Abstract
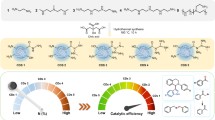
In this study, we report a simple and fast synthetic route to prepare pure and Ag doped SnO2 quantum dots via one step microwave irradiation method for the first time. Variety of analytical techniques including XRD, Raman, TEM, EDS, XPS, UV and PL were used to investigate the influence of Ag dopant concentration on structural, morphological, compositional and optical properties of SnO2 nanoparticles. The XRD pattern showed a dominant tetragonal rutile structure of both pure and Ag doped SnO2 and formed directly during the microwave irradiation process. TEM images revealed that quantum dots and the average particle size increases by Ag doping. The EDS and XPS results proved that the presence of silver as Ag3+ species. The optical properly of SnO2 was significantly improved and narrowing the band gap (3.54–3.09 eV) of pure SnO2 by Ag doping, which is confirmed through UV and PL results. The photocatalytic behavior of the catalyst powders were investigated using methylene blue and rhodamine B (RhB) as model organic pollutants. A maximum RhB degradation efficiency of 97.5% is achieved under visible light irradiation for Ag doped SnO2 catalyst. Furthermore, the Ag–SnO2 QDs catalyst demonstrates good reusability and stability after the seven cycles.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. M. Al-Hamdi, M. Sillanpää, and J. Dutta (2015). J. Rare Earths 33, 1275.
M. N. Chong, B. Jin, C. W. Chow, and C. Saint (2010). Water Res. 44, 2997.
D. H. Bremner, R. Molina, F. Martınez, J. A. Melero, and Y. Segura (2009). Appl. Catal. B 90, 380.
J. Yang, X. Zhang, C. Wang, P. Sun, L. Wang, B. Xia, and Y. Liu (2012). Solid State Sci. 14, 139.
C. Karunakaran, V. Rajeswari, and P. Gomathisankar (2011). Solid State Sci. 13, 923.
M. Qamar, Z. H. Yamani, M. A. Gondal, and K. Alhooshani (2011). Solid State Sci. 13, 1748.
A. Qurashi, Z. Zhong, and M. W. Alam (2010). Solid State Sci. 12, 1516.
E. J. Li, K. Xia, S. F. Yin, W. L. Dai, S. L. Luo, and C. T. Au (2011). Mater. Chem. Phys. 125, 236.
Z. J. Yang, L. L. Lv, Y. L. Dai, Z. H. Xv, and D. Qian (2010). Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 2898.
H. J. Snaith and C. Ducati (2010). Nano Lett. 10, 1259.
C. Wang, Y. Zhou, M. Ge, X. Xu, Z. Zhang, and J. Jiang (2009). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 46.
M. Parthibavarman, K. Vallalperuman, S. Sathishkumar, M. Durairaj, and K. Thavamani (2014). J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 730.
M. Parthibavarman, V. Hariharan, C. Sekar, and V. N. Singh (2010). J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 12, 1894.
F. P. Wang, X. T. Zhou, J. G. Zhou, T. K. Sham, and Z. F. Ding (2007). J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 18839.
Md T Uddin, Y. Nicolas, C. Olivier, T. Toupance, L. Servant, M. M. Müller, H.-J. Kleebe, J. Ziegler, and W. Jaegermann (2012). Inorg. Chem. 51, 7764.
V. Kumar, V. Kumar, S. Som, J. H. Neethling, M. Lee, O. M. Ntwaeaborwa, and H. C. Swart (2014). Nanotechnology 25, 135701–135709.
M. Parthibavarman, B. Renganathan, and D. Sastikumar (2013). Curr. Appl. Phys. 13, 1537.
V. Hariharan, R. Radhakrishnan, M. Parthibavarman, R. Dhilipkumar, and C. Sekar (2011). Talanta 85, 2166.
A. Bouaine and N. Brihi (2009). J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 2924.
C. V. Reddy, B. Babu, S. V. Prabhakar Vattikuti, R. V. S. S. N. Ravikumar, and J. Shim (2016). J. Lumin. 179, 26.
L. M. Fang, X. T. Zu, Z. J. Li, S. Zhu, C. M. Liu, L. M. Wang, and F. Gao (2008). J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 19, 868.
J. X. Zhou, M. S. Zhang, J. M. Hong, and Z. Yin (2006). Solid State Commun. 138, 242.
Y. Z. Li, H. Zhang, Z. M. Guo, J. J. Han, X. J. Zhao, Q. N. Zhao, and S. J. Kim (2008). Langmuir 24, 8351.
J. P. Huo, L. T. Fang, Y. L. Lei, G. C. Zeng, and H. P. Zeng (2014). J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 11040.
Yu-Yang Bai, Lu Yi, and Jin-Ku Liu (2016). J. Hazard. Mater. 307, 26.
S. Matsushima, Y. Teraoka, N. Miura, and N. Yamazoe (1988). Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 27, 1798.
X. Cao, L. Cao, W. Yao, and X. Ye (1996). Surf. Interface Anal. 24, 662.
S. A. Ansari, M. M. Khan, M. O. Ansari, J. Lee, and M. H. Cho (2014). New J. Chem. 38, 2462.
M. Arami, N. Y. Limaee, N. M. Mahmoodi, and N. Salman (2006). J. Hazard. Mater. 135, 171.
I. Konstantinou and T. Albanis (2004). Appl. Catal. B 49, 1.
S. Wu, H. Cao, S. Yin, X. Liu, and X. Zhang (2009). J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 17893.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parthibavarman, M., Sathishkumar, S., Jayashree, M. et al. Microwave Assisted Synthesis of Pure and Ag Doped SnO2 Quantum Dots as Novel Platform for High Photocatalytic Activity Performance. J Clust Sci 30, 351–363 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-018-01493-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-018-01493-5