Abstract
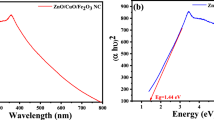
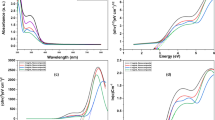
This research aims to explore the utilization of Ocimum basilicum leaf extract as a green and sustainable method for the synthesis of Fe3O4/NiO nanocomposites (Fe3O4/NiO NC) with potential applications in photocatalytic hydrogen evolution and organic dye degradation. The synthesized Fe3O4/NiO NC exhibited a unique bandgap energy of 2 eV, making it an effective visible-light photocatalyst. X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy confirmed the successful formation of the cubic crystal structure with an average crystallite size of 25.7 nm. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis revealed the presence of hydroxyl groups on the NC surface, which contributed to its photocatalytic properties. Under sunlight exposure, the Fe3O4/NiO NC demonstrated remarkable photocatalytic degradation efficiency of 99.3% for toluidine blue, 99.0% for 4-bromophenol, and 95.0% for methyl blue within 140 min. The photocatalyst also exhibited excellent reusability with only a slight decrease in efficiency after five cycles. Additionally, the Fe3O4/NiO NC displayed high photocatalytic activity in hydrogen evolution, generating 933.9 µmol/g of H2 over 8 h at a concentration of 0.7 g/L. This green synthesis approach, utilizing Ocimum basilicum extract, provides a cost-effective and eco-friendly method to produce Fe3O4/NiO NC with enhanced photocatalytic properties, holding great promise for sustainable energy and water purification applications. The study contributes to the understanding of novel nanocomposites and their potential for addressing urgent environmental challenges, underscoring their scientific value in green chemistry and renewable energy research.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
A.K. Sarker et al., Prospect of green hydrogen generation from hybrid renewable energy sources: a review. Energies 16(3), 1556 (2023)
A.J. Bard, M.A. Fox, Artificial photosynthesis: solar splitting of water to hydrogen and oxygen. Acc. Chem. Res. 28(3), 141–145 (1995)
D. Gust, T.A. Moore, A.L. Moore, Solar fuels via artificial photosynthesis. Acc. Chem. Res. 42(12), 1890–1898 (2009)
R. Zohra et al., Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of dyes and antibiotics with biosynthesized FeMn2O4 nanocomposite under sunlight irradiation: isotherm and kinetic study. Biomass Conv. Bioref. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-04497-y
J.A.A. Abdullah et al., Novel hybrid electrospun poly (ε-caprolactone) nanofibers containing green and chemical magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.54345
R. Mabindisa et al., Organic nanostructured materials for sustainable application in next generation solar cells. Appl. Sci. 11(23), 11324 (2021)
A. Fujishima, K. Honda, Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. nature. 238(5358), 37–38 (1972)
G. Deluga et al., Renewable hydrogen from ethanol by autothermal reforming. Science. 303(5660), 993–997 (2004)
S. Chu et al., Facile green synthesis of crystalline polyimide photocatalyst for hydrogen generation from water. J. Mater. Chem. 22(31), 15519–15521 (2012)
S. Mohanraj et al., Green synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles effect on fermentative hydrogen production by Clostridium acetobutylicum. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 173, 318–331 (2014)
F. Zhang et al., The survey of key technologies in hydrogen energy storage. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 41(33), 14535–14552 (2016)
S.Y. Foong et al., Progress in waste valorization using advanced pyrolysis techniques for hydrogen and gaseous fuel production. Bioresour. Technol. 320, 124299 (2021)
A. Boutalbi et al., Synthesis of Ag nanoparticles loaded with potassium polyacrylate hydrogel for rose bengal dye removal and antibacterial activity. Biomass Conv. Bioref. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-04337-z
H.A. Mohammed Mohammed et al., A novel biosynthesis of MgO/PEG nanocomposite for organic pollutant removal from aqueous solutions under sunlight irradiation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30(19), 57076–57085 (2023)
