Abstract
Microplastics are one of the emerging and ubiquitous environmental pollutants. Recent studies have proven their co-existence with pharmaceuticals in the environment wherein microplastics act as a potential vector for the transportation of pharmaceuticals. Both microplastics and pharmaceuticals are charged moieties enriched with diverse functional groups resulting in the possibility of multiple interactions. Major interactions could be electrostatic, hydrogen bonding, and hydrophobic, while minor interactions may occur through π-π interaction, cationic bridging mechanism, van der Waals interaction, partition, and pore-filling mechanism. These interactions have both short- and long-term effects over pharmaceutical sorption on microplastics and possibly, ensuing toxicity. This review analyses and summarises the currently reported interactions between microplastic particles and pharmaceuticals as well as establishes the link to various factors affecting the process, viz. pH, salinity, dissolved organic matter, and physiochemical properties of microplastics.
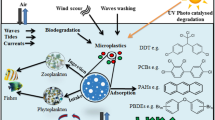
Graphical Abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Amarji, B., Kulkarni, A., Deb, P. K., Deepika, Maheshwari, R., & Tekade, R. K. (2018a). Chapter 15 - package development of pharmaceutical products: Aspects of packaging materials used for pharmaceutical products. In R. K. Tekade (Ed.), Dosage Form Design Parameters (pp. 521–552). Academic press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814421-3.00015-4
Amarji, B., Kulkarni, A., Deb, P. K., Maheshwari, R., & Tekade, R. K. (2018b). Package development of pharmaceutical products: Aspects of packaging materials used for pharmaceutical products. In Dosage Form Design Parameters (pp. 521–552). Elsevier.
Aristilde, L., & Sposito, G. (2010). Binding of ciprofloxacin by humic substances: A molecular dynamics study. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 29(1), 90–98. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.19
Atugoda, T., Vithanage, M., Wijesekara, H., Bolan, N., Sarmah, A. K., Bank, M. S., ... & Ok, Y. S. (2021). Interactions between microplastics, pharmaceuticals and personal care products: Implications for vector transport. Environment International, 149, 106367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.106367
Atugoda, T., Wijesekara, H., Werellagama, D., Jinadasa, K., Bolan, N. S., & Vithanage, M. (2020). Adsorptive interaction of antibiotic ciprofloxacin on polyethylene microplastics: Implications for vector transport in water. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 19, 100971.
Bakir, A., Rowland, S. J., & Thompson, R. C. (2014). Enhanced desorption of persistent organic pollutants from microplastics under simulated physiological conditions. Environmental Pollution, 185, 16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.10.007
Brennecke, D., Duarte, B., Paiva, F., Caçador, I., & Canning-Clode, J. (2016). Microplastics as vector for heavy metal contamination from the marine environment. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 178, 189–195.
Chen, W., Ouyang, Z. Y., Qian, C., & Yu, H. Q. (2018). Induced structural changes of humic acid by exposure of polystyrene microplastics: A spectroscopic insight. Environmental Pollution, 233, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.027
Elizalde-Velázquez, A., Subbiah, S., Anderson, T. A., Green, M. J., Zhao, X., & Cañas-Carrell, J. E. (2020). Sorption of three common nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to microplastics. Science of the Total Environment, 715, 136974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136974
Falk, Y. Z., Runnsjö, A., Pettigrew, A., Scherer, D., Engblom, J., & Kocherbitov, V. (2020). Interactions of perfluorohexyloctane with polyethylene and polypropylene pharmaceutical packaging materials. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 109(7), 2180–2188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2020.03.026
Fendall, L. S., & Sewell, M. A. (2009). Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: Microplastics in facial cleansers. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58(8), 1225–1228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2009.04.025
Fu, L., Li, J., Wang, G., Luan, Y., & Dai, W. (2021). Adsorption behavior of organic pollutants on microplastics. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 217, 112207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112207
Fu, Z., & Wang, J. (2019). Current practices and future perspectives of microplastic pollution in freshwater ecosystems in China. Science of The Total Environment, 691, 697–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.167
Gu, C., Karthikeyan, K. G., Sibley, S. D., & Pedersen, J. A. (2007). Complexation of the antibiotic tetracycline with humic acid. Chemosphere, 66(8), 1494–1501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.08.028
Guo, X., Pang, J., Chen, S., & Jia, H. (2018). Sorption properties of tylosin on four different microplastics. Chemosphere, 209, 240–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.06.100
Guo, X., & Wang, J. (2019). Sorption of antibiotics onto aged microplastics in freshwater and seawater. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 149, 110511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110511
Guo, X., Wang, X., Zhou, X., Kong, X., Tao, S., & Xing, B. (2012). Sorption of four hydrophobic organic compounds by three chemically distinct polymers: Role of chemical and physical composition. Environmental Science and Technology, 46(13), 7252–7259. https://doi.org/10.1021/es301386z
Hu, B., Li, Y., Jiang, L., Chen, X., Wang, L., An, S., & Zhang, F. (2020). Influence of microplastics occurrence on the adsorption of 17β-estradiol in soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 400, 123325.
