Abstract
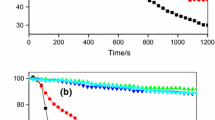
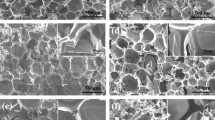
In this paper, ferrous powder has been used as flame retardant and smoke suppression synergism with ammonium polyphosphate (APP) in flame retardant thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) composites. The synergistic flame retardant and smoke suppression effects between ferrous powder and APP have been studied using cone calorimeter test (CCT), smoke density test (SDT), and limiting oxygen index (LOI). The CCT results showed that appropriate amount of ferrous powder can greatly decrease heat release rate, total heat release, mass loss, smoke production rate, total smoke release, and smoke factor. The SDT results indicated that ferrous powder can greatly improve the luminous flux of flame retardant TPU composites in the test with flame; however, the luminous flux decreases with the addition of ferrous powder in the test without flame. And the LOI results showed that the LOI value of the samples with ferrous powder is higher than that of the sample with only APP. The above results imply there are synergistic flame retardant and smoke suppression effects between ferrous powder and APP in TPU composites. Then, the thermo-gravimetric (TG) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were used to investigate the synergistic flame retardant and smoke suppression mechanism between ferrous powder and APP in TPU composites. The TG and DTG results showed that ferrous powder can decrease the initial decomposition temperature and improve the thermal stability at high temperature for flame retardant TPU composites. The SEM results showed that ferrous powder can improve the quality of char residues after CCT, resulting good flame retardant and smoke suppression properties for TPU composites containing both APP and ferrous powder. This is a very meaningful result in fire safety materials fields.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nie SB, Peng C, Yuan SJ, Zhang MX. Thermal and flame retardant properties of novel intumescent flame retardant polypropylene composites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;113:865–71.
Hatsuhiko H, Yoshihisa T, Takahito I. Synergistic effect of red phosphorus, novella and melamine ternary combination on flame retardancy of poly (oxymethylene). Polym Degrad Stab. 2006;91:1996–2002.
Kongkhlang T, Kousaka Y, Umemura T, Nakaya D, Thuamthong W, Pattamamongkolchai Y, Chirachanchai S. Role of primary amine in polyoxymethylene (POM)/bentonite nanocomposite formation. Polymer. 2008;49:1676–84.
Archodoulaki VM, Lüftl S, Seidler S. Degradation behavior of polyoxymethylene: Influence of different stabilizer packages. J Appl Polym Sci. 2007;105:3679–88.
Zhang Q, Chen YH. Synergistic effects of ammonium polyphosphate/melamine intumescent system with macromolecular char former in flame-retarding polyoxymethylene. J Polym Res. 2011;18:293–303.
Carty P, White S. Relationship between char, flammability and smoke production in blends of chlorinated polyvinyl chloride, CPVC, and acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene, ABS, containing a smoke suppressing iron compound. Polym Netw Blends. 1997;7:121–4.
Carty P, Whilte S. Anomalous flammability behavior of CPVC (chlorinated polyvinyl chloride) in blends with ABS (acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene) containing flame-retarding/smoke-suppressing compounds. Polymer. 1997;38:1111–9.
Carty P, Metcalfe E, Annison WN. The optimization of the smoke suppressant and flame retardant properties of flexible PVC. J Appl Polym Sci. 1990;41:901–6.
Skinner GA, Haines P, Evans SJ. The effects of structure on the thermal degradation of polyester resins. Thermochim Acta. 1996;278:77–89.
Morgan AB, Gilman JW. An overview of flame retardancy of polymeric materials: application, technology, and future directions. Fire Mater. 2013;37:259–79.
Green DW, Dallavia AJ. Alumina trihydrate in flexible PVC-effects of alumina particle morphology. J Vinyl Addit Technol. 1988;10:178–82.
Gann RG, Babrauskas V, Peacock RD, Hall JR. Fire conditions for smoke toxicity measurement. Fire Mater. 1994;18:193–9.
Prager FH, Cabos HP. Fire–gas hazards in rail traffic. Fire Mater. 1994;18:131–49.
Chen XL, Jiang YF, Jiao CM. Smoke suppression properties of ferrite yellow on flame retardant thermoplastic polyurethane based on ammonium polyphosphate. J Hazard Mater. 2014;266:114–21.
Fang Y, Wang Q, Guo C, Song Y, Cooper PA. Effect of zinc borate and wood flour on thermal degradation and fire retardancy of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) composites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;100:230–6.
Wang X, Hu Y, Song L, Xuan SY, Xing WY, Bai ZM, Lu HD. Flame retardancy and thermal degradation of intumescent flame retardant poly(lactic acid)/starch biocomposites. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2010;50:713–20.
Wu K, Hu Y, Song L, Lu HD, Wang ZZ. Flame retardancy and thermal degradation of intumescent flame retardant starch-based biodegradable composites. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2009;48:3150–7.