M. Althamthami et al., Improved photocatalytic activity under the sunlight of high transparent hydrophilic bi-doped TiO2 thin-films. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 443, 114818 (2023)
Y. Lai, A. Fakhri, B.J. Janani, Synergistic activities of silver indium sulfide/nickel molybdenum sulfide nanostructures anchored on clay mineral for light-driven bactericidal performance, and detection of uric acid from gout patient serum. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 234, 112526 (2022)
G.G. Hasan et al., Synergistic effect of novel biosynthesis SnO2@Fe3O4 nanocomposite: a comprehensive study of its photocatalytic, antibiotic, antibacterial, and antimutagenic activities. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 443, 114874 (2023)
S. Mouhamadou et al., Synthesis of piliostigma reticulatum decorated TiO2 based composite and its application towards Cr (VI) adsorption and bromophenol blue degradation: nonlinear kinetics, equilibrium modelling and optimisation photocatalytic parameters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 11, 109273 (2023)
M. Althamthami et al., Influence of hole-scavenger and different withdrawn speeds on photocatalytic activity of Co3O4 thin films under sunlight irradiation. Ceram. Int. 48(21), 31570–31578 (2022)
I. Kir et al., Biosynthesis and characterization of novel nanocomposite ZnO/BaMg2 efficiency for high-speed adsorption of AZO dye. Biomass Conv. Bioref. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-03985-5
H.A. Alhassani, M.A. Rauf, S.S. Ashraf, Efficient microbial degradation of Toluidine Blue dye by Brevibacillus sp. Dyes Pigm. 75(2), 395–400 (2007)
Y. Zidane et al., Green synthesis of multifunctional MgO@ AgO/Ag2O nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and toluidine blue. Front. Chem. (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2022.1083596
S. Haq et al., A novel shift in the absorbance maxima of methyl orange with calcination temperature of green tin dioxide nanoparticle-induced photocatalytic activity. Catalysts 12(11), 1397 (2022)
M. Ahmad et al., Phytogenic fabrication of ZnO and gold decorated ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9(1), 104725 (2021)
H. Sun et al., Ag@Fe3O4 core–shell surface-enhanced Raman scattering probe for trace arsenate detection. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 18(2), 1097–1102 (2018)
S. Venkateswarlu et al., A novel green synthesis of Fe3O4-Ag core shell recyclable nanoparticles using Vitis vinifera stem extract and its enhanced antibacterial performance. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 457, 30–35 (2015)
R. Selvaraj et al., Adsorptive removal of tetracycline from aqueous solutions using magnetic Fe2O3/activated carbon prepared from Cynometra ramiflora fruit waste. Chemosphere 310, 136892 (2023)
G.G. Hasan et al., Synergistic effect of novel biosynthesis SnO2@Fe3O4 nanocomposite: a comprehensive study of its photocatalytic of dyes & antibiotics, antibacterial, and antimutagenic activities. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 443, 114874 (2023)
M. Mehdipour, The Synthesis and Evaluation of magneto-plasmonic Nanoparticles for Biosensing Applications (UNSW Sydney, Sydney, 2021)
S. Laurent et al., Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles, in MRI Contrast Agents: From Molecules to Particles. (Springer, Singapore, 2017), pp.55–109
J.A.A. Abdullah et al., Green synthesis of FexOy nanoparticles with potential antioxidant properties. Nanomaterials. 12(14), 2449 (2022)
A.A. Alswat et al., Role of nanohybrid NiO–Fe3O4 in enhancing the adsorptive performance of activated carbon synthesized from Yemeni-Khat leave in removal of Pb (II) and Hg (II) from aquatic systems. Heliyon 9(3), e14301 (2023)
C. Salmi et al., Biosynthesis of Mn3O4/PVP nanocomposite for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes under sunlight irradiation. J. Cluster Sci. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-023-02475-y
