Abstract
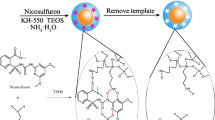
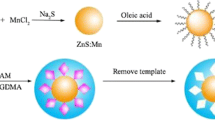
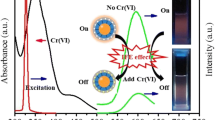
ZnO quantum dots (QDs) based molecularly imprinting polymer (MIP)-coated composite was described for specific detection of the dimethoate (DM) as a template. The MIP was synthesized by simple self-assembly of 3-aminopropyl triethoxysilane (APTES) monomers and tetraethyl ortho-silicate as cross linking agent in the presence of template molecules. The used imprinting course can improve the tendency of the prepared QDs toward the DM template molecules. The MIP-coated ZnO QDs showed a strong fluorescence emission which undergoes a quenching effect in the presence of DM. So, a selective probe could be designed based on these composites to recognize DM in water samples. Under optimized experimental conditions, a linear relationship between the emission intensity of MIP-coated ZnO QDs and concentration of DM, in the range of 0.02–3.2 mg L−1 with a detection limit of 0.006 mg L−1. Combination of high specificity of MIP element and distinct fluorescence features of ZnO QDs provides a sensitive and selective recognizing method for pesticide detection. The developed method was successfully applied for the determination of DM contamination in environmental water samples.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liang H, Song D, Gong J (2014) Signal-on electrochemiluminescence of biofunctional CdTe quantum dots for biosensing of organophosphate pesticides. Biosens Bioelectron 53:363–369
Lv Y, Lin Z, Feng W, Zhou X, Tan T (2007) Selective recognition and large enrichment of dimethoate from tea leaves by molecularly imprinted polymers. Biochem Eng J 36:221–229
Tadeo JL, Sanchez-Brunete C, González L (2008) Pesticides: classification and properties. In: Tadeo JL (ed) Analysis of pesticides in food and environmental samples. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group LLC, Boca Raton, pp 1–35
Khan BA, Farid A, Asi MR, Shah H, Badshah AK (2009) Determination of residues of trichlorfon and dimethoate on guava using HPLC. Food Chem 114:286–288
Bagyalakshmi J, Kavitha G, Ravi TK (2011) Residue determination of dimethoate in leafy vegetables (spinach) using RP-HPLC. Int J Pharm Sci Res 2:62–64
Barrek S, Olivier P, Marie-Florence GL (2003) Determination of residual pesticides in olive oil by GC–MS and HPLC–MS after extraction by size-exclusion chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem 376:355–359
Polgár L, Kmellár B, García-Reyes JF, Fodor P (2012) Comprehensive evaluation of the clean-up step in QuEChERS procedure for the multi-residue determination of pesticides in different vegetable oils using LC-MS/MS. Anal Methods 4:1142–1148
Salm P, Taylor PJ, Roberts D, de Silva J (2009) Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous quantitative determination of the organophosphorus pesticides dimethoate, fenthion, diazinon and chlorpyrifos in human blood. J Chromatogr B 877:568–574
Cui L, He XP, Chen GR (2015) Recent progress in quantum dot based sensors. RSC Adv 5:26644–26663
Chan WC, Nie S (1998) Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 281(5385):2016–2018
Ren X, Chen L (2015a) Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer coated quantum dots to detect nicosulfuron in water samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:8087–8095
Xu SF, Lu HZ, Li JH, Song XL, Wang AX, Chen LX, Han SB (2013) Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers-capped CdTe quantum dots for the fluorescent sensing of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. Appl Mater Interfaces 5:8146–8154
Zhang Z, Li JH, Wang XY, Shen DZ, Chen LX (2015) Quantum dots based mesoporous structured imprinting microspheres for the sensitive fluorescent detection of phycocyanin. Appl Mater Interfaces 7:9118–9127
Hagura N, Ogi T, Shirahama T, Iskandar F, Okuyama K (2011a) Highly luminescent silica-coated ZnO nanoparticles dispersed in an aqueous medium. J Lumin 131:921–925
Hagura N, Takeuchi T, Takayama S, Iskandar F, Okuyama K (2011b) Enhanced photoluminescence of ZnO–SiO2 nanocomposite particles and the analyses of structure and composition. J Lumin 131:138–146
Fonoberov VA, Alim KA, Balandin AA, Xiu F, Liu J (2006) Photoluminescence investigation of the carrier recombination processes in ZnO quantum dots and nanocrystals. Phys Rev B 73:165317
Segets D, Gradl J, Taylor RK, Vassilev V, Peukert W (2009) Analysis of optical absorbance spectra for the determination of ZnO nanoparticle size distribution, solubility, and surface energy. ACS Nano 3:1703–1710
Asok A, Gandhi MN, Kulkarni AR (2012) Enhanced visible photoluminescence in ZnO quantum dots by promotion of oxygen vacancy formation. Nano 4:4943–4946
Xiong HM, Shchukin DG, Möhwald H, Xu Y, Xia YY (2009) Sonochemical synthesis of highly luminescent zinc oxide nanoparticles doped with magnesium (II). Angew Chem Int Ed 48:2727–2731
Xu X, Xu C, Shi Z, Yang C, Yu B, Hu J (2012) Identification of visible emission from ZnO quantum dots: excitation-dependence and size-dependence. J Appl Phys 111:083521
