Abstract
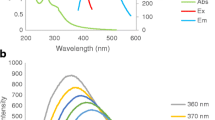
Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) as a new type of fluorescent carbon nanomaterials, showing excellent photoluminescence properties, biocompatibility, photoelectric properties, have become the current research focus. Iron element as an essential element in the human body and an important part of hemoglobin, is very important for human health, so the detection of ferric ions has great significance. In this paper, GQDs with strong blue light emission were prepared through pyrolysis treatment using citric acid as a carbon source. Through characterization by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and fluorescence spectrometer, it was observed that the GQDs have a uniform particle size distribution and highly fluorescent intensity with a quantum yield of 27.4%. Due to the strong quenching effect of Fe3+ on GQDs fluorescence, GQDs was used as a green and facile fluorescence sensor to detect Fe3+ selectively and sensitively. The GQDs fluorescence sensor shows a sensitive response to Fe3+ in a wide linear range (3.5 × 10−6-6.7 × 10−4 M), a low detection limit of 1.6 μM (S/N = 3) and good selectivity. Importantly, the new sensor realizes the detection of Fe3+ ions in tap water because of its low detection limit, wide linear range, and high sensitivity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shen J, Zhu Y, Yang X, Li C (2012) Graphene quantum dots: emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Cheminform 48(31):3686–3699
Dutta CA, Doong RA (2016) Highly sensitive and selective detection of Nanomolar ferric ions using dopamine functionalized graphene quantum dots. ACS Appl Mat Interfaces 8(32):21002–21010
Xing L, Shoujun Z, Bin X, Ke M, Junhu Z, Bai Y, Wenjing T (2013) Self-assembled graphene quantum dots induced by cytochrome c: a novel biosensor for trypsin with remarkable fluorescence enhancement. Nanoscale 5(17):7776–7779
Liu J, Liu Z, Barrow CJ, Yang W (2015) Molecularly engineered graphene surfaces for sensing applications: a review. Anal Chim Acta 859:1–19
Peng J, Gao W, Gupta BK, Liu Z, Romero-Aburto R, Ge L, Song L, Alemany LB, Zhan X, Gao G (2012) Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett 12(2):844–849
Zhu S, Zhang J, Tang S, Qiao C, Wang L, Wang H, Liu X, Li B, Li Y, Yu W (2012) Surface chemistry routes to modulate the photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots: from fluorescence mechanism to up-conversion bioimaging applications. Adv Funct Mater 22(22):4732–4740
Tabaraki R, Nateghi A (2016) Nitrogen- doped graphene quantum dots: “turn-off” fluorescent probe for detection of ag(+) ions. J Fluoresc 26(1):297–305
Salehnia F, Faridbod F, Dezfuli AS, Ganjali MR, Norouzi P (2016) Cerium(III) ion sensing based on graphene quantum dots fluorescent turn-off. J Fluoresc 27(1):1–8
Jiang Y, Wang Z, Dai Z (2016) Preparation of silicon-carbon-based dots@dopamine and its application in intracellular ag(+) detection and cell imaging. ACS Appl Mat Interfaces 8(6):3644–3650
Xin Y, Xiao C, Liang-Shi L (2010) Synthesis of large, stable colloidal graphene quantum dots with tunable size. J Am Chem Soc 132(17):5944–5945
Sung K, Sung Won H, Min-Kook K, Yeol SD, Hee SD, Oh KC, Seung Bum Y, Jae Hee P, Euyheon H, Suk-Ho C (2012) Anomalous behaviors of visible luminescence from graphene quantum dots: interplay between size and shape. ACS Nano 6(9):8203–8208
Nai Gui S, Pagona P, Surbhi S, Gennady L, Meixian L, Mcneill DW, Quinn AJ, Wuzong Z, Ross B (2012) Controllable selective exfoliation of high-quality graphene nanosheets and nanodots by ionic liquid assisted grinding. Chem Commun 48(13):1877–1879
Dengyu P, Jingchun Z, Zhen L, Minghong W (2010) Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue-luminescent graphene quantum dots. Adv Mater 22(6):734–738
Yan L, Yue H, Yang Z, Gaoquan S, Lier D, Yanbing H, Liangti Q (2011) An electrochemical avenue to green-luminescent graphene quantum dots as potential electron-acceptors for photovoltaics. Adv Mater 23(6):776–780
Deng D, Pan X, Yu L, Cui Y, Jiang Y, Qi J, Li WX, Fu Q, Ma X, Xue Q (2011) Toward N-doped graphene via Solvothermal synthesis. Chem Mater 23(5):1188–1193
Feng Y, Zhao J, Yan X, Tang F, Xue Q (2014) Enhancement in the fluorescence of graphene quantum dots by hydrazine hydrate reduction. Carbon 66(3):334–339