V.B. Shet et al., Cocoa pod shell mediated silver nanoparticles synthesis, characterization, and their application as nanocatalyst and antifungal agent. Appl. Nanosci. 13(6), 4235–4245 (2023)
H. Sridevi et al., Structural characterization of cuboidal α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles synthesized by a facile approach. Appl. Nanosci. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-023-02780-y
J.A.A. Abdullah et al., Green synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles by pheonix dactylifera leaf extract and evaluation of their antioxidant activity. Sustainable Chem. Pharm. 17, 100280 (2020)
J. Singh et al., Green’synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 16(1), 1–24 (2018)
M. Nasrollahzadeh et al., Green-synthesized nanocatalysts and nanomaterials for water treatment: current challenges and future perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 401, 123401 (2021)
A.S. Abdelsattar et al., Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ocimum basilicum L. and Hibiscus sabdariffa L. extracts and their antibacterial activity in combination with phage ZCSE6 and sensing properties. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 32(6), 1951–1965 (2022)
J.A.A. Abdullah et al., Biopolymer-based films reinforced with FexOy-nanoparticles. Polymers 14, 4487 (2022)
K. Solanki et al., Hierarchical 3D flower-like metal oxides micro/nanostructures: fabrication, surface modification, their crucial role in environmental decontamination, mechanistic insights, and future perspectives. Small (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202300394
K. He et al., Method for determining crystal grain size by X-ray diffraction. Cryst. Res. Technol. 53(2), 1700157 (2018)
M. Shi et al., Temperature-controlled crystal size of wide band gap nickel oxide and its application in electrochromism. Micromachines. 12(1), 80 (2021)
S. Ananthi et al., Natural tannic acid (green tea) mediated synthesis of ethanol sensor based Fe3O4 nanoparticles: investigation of structural, morphological, optical properties and colloidal stability for gas sensor application. Sens. Actuators B 352, 131071 (2022)
X. Liu et al., Noble metal–metal oxide nanohybrids with tailored nanostructures for efficient solar energy conversion, photocatalysis and environmental remediation. Energy Environ. Sci. 10(2), 402–434 (2017)
W. Yang, C. Wang, V. Arrighi, An organic silver complex conductive ink using both decomposition and self-reduction mechanisms in film formation. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 2771–2783 (2018)
T.C.P. Veettil et al., Characterization of freeze-dried oxidized human red blood cells for pre-transfusion testing by synchrotron FTIR microspectroscopy live-cell analysis. Analyst. 148(7), 1595–1602 (2023)
R. Eshaghi Malekshah, B. Fahimirad, A. Khaleghian, Synthesis, characterization, biomedical application, molecular dynamic simulation and molecular docking of Schiff base complex of Cu (II) supported on Fe3O4/SiO2/APTS. Int. J. Nanomed. 15, 2583–2603 (2020)
W. Cai, J. Wan, Facile synthesis of superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles in liquid polyols. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 305(2), 366–370 (2007)
M. Sundrarajan, M. Ramalakshmi, Novel cubic magnetite nanoparticle synthesis using room temperature ionic liquid. E-J. Chem. 9(3), 1070–1076 (2012)
A. Rahdar, M. Aliahmad, Y. Azizi, NiO nanoparticles: synthesis and characterization. J. Nanostruct. 5, 145 (2015)
Z. Fereshteh et al., Synthesis of nickel oxide nanoparticles from thermal decomposition of a new precursor. J. Cluster Sci. 23, 577–583 (2012)
H. Lv et al., Efficient degradation of high concentration azo-dye wastewater by heterogeneous Fenton process with iron-based metal-organic framework. J. Mol. Catal. A 400, 81–89 (2015)
P. Sheena et al., Characterization of NiO/CoPc nanocomposite material synthesized by solvent evaporation route. J. Nanostructure Chem. 8, 207–215 (2018)
J.A.A. Abdullah et al., Effect of Calcination temperature and time on the synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Green vs. Chemical Method. Materials. 16(5), 1798 (2023)