Zhao D, Song H, Hao L, Liu X, Zhang L, Lv Y (2013) Luminescent ZnO quantum dots for sensitive and selective detection of dopamine. Talanta 107:133–139
Fonoberov VA, Balandin AA (2004) Origin of ultraviolet photoluminescence in ZnO quantum dots: confined excitons versus surface-bound impurity exciton complexes. Appl Phys Lett 85:5971–5973
Wu YL, Lim CS, Fu S, Tok AIY, Lau HM, Boey FYC, Zeng XT (2007) Surface modifications of ZnO quantum dots for bio-imaging. Nanotechnology 18:215604
Qu F, Santos DR, Dantas NO, Monte AFG, Morais PC (2004) Effects of nanocrystal shape on the physical properties of colloidal ZnO quantum dots. Phys E 23:410–415
Patra MK, Manoth M, Singh VK, Gowd GS, Choudhry VS, Vadera SR, Kumar N (2009) Synthesis of stable dispersion of ZnO quantum dots in aqueous medium showing visible emission from bluish green to yellow. J Lumin 129:320–324
Ren X, Chen L (2015b) Quantum dots coated with molecularly imprinted polymer as fluorescence probe for detection of cyphenothrin. Biosens Bioelectron 64:182–188
Singh K, Mehta SK (2016) Luminescent ZnO quantum dots as an efficient sensor for free chlorine detection in water. Analyst 141:2487–2492
Chen LX, Xu SF, Li JH (2011) Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem Soc Rev 40:2922–2942
Garcia R, Freitas AMC (2011) Application of molecularly imprinted polymers for the analysis of pesticide residues in food—a highly selective and innovative approach. Am J Anal Chem 2(08):16
Bedwell TS, Whitcombe MJ (2016) Analytical applications of MIPs in diagnostic assays: future perspectives. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:1735–1751
Martins N, Carreiro EP, Simões M, Cabrita MJ, Burke AJ, Garcia R (2015) An emerging approach for the targeting analysis of dimethoate in olive oil: the role of molecularly imprinted polymers based on photo-iniferter induced “living” radical polymerization. React Funct Polym 86:37–46
Vasapollo G, Sole RD, Mergola L, Lazzoi MR, Scardino A, Scorrano S, Mele G (2011) Molecularly imprinted polymers: present and future prospective. Int J Mol Sci 12:5908–5945
Tang J, Xiang L (2016) Development of a probe based on quantum dots embedded with molecularly imprinted polymers to detect parathion. Pol J Environ Stud 25:787–793
Abbasifar J, Samadi-Maybodi A (2016) Selective determination of atropine using poly dopamine-coated molecularly imprinted Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots. J Fluoresc 26:1645–1652
Huy BT, Seo MH, Zhang X, Lee YI (2014) Selective optosensing of clenbuterol and melamine using molecularly imprinted polymer-capped CdTe quantum dots. Biosens Bioelectron 57:310–316
Chantada-Vázquez MP, Sánchez-González J, Peña-Vázquez E, Tabernero MJ, Bermejo AM, Bermejo-Barrera P, Moreda-Piñeiro A (2016) Synthesis and characterization of novel molecularly imprinted polymer–coated Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots for specific fluorescent recognition of cocaine. Biosens Bioelectron 75:213–221
Amjadi M, Jalili R, Manzoori JL (2015) A sensitive fluorescent nanosensor for chloramphenicol based on molecularly imprinted polymer-capped CdTe quantum dots. Luminescence 31:633–639
Ge S, Lu J, Ge L, Yan M, Yu J (2011) Development of a novel deltamethrin sensor based on molecularly imprinted silica nanospheres embedded CdTe quantum dots. Spectrochim Acta A 79:1704–1709
Liu J, Chen H, Lin Z, Lin JM (2010) Preparation of surface imprinting polymer capped Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots and their application for chemiluminescence detection of 4-nitrophenol in tap water. Anal Chem 82:7380–7386
Wei F, Wu Y, Xu G, Gao Y, Yang J, Liu L, Zhou P, Hu Q (2014) Molecularly imprinted polymer based on CdTe@ SiO2 quantum dots as a fluorescent sensor for the recognition of norepinephrine. Analyst 139:5785–5792
Wang HF, HeY JTR, Yan XP (2009) Surface molecular imprinting on Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots for room-temperature phosphorescence optosensing of pentachlorophenol in water. Anal Chem 81:1615–1621
Zhang W, He XW, Chen Y, Li WY, Zhang YK (2011) Composite of CdTe quantum dots and molecularly imprinted polymer as a sensing material for cytochrome c. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2553–2558
Zhao Y, Ma Y, Li H, Wang L (2011) Composite QDs@MIP nanospheres for specific recognition and direct fluorescent quantification of pesticides in aqueous media. Anal Chem 84:386–395
Singh K, Chaudhary GR, Singh S, Mehta SK (2014) Synthesis of highly luminescent water stable ZnO quantum dots as photoluminescent sensor for picric acid. J Lumin 154:148–154
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Tabriz Branch, Islamic Azad University for the financial support of this research, which is based on a research project contract.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vahid, B. Specific Fluorescence Probe for Direct Recognition of Dimethoate Using Molecularly Imprinting Polymer on ZnO Quantum Dots. J Fluoresc 27, 1339–1347 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-017-2068-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-017-2068-4