Li LL, Ji J, Fei R, Wang CZ, Lu Q, Zhang JR, Jiang LP, Zhu JJ (2012) A facile microwave avenue to Electrochemiluminescent two-color graphene quantum dots. Adv Funct Mater 22(14):2971–2979
Ruili L, Dongqing W, Xinliang F, Klaus M (2011) Bottom-up fabrication of photoluminescent graphene quantum dots with uniform morphology. J Am Chem Soc 133(39):15221–15223
Dong Y, Shao J, Chen C, Li H, Wang R, Chi Y, Lin X, Chen G (2012) Blue luminescent graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide prepared by tuning the carbonization degree of citric acid. Carbon 50(12):4738–4743
Zheng M, Tan H, Xie Z, Zhang L, Jing X, Sun Z (2013) Fast response and high sensitivity europium metal organic framework fluorescent probe with chelating terpyridine sites for Fe(3+). ACS App Mat Interfaces 5(3):1078–1083
Li S, Li Y, Cao J, Zhu J, Fan L, Li X (2014) Sulfur-doped graphene quantum dots as a novel fluorescent probe for highly selective and sensitive detection of Fe(3+). Anal Chem 86(20):10201–10207
Zecca L, Youdim M, P, Connor J, Crichton R (2004) Iron, brain ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 5 (11):863–873
Sadeghi S, Ashoori V (2016) Sequential determination of iron species in food samples by new task specific ionic liquid based in situ dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction prior to flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Methods 8(25):5031–5038
Ju J, Chen W (2014) Synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for sensitive, label-free detection of Fe (III) in aqueous media. Biosens Bioelectron 58(10):219–225
García-Fernández J, Bettmer J, Jakubowski N, Panne U, Añón E, Montes-Bayón M, Sanz-Medel A (2017) The fate of iron nanoparticles used for treatment of iron deficiency in blood using mass-spectrometry based strategies. Microchim Acta 184(10):3673–3680
Li C, Wu C, Pan D, Feng X, Ping W, Cai C (2017) Electrolyzing synthesis of boron-doped graphene quantum dots for fluorescence determination of Fe(3+) ions in water samples. Talanta 164:100–109
Zhang Y, Jiang H, Wang X (2015) Cytidine-stabilized gold nanocluster as a fluorescence turn-on and turn-off probe for dual functional detection of ag(+) and hg(2+). Anal Chim Acta 870:1–7
Tam TV, Trung NB, Kim HR, Jin SC, Choi WM (2014) One-pot synthesis of N-doped graphene quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing platform for Fe(3+) ions detection. Sensor Actuat B Chem 202:568–573
Lohani CR, Lee K-H (2010) The effect of absorbance of Fe(3+) on the detection of Fe(3+) by fluorescent chemical sensors. Sensor Actuat B Chem 143(2):649–654
Liu X, Theil EC (2005) Ferritins: dynamic management of biological iron and oxygen chemistry. Acc Chem Res 38(3):167–175
Mu X, Li Q, Ping D, Qiao J, Jian H, Nie Z, Ma H (2013) Facile one-pot synthesis of l -proline-stabilized fluorescent gold nanoclusters and its application as sensing probes for serum iron. Biosens Bioelectron 49(22):249–255
J-a AH, Chang H-C, Su W-T (2012) DOPA-mediated reduction allows the facile synthesis of fluorescent gold nanoclusters for use as sensing probes for ferric ions. Anal Chem 84(7):3246–3253
Wu Z, Li W, Chen J, Yu C (2014) A graphene quantum dot-based method for the highly sensitive and selective fluorescence turn on detection of biothiols. Talanta 119(4):538–543
Ananthanarayanan A, Wang X, Routh P, Sana B, Lim S, Kim DH, Lim KH, Li J, Peng C (2014) Facile synthesis of graphene quantum dots from 3D graphene and their application for Fe(3+) sensing. Adv Funct Mater 24(20):3021–3026
Wu F, Yang M, Zhang , Zhu S, Zhu X, Wang K (2018) Facile synthesis of sulfur-doped carbon quantum dots from vitamin b1 for highly selective detection of Fe(3+) ion. Opt Mater 77:258–263
Wu H, Jiang J, Gu X, Tong C (2017) Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon quantum dots for highly selective and sensitive fluorescent detection of Fe(3+) ions and l-cysteine. Microchim Acta 184(7):2291–2298
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Natural Foundation of China (11532004), Natural Science Key Foundation Project of CQ in China (CSTC2015JCYJBX0003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Yang, X., Pu, Y. et al. Selective, Sensitive and Label-Free Detection of Fe3+ Ion in Tap Water Using Highly Fluorescent Graphene Quantum Dots. J Fluoresc 29, 541–548 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-019-02365-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-019-02365-5