Chen XL, Jiao CM, Wang Y. Synergistic effects of iron powder on intumescent flame retardant polypropylene system. Express Polym Lett. 2009;3:359–65.
Tsai KC. Orientation effect on cone calorimeter test results to assess fire hazard of materials. J Hazard Mater. 2009;172:763–72.
Schartel B, Hull TR. Development of fire-retarded materials—interpretation of cone calorimeter data. Fire Mater. 2007;31:327–54.
Wang XY, Li Y, Liao WW, Gu J, Li D. A new intumescent flame-retardant: preparation, surface modification, and its application in polypropylene. Polym Adv Technol. 2008;19:1055–61.
Qian Y, Wei P, Zhao XM, Jiang PK, Yu HZ. Flame retardancy and thermal stability of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanocomposites. Fire Mater. 2012;22:22037–43.
Chen XL, Jiao CM. Flammability and thermal degradation of epoxy acrylate modified with phosphorus-containing compounds. Polym Adv Technol. 2010;21:490–5.
Babrauskas V, Peacock RD. Heat release rate: the single most important variable in fire hazard. Fire Saf J. 1992;18:255–72.
Almeras X, Bras ML, Hornsby P, Bourbigot S, Marosi G, Keszei S, Poutch F. Effect of fillers on the fire retardancy of intumescent polypropylene compounds. Polym Degrad Stab. 2003;82:325–31.
Jiao CM, Chen XL. Flammability and thermal degradation of intumescent flame-retardant polypropylene composites. Polym Eng Sci. 2010;10:767–72.
Dong YY, Gui Z, Hu Y, Wu Y, Jiang SH. The influence of titanate nanotube on the improved thermal properties and the smoke suppression in poly(methyl methacrylate). J Hazard Mater. 2012;209:34–9.
Carty P, White S, Creghton JR. TG and flammability studies on polymer blends containing acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene and chlorinated poly(vinyl chloride). J Therm Anal Calorim. 2001;63:679–87.
Carty P, White S. The effect of temperature on char formation in polymer blends: an explanation of the role of the smoke suppressant FeOOH acting in ABS/CPVC polymer blends. Polym Degrad Stab. 2002;75:173–84.
Ricciardi MR, Antonucci V, Zarrelli M, Giordano M. Fire behavior and smoke emission of phosphate-based inorganic fire-retarded polyester resin. Fire Mater. 2012;36:203–15.
Chen XL, Jiao CM, Zhang J. Thermal and combustion behavior of ethylene–vinyl acetate/aluminum trihydroxide/Fe-montmorillonite composites. Polym Eng Sci. 2012;10:414–9.
Chen XL, Hu Y, Jiao CM, Song L. Preparation and thermal properties of a novel flame-retardant coating. Polym Degrad Stab. 2007;92:1141–50.
Kimura T. Advanced topics of 15th international congress of thermal analysis and calorimetry. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;113:999–1002.
Li LL, Wang G, Wang SY, Qin S. Thermogravimetric and kinetic analysis of energy crop Jerusalem artichoke using the distributed activation energy model. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;114:1183–9.
Kubranová M, Jóna E, Rudinská E, Nemčeková K, Ondrušová D, Pajtášová M. Thermal properties of Co-, Ni- and Cu-exchanged montmorillonite with 3 hydroxypyridine. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2003;74:251–7.
Jona E, Sapietova M, Nircova S, Pajtasova M, Ondrusova D, Pavlık V, Lajdova L, Mojumdar SC. Characterization and thermal properties of Ni-exchanged montmorillonite with benzimidazole. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;94:69–73.
Zhao K, Xu W, Song L, Wang B, Feng H, Hu Y. Synergistic effects between boron phosphate and microencapsulated ammonium polyphosphate in flame-retardant thermoplastic polyurethane composites. Polym Adv Technol. 2012;23:894–900.
Lin M, Li B, Li Q, Li S, Zhang SQ. Synergistic effect of metal oxides on the flame retardancy and thermal degradation of novel intumescent flame-retardant thermoplastic polyurethanes. J Appl Polym Sci. 2011;121:1951–60.
Zhang Y, Chen X, Fang Z. Synergistic effects of expandable graphite and ammonium polyphosphate with a new carbon source derived from biomass in flame retardant ABS. J Appl Polym Sci. 2013;128:2424–32.
Fang G, Li H, Chen Z, Liu X. Preparation and characterization of flame retardant n-hexadecane/silicon dioxide composites as thermal energy storage materials. J Hazard Mater. 2010;181:1004–9.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51106078, 51206084), the Out-standing Young Scientist Research Award Fund from Shandong Province (BS2011CL018), and the University Research and Development Projects Shandong Province (J14LA13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, C., Zhao, X., Song, W. et al. Synergistic flame retardant and smoke suppression effects of ferrous powder with ammonium polyphosphate in thermoplastic polyurethane composites. J Therm Anal Calorim 120, 1173–1181 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4377-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4377-z