Kasyanenko, N., Afanasieva, D., Dribinsky, B., Mukhin, D., Nazarova, O., & Panarin, E. (2007). DNA interaction with synthetic polymers in solution. Structural Chemistry, 18(4), 519–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-007-9162-1
Kebede, T. G., Dube, S., & Nindi, M. M. (2019). Biopolymer electrospun nanofibres for the adsorption of pharmaceuticals from water systems. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7(5), 103330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103330
Li, J., Zhang, K., & Zhang, H. (2018). Adsorption of antibiotics on microplastics. Environmental Pollution, 237, 460–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.050
Li, Y., Li, M., Li, Z., Yang, L., & Liu, X. (2019). Effects of particle size and solution chemistry on Triclosan sorption on polystyrene microplastic. Chemosphere, 231, 308–314.
Liu, G., Zhu, Z., Yang, Y., Sun, Y., Yu, F., & Ma, J. (2019a). Sorption behavior and mechanism of hydrophilic organic chemicals to virgin and aged microplastics in freshwater and seawater. Environmental Pollution, 246, 26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.100
Liu, P., Lu, K., Li, J., Wu, X., Qian, L., Wang, M., & Gao, S. (2020a). Effect of aging on adsorption behavior of polystyrene microplastics for pharmaceuticals: Adsorption mechanism and role of aging intermediates. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 384, 121193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121193
Liu, P., Zhan, X., Wu, X., Li, J., Wang, H., & Gao, S. (2020b). Effect of weathering on environmental behavior of microplastics: Properties, sorption and potential risks. Chemosphere, 242, 125193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125193
Liu, X., Xu, J., Zhao, Y., Shi, H., & Huang, C. H. (2019b). Hydrophobic sorption behaviors of 17β-Estradiol on environmental microplastics. Chemosphere, 226, 726–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.162
Pareek, V., & Khunteta, A. (2014). Pharmaceutical packaging: Current trends and future. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 6(6), 480–485.
Pettit, R. E. (2004). Organic matter, humus, humate, humic acid, fulvic acid and humin: Their importance in soil fertility and plant health. CTI Research, 10, 1–7.
Puckowski, A., Cwięk, W., Mioduszewska, K., Stepnowski, P., & Białk-Bielińska, A. (2021). Sorption of pharmaceuticals on the surface of microplastics. Chemosphere, 263, 127976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127976
Qiu, Y., Zheng, M., Wang, L., Zhao, Q., Lou, Y., Shi, L., & Qu, L. (2019). Sorption of polyhalogenated carbazoles (PHCs) to microplastics. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 146, 718–728.