P. Yadav, A. Bhaduri, Photocatalytic performances of manganese oxide nanorods decorated graphene oxide nanocomposites. Diam. Relat. Mater. 135, 109820 (2023)
T. Li et al., Synthesis of magnetically recyclable Fe3O4@NiO nanostructures for styrene epoxidation and adsorption application. Ceram. Int. 41(2), 2214–2220 (2015)
P. Koohi, A. Rahbar-kelishami, H. Shayesteh, Efficient removal of congo red dye using Fe3O4/NiO nanocomposite: synthesis and characterization. Environ. Technol. Innov. 23, 101559 (2021)
T. Saleem et al., Synthesis and characterization of nanostructured ternary composites of graphene oxide/Fe3 O4/NiO for waste water treatment. Dig. J. Nanomater Biostruct. 17, 1203–1210 (2022)
P. Hariani et al., Synthesis of Fe3O4/SiO2/NiO magnetic composite: evaluation of its catalytic activity for methylene blue degradation. GLOBAL NEST JOURNAL. 25(2), 36–43 (2023)
N. Soltani et al., Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue under visible light using PVP-capped ZnS and CdS nanoparticles. Sol. Energy. 97, 147–154 (2013)
M. Dudita et al., The influence of the additives composition and concentration on the properties of SnOx thin films used in photocatalysis. Mater. Lett. 65(14), 2185–2189 (2011)
A.S. Priya et al., Investigations on the enhanced photocatalytic activity of (Ag, La) substituted nickel cobaltite spinels. Solid State Sci. 98, 105992 (2019)
K. Kannan et al., Photocatalytic and antimicrobial properties of microwave synthesized mixed metal oxide nanocomposite. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 125, 108429 (2021)
M. Ikram et al., Photocatalytic and bactericidal properties and molecular docking analysis of TiO 2 nanoparticles conjugated with zr for environmental remediation. RSC Adv. 10(50), 30007–30024 (2020)
M. Meshesha et al., Remarkable photoelectrochemical activity of titanium dioxide nanorod arrays sensitized with transition metal sulfide nanoparticles for solar hydrogen production. Mater. Today Chem. 26, 101216 (2022)
K. Kannan et al., Hydrothermally Synthesized Mixed Metal Oxide Nanocomposites for Electrochemical Water Splitting and Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production (International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023)
K. Kannan et al., Two dimensional MAX supported copper oxide/nickel Oxide/MAX as an efficient and novel photocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 48(20), 7273–7283 (2023)
S. Nayak, L. Mohapatra, K. Parida, Visible light-driven novel gC 3 N 4/NiFe-LDH composite photocatalyst with enhanced photocatalytic activity towards water oxidation and reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(36), 18622–18635 (2015)
Y. He et al., Remarkably enhanced visible-light photocatalytic hydrogen evolution and antibiotic degradation over g-C3N4 nanosheets decorated by using nickel phosphide and gold nanoparticles as cocatalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 517, 146187 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Algerian Directorate General for Scientific Research and Technological Development-DGRSDT for financial assistance, Laboratory of Biotechnology Biomaterial and Condensed Matter, Faculty of Technology, El Oued University, El-Oued 39000, Algeria. And Authors extend their thanks to Researchers Supporting Project (RSP2023R160), King Saud University (Riyadh, Saudi Arabia).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Investigation, data acquisition, Con-capitalization: LSE, HAM, CS; formal analysis: GGH, HAM, CS; methodology: HAM, GGH, CS; writing—original draft: HAM, GGH, CS; review and editing: HAM, JAAA, LS; data curation: HAM, SM, GGH, CS, JAAA; data analysis: HAM, JAAA, FA; resources: HAM, JAA A, FA, CS; supervision: LSE, SM.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Eddine, L.S., Mohammed, H.A., Salmi, C. et al. Biogenic synthesis of Fe3O4/NiO nanocomposites using Ocimum basilicum leaves for enhanced degradation of organic dyes and hydrogen evolution. J Porous Mater 31, 213–226 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-023-01509-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-023-01509-0