Abstract
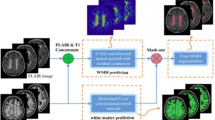
Existing brain region segmentation algorithms based on deep convolutional neural networks (CNN) are inefficient for object boundary segmentation. In order to enhance the segmentation accuracy of brain tissue, this paper proposed an object region segmentation algorithm that combines pixel-level information and semantic information. Firstly, we extract semantic information by CNN with the attention module and get the coarse segmentation results through a specific pixel-level classifier. Then, we exploit conditional random fields to model the relationship between the underlying pixels so as to get local features. Finally, the semantic information and the local pixel-level information are respectively used as the unary potential and the binary potential of the Gibbs distribution, and the combination of both can obtain the fine region segmentation algorithm based on the fusion of pixel-level information and the semantic information. A large number of qualitative and quantitative test results show that our proposed algorithm has higher precision than the existing state-of-the-art deep feature models, which can better solve the problem of rough edge segmentation and produce good 3D visualization effect.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang, Z., Wang, S., Huo, J. et al. Bayesian Framework with Non-local and Low-rank Constraint for Image Reconstruction[C]//. Journal of Physics Conference Series. 1–12, 2017.
Zhao, X., Wu, Y., Song, G. et al., A deep learning model integrating FCNNs and CRFs for brain tumor segmentation[J]. Medical Image Analysis 43:98–111, 2017.
Sauwen, N., Acou, M., Sima, D. M. et al., Semi-automated brain tumor segmentation on multi-parametric MRI using regularized non-negative matrix factorization[J]. BMC Medical Imaging 17(1):11–19, 2017.
Gholipour, A., Rollins, C. K., Velasco-Annis, C. et al., A normative spatiotemporal MRI atlas of the fetal brain for automatic segmentation and analysis of early brain growth[J]. Scientific Reports 7(1):476–488, 2017.
Heudorfer, L., and Stammberger, T., Optimization and validation of a rapid high-resolution T1-w 3D FLASH water excitation MRI sequence for the quantitative assessment of articular cartilage volume and thickness - magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging 19(2):177–185, 2001.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E. et al., Whole brain segmentation[J]. Neuron 33(3):341–355, 2002.
Chen, H., Dou, Q., Yu, L. et al., VoxResNet: Deep voxelwise residual networks for brain segmentation from 3D MR images[J]. NeuroImage 53(8):119–127, 2017.
Kauppi, J. P., Pajula, J., Niemi, J. et al., Functional brain segmentation using inter-subject correlation in fMRI[J]. Human Brain Mapping 38(5):2643–2665, 2017.
Keshavan A, Datta E, M. Mcdonough I, et al. Mindcontrol: A web application for brain segmentation quality control[J]. NeuroImage, 2017,10(5):381–407.
Mahbod, A., Chowdhury, M., Smedby, Ö. et al., Automatic brain segmentation using artificial neural networks with shape context[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters 10(1):74–79, 2018.
Biscay, R. J., Bosch-Bayard, J. F., and Pascual-Marqui, R. D., Unmixing EEG inverse solutions based on brain segmentation[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience 12:325–328, 2018.
Wang, Y., Zu, C., Ma, Z. et al., Patch-wise label propagation for MR brain segmentation based on multi-atlas images[J]. Multimedia Systems 12(12):25–35, 2017.
Kong, Y., Chen, X., Wu, J. et al., Automatic brain tissue segmentation based on graph filter[J]. BMC Medical Imaging 18(1):174–179, 2018.
Xuan, T. P., Siarry, P., and Oulhadj, H., Integrating fuzzy entropy clustering with an improved PSO for MRI brain image segmentation[J]. Applied Soft Computing 24(1):183–197, 2018.
Akkus, Z., Galimzianova, A., Hoogi, A. et al., Deep learning for brain MRI segmentation: State of the art and future directions[J]. Journal of Digital Imaging 9(4):597–609, 2017.
Kernel sparse representation for MRI image analysis in automatic brain tumor segmentation[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 19(04):5–14, 2018.
Chenfei, Y., Ting, M., Dan, W. et al., Atlas pre-selection strategies to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of multi-atlas brain segmentation tools[J]. PLOS ONE 13(7):280–294, 2018.