Razanajatovo, R. M., Ding, J., Zhang, S., Jiang, H., & Zou, H. (2018). Sorption and desorption of selected pharmaceuticals by polyethylene microplastics. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 136, 516–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.09.048
Seidensticker, S., Zarfl, C., Cirpka, O. A., Fellenberg, G., & Grathwohl, P. (2017). Shift in mass transfer of wastewater contaminants from microplastics in the presence of dissolved substances. Environmental Science and Technology, 51(21), 12254–12263. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02664
Selvam, S., Jesuraja, K., Venkatramanan, S., Roy, P. D., & Jeyanthi Kumari, V. (2021). Hazardous microplastic characteristics and its role as a vector of heavy metal in groundwater and surface water of coastal south India. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 402, 123786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123786
Singh, S., Kalyanasundaram, M., & Diwan, V. (2021). Removal of microplastics from wastewater: Available techniques and way forward. Water Science and Technology, 84, 3689–3704. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2021.472
Singh, S., Trushna, T., Kalyanasundaram, M., Tamhankar, A. J., & Diwan, V. (2022). Microplastics in drinking water: A macro issue. Water Supply, 22, 5650–5674. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2022.189
Tourinho, P. S., Kočí, V., Loureiro, S., & van Gestel, C. A. M. (2019). Partitioning of chemical contaminants to microplastics: Sorption mechanisms, environmental distribution and effects on toxicity and bioaccumulation. Environmental Pollution, 252(Pt B), 1246–1256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.06.030
Ustabasi, G. S., & Baysal, A. (2019). Occurrence and risk assessment of microplastics from various toothpastes. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(7), 438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7574-1
Vieira, Y., Lima, E. C., Foletto, E. L., & Dotto, G. L. (2021). Microplastics physicochemical properties, specific adsorption modeling and their interaction with pharmaceuticals and other emerging contaminants. Science of the Total Environment, 753, 141981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141981
Wan, T., Lu, S., Cheng, W., Ren, J., Wang, M., Hu, B., ... & Sun, Y. (2019). A spectroscopic and theoretical investigation of interaction mechanisms of tetracycline and polystyrene nanospheres under different conditions. Environmental Pollution, 249, 398–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.049
Wang, F., Zhang, M., Sha, W., & Wang, Y. (2020). Sorption behavior and mechanisms of organic contaminants to nano and microplastics. 25(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081827
Weber, J. H., & Wilson, S. A. (1975). The isolation and characterization of fulvic acid and humic acid from river water. Water Research, 9(12), 1079–1084.
Xu, B., Liu, F., Brookes, P. C., & Xu, J. (2018a). Microplastics play a minor role in tetracycline sorption in the presence of dissolved organic matter. Environmental Pollution, 240, 87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.113
Xu, B., Liu, F., Brookes, P. C., & Xu, J. (2018b). The sorption kinetics and isotherms of sulfamethoxazole with polyethylene microplastics. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 131(Pt A), 191–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.04.027
Yu, F., Yang, C., Huang, G., Zhou, T., Zhao, Y., & Ma, J. (2020). Interfacial interaction between diverse microplastics and tetracycline by adsorption in an aqueous solution. Science of the Total Environment, 721, 137729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137729
Zadbuke, N., Shahi, S., Gulecha, B., Padalkar, A., & Thube, M. (2013). Recent trends and future of pharmaceutical packaging technology. Journal of Pharmacy & Bioallied Sciences, 5(2), 98–110. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-7406.111820
Zeng, Z., Patel, J., Lee, S.-H., McCallum, M., Tyagi, A., Yan, M., & Shea, K. J. (2012). Synthetic polymer nanoparticle–polysaccharide interactions: A systematic study. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 134(5), 2681–2690. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja209959t
Zhang, H., Liu, F. F., Wang, S. C., Huang, T. Y., Li, M. R., Zhu, Z. L., & Liu, G. Z. (2020). Sorption of fluoroquinolones to nanoplastics as affected by surface functionalization and solution chemistry. Environmental Pollution, 262, 114347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114347
Zhang, H., Wang, J., Zhou, B., Zhou, Y., Dai, Z., Zhou, Q., ... & Luo, Y. (2018). Enhanced adsorption of oxytetracycline to weathered microplastic polystyrene: Kinetics, isotherms and influencing factors. Environmental Pollution, 243(Pt B), 1550–1557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.122
Zhang, K., Hamidian, A. H., Tubić, A., Zhang, Y., Fang, J. K. H., Wu, C., & Lam, P. K. S. (2021). Understanding plastic degradation and microplastic formation in the environment: A review. Environmental Pollution, 274, 116554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116554
Funding
The work was partly supported by the Society of Toxicology Undergraduate Faculty Research grant (principal investigator—Gurjot Kaur—Shoolini University, Solan) and Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi grant (vide project grant number ICMR-NIREH/BPL/IMP-PJ-44/2021–22/469: principal investigator—Surya Singh, ICMR—NIREH, Bhopal).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The review was conceptualised by GK. Original draft of the manuscript was written by RU under the guidance of GK. Further editing and finalisation of the manuscript for submission was done by SS and GK. GK and SS share equal corresponding authorship.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Upadhyay, R., Singh, S. & Kaur, G. Sorption of pharmaceuticals over microplastics’ surfaces: interaction mechanisms and governing factors. Environ Monit Assess 194, 803 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10475-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10475-0