, J., & Sun, G. P. (2016). Application of modified water quality indices as indicators to assess the spatial and temporal trends of water quality in the Dongjiang River. Ecological Indicators, 66, 306–312.
Sutadian, A. D., Muttil, N., Yilmaz, A. G., & Perera, B. J. C. (2016). Development of river water quality indices—a review. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(1), 58.
Stockner, J. G., Rydin, E., & Hyenstrand, P. (2000). Cultural oligotrophication: Causes and consequences for fisheries resources. Fisheries, 25(5), 7–14.
Taylor, J. D., & Cunliffe, M. (2016). Multi-year assessment of coastal planktonic fungi reveals environmental drivers of diversity and abundance. The ISME Journal, 10(9), 2118–2128.
Tian, Y. L., Jiang, Y., Liu, Q., Dong, M. Y., Xu, D. X., Liu, Y., & Xu, X. (2019). Using a water quality index to assess the water quality of the upper and middle streams of the Luanhe River, northern China. Science of the Total Environment, 667, 142–151.
Tripathi, M., & Singal, S. K. (2019a). Allocation of weights using factor analysis for development of a novel water quality index. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 183, 109510.
Tripathi, M., & Singal, S. K. (2019b). Use of principal component analysis for parameter selection for development of a novel water quality index: A case study of river Ganga India. Ecological Indicators, 96, 430–436.
Usman, Q. A., Muhammad, S., Ali, W., Yousaf, S., & Jadoon, I. (2020). Spatial distribution and provenance of heavy metal contamination in the sediments of the Indus River and its tributaries, North Pakistan: Evaluation of pollution and potential risks. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 21, 101184.
Wang, A., Yang, D. W., & Tang, L. H. (2020). Spatiotemporal variation in nitrogen loads and their impacts on river water quality in the upper Yangtze River basin. Journal of Hydrology, 590, 125487.
Wang, J. L., Fu, Z. S., Qiao, H. X., & Liu, F. X. (2019). Assessment of eutrophication and water quality in the estuarine area of Lake Wuli, Lake Taihu, China. Science of the Total Environment, 650, 1392–1402.
Wu, Z. S., Wang, X. L., Chen, Y. W., Cai, Y. J., & Deng, J. C. (2018). Assessing river water quality using water quality index in Lake Taihu basin, China. Science of the Total Environment, 612, 914–922.
Wong, Y. J., Shimizu, Y., He, K., & Sulaiman, N. M. N. (2020). Comparison among different ASEAN water quality indices for the assessment of the spatial variation of surface water quality in the Selangor river basin. Malaysia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 644.
Wu, Z. S., Lai, X. J., & Li, K. Y. (2021). Water quality assessment of rivers in Lake Chaohu Basin (China) using water quality index. Ecological Indicators, 121, 107021.
Xu, J., Wang, Y. G., Chen, Y., Tong, H. J., Wei, Y., & Bai, H. (2020). Characteristics on spatiotemporal variations of surface water environmental quality in Tuojiang River in upper reaches of Yangtze River basin. Earth Science, 45(6), 1937–1947. (in Chinese).
Zanotti, C., Rotiroti, M., Fumagalli, L., Stefania, G. A., Canonaco, F., Stefenelli, G., Prevot, A. S. H., Leoni, B., & Bonomi, T. (2019). Groundwater and surface water quality characterization through positive matrix factorization combined with GIS approach. Water Research, 159, 122–134.
Zhao, P., Tang, X. Y., Tang, J. L., & Wang, C. (2013). Assessing water quality of Three Gorges Reservoir, China, over a five-year period from 2006 to 2011. Water Resources Management, 27(13), 4545–4558.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2020YFS0306).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, D., Chen, S., Chen, Y. et al. Development of modified integrated water quality index to assess the surface water quality: a case study of Tuo River, China. Environ Monit Assess 194, 333 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09998-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09998-3