Abstract
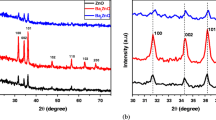
Ba-doped ZnO nanostructures (0.8–4 mmol) were successfully fabricated by the co-precipitation method. X-ray diffraction analysis indicated that all samples exhibited a typical hexagonal wurtzite ZnO structure with the emergence of BaO phase. Moreover, the incorporation of Ba resulted in an increase of crystallite size and lattice parameter while microstrain decreases. The broadening of the Zn–O vibrational band and the redshift in Raman vibrational modes provided clear evidence of the incorporation of Ba within ZnO host lattice. Furthermore, Ba doping prompted an increase of the dielectric constant and ac conductivity (σac). Additionally, the subsequent decrease in tangent loss with increasing the applied field frequency was associated with the hopping frequency of electron that enhances the charge carriers’ mobility.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Matsumura, R.P. Camata, Pulsed laser deposition and photoluminescence measurements of ZnO thin films on flexible polyimide substrates. Thin Solid Films 476(2), 317–321 (2005)
Y. Heo et al., ZnO nanowire growth and devices. Mater. Sci. Eng.: R: Rep. 47(1–2), 1–47 (2004)
J.-H. Lee, K.-H. Ko, B.-O. Park, Electrical and optical properties of ZnO transparent conducting films by the sol–gel method. J. Cryst. Growth 247(1–2), 119–125 (2003)
S. Henley, M. Ashfold, D. Cherns, The growth of transparent conducting ZnO films by pulsed laser ablation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 177, 271–276 (2004)
K. Karthik, S.K. Pandian, N.V. Jaya, Effect of nickel doping on structural, optical and electrical properties of TiO2 nanoparticles by sol–gel method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256(22), 6829–6833 (2010)
J. Lu et al., Conductivity enhancement and semiconductor–metal transition in Ti-doped ZnO films. Opt. Mater. 29(11), 1548–1552 (2007)
A. Modwi et al., Fast and high efficiency adsorption of Pb (II) ions by Cu/ZnO composite. Mater. Lett. 195, 41–44 (2017)
A. Modwi et al., Silver decorated Cu/ZnO photocomposite: efficient green degradation of malachite. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 3629–3638 (2019)
Y. Yang et al., Size control of ZnO nanoparticles via thermal decomposition of zinc acetate coated on organic additives. J. Cryst. Growth 263(1–4), 447–453 (2004)
D. Li, H. Haneda, Synthesis of nitrogen-containing ZnO powders by spray pyrolysis and their visible-light photocatalysis in gas-phase acetaldehyde decomposition. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 155(1–3), 171–178 (2003)
C. Cheng et al., Hydrothermal synthesis Ni-doped ZnO nanorods with room-temperature ferromagnetism. Mater. Lett. 62(10–11), 1617–1620 (2008)
L. Khezami et al., (x)ZnO(1−x)Fe2O3 nanocrystallines for the removal of cadmium (II) and nickel (II) from water: kinetic and adsorption studies. J. Water Supply: Res. Technol. AQUA 66(6), 381–391 (2017)
K. Raja, P. Ramesh, D. Geetha, Structural, FTIR and photoluminescence studies of Fe doped ZnO nanopowder by co-precipitation method. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 131, 183–188 (2014)
S.D. Bukkitgar et al., Electro-oxidation of nimesulide at 5% barium-doped zinc oxide nanoparticle modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 762, 37–42 (2016)
G. Srinet, R. Kumar, V. Sajal, High Tc ferroelectricity in Ba-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 126, 274–277 (2014)
A.S.H. Hameed et al., Impact of alkaline metal ions Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+ on the structural, optical, thermal and antibacterial properties of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by the co-precipitation method. J. Mater. Chem. B 1(43), 5950–5962 (2013)
S. Bakand, A. Hayes, F. Dechsakulthorn, Nanoparticles: a review of particle toxicology following inhalation exposure. Inhal. Toxicol. 24(2), 125–135 (2012)
P. Nasehi et al., Preparation and characterization of a novel Mn-Fe2O4 nanoparticle loaded on activated carbon adsorbent for kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm surveys of aluminum ion adsorption. Sep. Sci. Technol. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2019.1585456
S. Yari et al., Adsorption of Pb (II) and Cu (II) ions from aqueous solution by an electrospun CeO2 nanofiber adsorbent functionalized with mercapto groups. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 94, 159–171 (2015)