Van d, K. L. A., Jeroen, D. B., Jeroen, H. et al., Fast CSF MRI for brain segmentation; cross-validation by comparison with 3D T1-based brain segmentation methods[J]. PLOS ONE 13(4):196–219, 2018.
Craddock, R. C., Bellec, P., and Jbabdi, S., Brain segmentation review[J]. NeuroImage 53(8):119–137, 2017.
Havaei, M., Davy, A., Warde-Farley, D. et al., Brain tumor segmentation with deep neural networks[J]. Medical Image Analysis 35:18–31, 2015.
Ley-Zaporozhan, J., Ley, S., Eberhardt, R. et al., Visualization of morphological parenchymal changes in emphysema: Comparison of different MRI sequences to 3D-HRCT[J]. European Journal of Radiology 73(1):29–49, 2010.
Bomans, M., Laub, G. et al., Improvement of 3D acquisition and visualization in MRI[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging 9(4):597–609, 1991.
Watanabe, Y., Mooij, R., Mark Perera, G. et al., Heterogeneity phantoms for visualization of 3D dose distributions by MRI-based polymer gel dosimetry[J]. Medical Physics 31(5):975–985, 2004.
Kuder, T. A., Risse, F., Eichinger, M. et al., New method for 3D parametric visualization of contrast-enhanced pulmonary perfusion MRI data[J]. European Radiology 18(2):291–297, 2008.
Kalia, V., Fritz, B., Johnson, R. et al., CAIPIRINHA accelerated SPACE enables 10-min isotropic 3D TSE MRI of the ankle for optimized visualization of curved and oblique ligaments and tendons[J]. European Radiology 19(4):97–109, 2017.
Xia, K., Liu, Z. Renal Segmentation Algorithm Combined Low-level Features with Deep Coding Feature. 2018 27th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Nanjing, pp. 752–757, 2018.
Otsubo, H., Akatsuka, Y., Takashima, H., et al. MRI depiction and 3D visualization of three anterior cruciate ligament bundles[J]. Clinical Anatomy, 2016.
Qian, P., Sun, S., Jiang, Y., Kuan-Hao, S., Ni, T., Wang, S., and Muzic, Jr., R. F., Cross-domain, soft-partition clustering with diversity measure and knowledge reference. Pattern Recognition 50:155–177, 2016.
Qian, P., Zhou, J., Jiang, Y., Liang, F., Zhao, K., Wang, S., Su, K.-H., and Muzic, Jr., R. F., Multi-view maximum entropy clustering by jointly leveraging inter-view collaborations and intra-view-weighted attributes. IEEE Access 6:28594–28610, 2018.
Qian, P., Chung, F.-L., Wang, S., and Deng, Z., Fast graph-based relaxed clustering for large data sets using minimal enclosing ball. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics- Part B 42(3):672–687, 2012.
Jiang, Y., Wu, D., Deng, Z., Qian, P., Wang, J., Wang, G., Chung, F.-L., Choi, K.-S., and Wang, S., Seizure classification from EEG signals using transfer learning, semi-supervised learning and TSK fuzzy system. IEEE Trans. Neural Systems & Rehabilitation Engineering 25(12):2270–2284, 2017.
Jiang, Y., Deng, Z., Chung, F.-L., Wang, G., Qian, P., Choi, K.-S., and Wang, S., Recognition of epileptic EEG signals using a novel multi-view TSK fuzzy system. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Systems 25(1):3–20, 2017.
Jiang, Y., Chung, F.-L., Wang, S., Deng, Z., Wang, J., and Qian, P., Collaborative fuzzy clustering from multiple weighted views. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 45(4):688–701, 2015.
Xia, K.-j., Yin, H.-s., and Zhang, Y.-d., Deep semantic segmentation of kidney and Space-occupying lesion area based on SCNN and ResNet models combined with SIFT-flow algorithm. Journal of medical systems 43(1):2, 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The paper does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Image & Signal Processing
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, J., Li, H. An Improved Full Convolutional Network Combined with Conditional Random Fields for Brain MR Image Segmentation Algorithm and its 3D Visualization Analysis. J Med Syst 43, 292 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1424-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-019-1424-0