Abstract
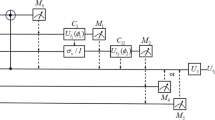
We present an efficient three-party quantum secure direct communication (QSDC) protocol with single photos in both polarization and spatial-mode degrees of freedom. The three legal parties’ messages can be encoded on the polarization and the spatial-mode states of single photons independently with desired unitary operations. A party can obtain the other two parties’ messages simultaneously through a quantum channel. Because no extra public information is transmitted in the classical channels, the drawback of information leakage or classical correlation does not exist in the proposed scheme. Moreover, the comprehensive security analysis shows that the presented QSDC network protocol can defend the outsider eavesdropper’s several sorts of attacks. Compared with the single photons with only one degree of freedom, our protocol based on the single photons in two degrees of freedom has higher capacity. Since the preparation and the measurement of single photon quantum states in both the polarization and the spatial-mode degrees of freedom are available with current quantum techniques, the proposed protocol is practical.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scarani, V., Bechmann-Pasquinucci, H., Cerf, N.J., Dusek, M., Lutkenhaus, N., Peev, M.: The security of practical quantum key distribution. Rev. Mod. Phys 81(3), 1301–1350 (2009)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceeding of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore, India, pp 175–179. IEEE Press, New York (1984)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bells theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett 67(6), 661–663 (1991). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.67.661
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Mermin, N.D.: Quantum cryptography without Bells theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett 68(5), 557–559 (1992)
Bennett, C.H.: Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogal states. Phys. Rev. Lett 68(21), 3121–3124 (1992)
Cabello, A.: Qutntum key distribution in the Holevo limit. Phys. Rev. Lett 85 (26), 5635–5638 (2000)
Kulik, S.P., Molotkov, S.N., Radchenko, I.V.: Quantum key distribution on composite photons, polarization qutrits. JETP lett 96(5), 336–341 (2012)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032302 (2002)
Beige, A., Englert, B.G., Kurtsiefer, Ch., Weinfurter, H.: Secure communication with a publicly known key. Acta. Phys. Pol 101(3), 357–368 (2002)
Boström, K., Felbinger, T.: Deterministic secure direct communication using entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett 89(18), 187–902 (2002). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.187902
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: A Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein-Pololsky-Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68, 042317 (2003)
Gu, B., Huang, Y.G., Xia, F., Zhang, Ch.Y.: A two-step quantum secure direct communication protocol with hyperentanglement. Chin. Phys. B 20(10), 100309 (2011)
Chang, W.L., Lin, F.J., Zeng, G.J., Chou, Y.H.: Controlled quantum secure direct communication based on single photons. In: Advances in intelligent systems and applications, vol. 2, pp 195–204. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Liu, D., Chen, J.L., Jiang, W.: High-capacity quantum secure direct communication with single photons in both polarization and spatial-mode degrees of freedom. Int. J. Theor. Phys 51(9), 2923–2929 (2012)
Gu, B., Huang. Y.G., Xia, F., et al.: Bidirectional quantum secure direct communication network protocol with hyperentanglement. Commun. Theor. Phys 56 (4), 659 (2011)
Jin, X.R., Ji, X., Zhang, Y.Q., et al.: Three-party quantum secure direct communication based on GHZ states. Phys. Lett. A 354(1), 67–70 (2006)
Man, Zh.X., Xia, Y.J.: Improvement of security of three-party quantum secure direct communication based on GHZ states. Chin. Phys. Lett 24(1), 15 (2007)
Gao, F., Qin, S.J., Wen, Q.Y., et al.: Comment on: Three-party quantum secure direct communication based on GHZ states. Phys. Lett. A 354, 67 (2006). Phys. Lett. A, 372(18), 3333-3336(2008)
Wang, M.Y., Yan, F.l.: Three-party simultaneous quantum secure direct communication scheme with EPR pairs. Chin. Phys. Lett 24(9), 2486 (2007)
Chong, S.K., Hwang, T.: The enhancement of three-party simultaneous quantum secure direct communication scheme with EPR pairs. Opt. Commun 284(1), 515–518 (2011)
Wang, L.Y., Chen, X.B., Xu, G., et al.: Information leakage in three-party simultaneous quantum secure direct communication with EPR pairs. Opt. Commun 284(7), 1719–1720 (2011)
Yin, X.R., Ma, W.P., Shen, D.S., et al.: Efficient Three-Party Quantum Secure Direct Communication with EPR Pairs. Journal of Quantum Information Science 1, 3 (2013)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett 85(2), 441–444 (2000)
Deng, F.G., Li, X.H., Zhou, H.Y., Zhang, Zh.J.: Erratum: Improving the security of multiparty quantum secret sharing against Trojan horse attack. Phys. Rev. A 72, 044302 (2005). Phys. Rev. A 73(4), 049901 (2006)
Cai, Q.Y.: Eavesdropping on the two-way quantum communication protocols with invisible photons. Phys. Lett. A 351(1-2), 23–25 (2006)
Li, X.H., Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y.: Improving the security of secure direct communication based on the secret transmitting order of particles. Phys. Rev. A 74(5), 054302 (2006)
Deng, F.G., Zhou, P., et al.: Robustness of two-way quantum communication protocols against Trojan horse attack. arXiv:e-printquant-ph/0508168
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China under grant No.61072140, 61373171; the 111 Project No.B08038; the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education under Grant No.20100203110003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Ma, W., Wang, M. et al. Three-party Quantum Secure Direct Communication with Single Photons in both Polarization and Spatial-mode Degrees of Freedom. Int J Theor Phys 55, 2490–2499 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-015-2886-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-015-2886-6