S. Jesudoss et al., Effects of Ba doping on structural, morphological, optical, and photocatalytic properties of self-assembled ZnO nanospheres. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 18(3), 729–741 (2016)
K. Taha et al., Simplistic one pot synthesis of ZnO via chelating with carboxylic acids. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 13(4), 1213–1222 (2018)
A. Modwi et al., Structural and optical characteristic of chalcone doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29(4), 2791–2796 (2018)
V. Mote, Y. Purushotham, B. Dole, Williamson–Hall analysis in estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized ZnO particles. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 6(1), 6 (2012)
K. Karthika, K. Ravichandran, Tuning the microstructural and magnetic properties of ZnO nanopowders through the simultaneous doping of Mn and Ni for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 31(11), 1111–1117 (2015)
S. Snega et al., Simultaneous enhancement of transparent and antibacterial properties of ZnO films by suitable F doping. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 31(7), 759–765 (2015)
O. Lupan et al., Effects of annealing on properties of ZnO thin films prepared by electrochemical deposition in chloride medium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256(6), 1895–1907 (2010)
A. Modwi et al., Structural, surface area and FTIR characterization of Zn0.95−xCu0.05Fe0.0xO nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29(3), 2184–2192 (2018)
S. Yakout, Pure and Gd-based Li, Na, Mn or Fe codoped ZnO nanoparticles: insights into the magnetic and photocatalytic properties. Solid State Sci. 83, 207–217 (2018)
M. Ashokkumar, S. Muthukumaran, Zn0.96−xCu0.04FexO (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.04) alloys–optical and structural studies. Superlatt. Microstruct. 69, 53–64 (2014)
C. Belkhaoui, N. Mzabi, H. Smaoui, Investigations on structural, optical and dielectric properties of Mn doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. Mater. Res. Bull. 111, 70–79 (2019)
C. Mrabet et al., Some physical investigations on hexagonal-shaped nanorods of lanthanum-doped ZnO. J. Alloy. Compd. 648, 826–837 (2015)
A.K. Zak et al., X-ray analysis of ZnO nanoparticles by Williamson-Hall and size–strain plot methods. Solid State Sci. 13(1), 251–256 (2011)
C. Barrett, T. Massalski, Structure of Metals, Crystallographic Methods, Principles and Data, International Series on Materials Science and Technology (Pergamon, New York, 1980)
K.K. Taha et al., Green and sonogreen synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles for the photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue in water. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 4(1), 10 (2019)
C.Y. Panicker et al., FT-IR, FT-Raman and SERS spectra of pyridine-3-sulfonic acid. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 64(3), 744–747 (2006)
M. Sathya, K. Pushpanathan, Synthesis and optical properties of Pb doped ZnO nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 449, 346–357 (2018)
N. Nickel, K. Fleischer, Hydrogen local vibrational modes in zinc oxide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90(19), 197402 (2003)
R.S. Alam et al., Structural, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of doped Ba-hexaferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 381, 1–9 (2015)
J. Calleja, M. Cardona, Resonant raman scattering in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 16(8), 3753 (1977)
G. Wu et al., Controlled synthesis of ZnO nanowires or nanotubes via sol–gel template process. Solid State Commun. 134(7), 485–489 (2005)
Y. Chen et al., Optical properties of ZnO and ZnO: in nanorods assembled by sol-gel method. J. Chem. Phys. 123(13), 134701 (2005)
B. Zhang et al., Ni-doped zinc oxide nanocombs and phonon spectra properties. Phys. Lett. A 372(13), 2300–2303 (2008)
T.C. Damen, S. Porto, B. Tell, Raman effect in zinc oxide. Phys. Rev. 142(2), 570 (1966)
A. Jaramillo et al., Estimation of the surface interaction mechanism of ZnO nanoparticles modified with organosilane groups by Raman spectroscopy. Ceram. Int. 43(15), 11838–11847 (2017)
A. Umar, Y. Hahn, Aligned hexagonal coaxial-shaped ZnO nanocolumns on steel alloy by thermal evaporation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88(17), 173120 (2006)
F. Wang et al., Synthesis and properties of Cd-doped ZnO nanotubes. Physica E 41(5), 879–882 (2009)
J. Wang et al., ZnO nanostructured microspheres and grown structures by thermal treatment. Bull. Mater. Sci. 31(4), 597–601 (2008)
H.K. Yadav et al., Structural studies and Raman spectroscopy of forbidden zone boundary phonons in Ni-doped ZnO ceramics. J. Raman Spectrosc. 40(4), 381–386 (2009)
E. Islam, A. Sakai, A. Onodera, Li-concentration dependence of micro-Raman spectra in ferroelectric-semiconductor Zn1−xLixO. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 71(6), 1594–1597 (2002)
L. Yang et al., In situ synthesis of Mn-doped ZnO multileg nanostructures and Mn-related Raman vibration. J. Appl. Phys. 97(1), 014308 (2005)
C. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audiofrequencies. Phys. Rev. 83(1), 121 (1951)
M.N. Ashiq, M.J. Iqbal, I.H. Gul, Effect of Al–Cr doping on the structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of strontium hexaferrite nanomaterials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323(3–4), 259–263 (2011)
T. Prodromakis, C. Papavassiliou, Engineering the Maxwell-Wagner polarization effect. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255(15), 6989–6994 (2009)
R. Zamiri et al., Er doped ZnO nanoplates: synthesis, optical and dielectric properties. Ceram. Int. 40(1), 1635–1639 (2014)
M. Ashokkumar, S. Muthukumaran, Effect of Ni doping on electrical, photoluminescence and magnetic behavior of Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 162, 97–103 (2015)
M. Ashokkumar, S. Muthukumaran, Effect of Cr-doping on dielectric, electric and magnetic properties of Zn0.96Cu0.04O nanopowders. Powder Technol. 268, 80–85 (2014)
M.K. Gupta, B. Kumar, Enhanced ferroelectric, dielectric and optical behavior in Li-doped ZnO nanorods. J. Alloy. Compd. 509(23), L208–L212 (2011)
M. Ashokkumar, S. Muthukumaran, Electrical, dielectric, photoluminescence and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles co-doped with Co and Cu. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 374, 61–66 (2015)
F. Alam et al., Synthesis, structural, optical and electrical properties of in-situ synthesized polyaniline/silver nanocomposites. Funct. Mater. Lett. 5(03), 1250026 (2012)
W. Fan et al., Materials science and integration bases for fabrication of (BaxSr1−x) TiO3 thin film capacitors with layered Cu-based electrodes. J. Appl. Phys. 94(9), 6192–6200 (2003)
M.M. Hassan et al., Structural and frequency dependent dielectric properties of Fe3+ doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 47(12), 3952–3958 (2012)
R. Zamiri et al., Structural and dielectric properties of Al-doped ZnO nanostructures. Ceram. Int. 40(4), 6031–6036 (2014)
S. Kurien et al., Dielectric behavior and ac electrical conductivity of nanocrystalline nickel aluminate. Mater. Chem. Phys. 98(2–3), 470–476 (2006)
P. Sivakumar et al., Structural, thermal, dielectric and magnetic properties of NiFe2O4 nanoleaf. J. Alloy. Compd. 537, 203–207 (2012)
M.M. Hassan et al., Influence of Cr incorporation on structural, dielectric and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 21, 283–291 (2015)
Y. Liu et al., Niobium-doped titania nanoparticles: synthesis and assembly into mesoporous films and electrical conductivity. ACS Nano 4(9), 5373–5381 (2010)
R. Nongjai et al., Magnetic and electrical properties of In doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 112(8), 084321 (2012)
A. Jonscher, Chelsea Dielectric Press (Google Scholar, London, 1983)
M. El Hiti, AC electrical conductivity of Ni-Mg ferrites. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 29(3), 501 (1996)
P.J. Gellings, H. Bouwmeester, Handbook of Solid State Electrochemistry (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1997)
A. Tabib et al., Investigations on electrical conductivity and dielectric properties of Na doped ZnO synthesized from sol gel method. J. Alloy. Compd. 622, 687–694 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that could potentially influence or bias the submitted work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Modwi, A., Taha, K.K., Khezami, L. et al. Structural and Electrical Characterization of Ba/ZnO Nanoparticles Fabricated by Co-precipitation. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30, 2633–2644 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01425-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01425-4