Abstract
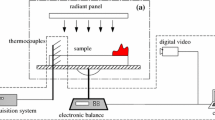
Experiments were carried out on insulation foams of EPS and XPS in a small-scale flame spread experimental bench in the Tibetan plateau area of Lhasa and the plain area of Hefei both in China, respectively. The effects of altitude and sample orientation on flame spread behavior were quantitatively analyzed. The results show that extinction and secondary ignition occur for XPS on plateau, as the oxygen concentration in air entrainment is influenced by the generated smoke in the pool fire zone. The flame spread speed of EPS increases with the incline angle both in Lhasa and in Hefei, but for XPS (downward flame spread), the flame spread speed increases with the decrease in incline angle, especially in Lhasa. It is found that the heat transfer process is different for EPS and XPS. The transition fire zone plays an important role in heat transfer over XPS for downward flame spread resulting in total heat transfer including the flame convective and radiative heat \( q_{\text{f}}^{\prime \prime } \delta_{\text{f}} \) and the conductive heat \( q_{\text{c}}^{\prime \prime } L \) increase with the decrease in incline angle, while for EPS, the surface flame zone dominates the heat transfer in two places.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
An W, Jiang L, Sun J, Liew KM. Correlation analysis of sample thickness, heat flux, and cone calorimetry test data of polystyrene foam. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119:229–38.
Xu Q, Majlingova A, Zachar M, Jin C, Jiang Y. Correlation analysis of cone calorimetry test data assessment of the procedure with tests of different polymers. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;110:65–70.
Luo F, Wu K, Lu M, Nie S, Li X, Guan X. Thermal degradation and flame retardancy of microencapsulated ammonium polyphosphate in rigid polyurethane foam. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;. doi:10.1007/s10973-015-4425-3.
Morgan A, Chu L, Harris J. A flammability performance comparison between synthetic and natural clays in polystyrene nanocomposites. Fire Mater. 2005;29:213–29.
Doroudiani S, Omidian H. Environmental, health and safety concerns of decorative mouldings made of expanded polystyrene in buildings. Build Environ. 2010;45:647–54.
An W, Xiao H, Liew KM, Jiang L, Yan W, Zhou Y, Huang X, Sun J, Gao L. Downward flame spread over extruded polystyrene: effects of sample thickness, pressure, and sidewalls. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119:1091–103.
Zhou Y, Xiao H, Yan W, An W, Jiang L, Sun J. Horizontal flame spread characteristics of rigid polyurethane and molded polystyrene foams under externally applied radiation at two different altitudes. Fire Technol. 2014;. doi:10.1007/s10694-014-0443-0.
Zhang Y, Huang X, Wang Q, Ji J, Sun J, Yin Y. Experimental study on the characteristics of horizontal flame spread over XPS surface on plateau. J Hazard Mater. 2011;189:34–9.
Huang X, Sun J, Ji J, Zhang Y, Wang Q, Zhang Y. Flame spread over the surface of thermal insulation materials in different environments. Chin Sci Bull. 2011;56(15):1617–22.
Griffin GJ, Bicknell AD, Bradbury GP, White N. Effect of construction method on the fire behavior of sandwich panels with expanded polystyrene cores in room fire tests. J Fire Sci. 2006;24:275–94.
Tsai KC. Orientation effect on cone calorimeter test results to assess fire hazard of materials. J Hazard Mater. 2009;172:763–72.
Drysdale DD, Macmillan AJR. Flame spread on inclined surfaces. Fire Saf J. 1992;18:245–54.
Li J, Ji J, Zhang Y, Sun J. Characteristics of flame spread over the surface of charring solid combustibles at high altitude. Chin Sci Bull. 2009;54(8):1127–32.
Zhang Y, Ji J, Wang QS, Huang XJ, Wang QH, Sun JH. Prediction of the critical condition for flame acceleration over wood surface with different sample orientations. Combust Flame. 2012;159(9):2999–3002.
Quintiere JG. Fundamentals of fire phenomena. London: Wiley; 2006. p. 195–231.
Murrell J. Multi-layer paint surfaces-a hidden fire hazard. Fire. 1998; 19–20.
Wu Y, Xing HJ, Atkinson G. Interaction of fire plume with inclined surface. Fire Saf J. 2000;35(4):391–403.
Jeff W, Matt K, Subrata BI, Altenkirch RA. Heat transfer pathways in flame spreading over thick fuels as a function of the flame spread regime: microgravity, thermal, and kinetic. Combust Sci Technol. 1997;127(1):119–40.
Thomas PH. Rates of spread of some wind driven fires. J Forest. 1971;44(2):155–7.
Hirano T, Noreikis SE, Waterman TE. Postulations of flame spread mechanisms. Combust Flame. 1974;22(3):353–63.
Ohlemiller TJ, Shields JR. Aspects of the fire behavior of thermoplastic materials, National Institute of Standards and Technology. 2007. p.1–30.
Chow WK, Leung CW. Necessity of testing fire behaviour of plastic materials under flashover. Polym Test. 2006;25:853–8.
Xie QY, Zhang HP, Ye RB. Experimental study on melting and flowing behavior of thermoplastics combustion based on a new setup with a T-shape trough. J Hazard Mater. 2009;166:1321–5.
Wang Y, Zhang F, Chen XL, Jin Y, Zhang J. Burning and dripping behaviors of polymers under the UL94 vertical burning test conditions. Fire Mater. 2010;34:203–15.
Wang XG, Cheng XD, Li LM, Lo S, Zhang HP. Effect of ignition condition on typical polymer’s melt flow flammability. J Hazard Mater. 2011;190(1–3):766–71.
Ansari M, Hatzikiriakos SG, Mitsoulis E. Slip effects in HDPE flows. J Non-Newton Fluid. 2012;167–168:18–29.
Gollner MJ, Overholt K, Williams FA, Rangwala AS, Perricone J. Warehouse commodity classification from fundamental principles. Part I: commodity and burning rates. Fire Saf J. 2011;46:305–16.
Overholt KJ, Gollner MJ, Perricone J, Rangwala AS, Williams FA. Warehouse commodity classification from fundamental principles. Part II: flame heights and flame spread. Fire Saf J. 2011;46:317–29.
Zhang Y, Sun JH, Huang XJ, Chen XF. Heat transfer mechanisms in horizontal flame spread over wood and extruded polystyrene surfaces. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2013;61:28–34.
Jiang L, Xiao H, Zhou Y, An W, Yan W, He J, Sun J. Theoretical and experimental study of width effects on horizontal flame spread over extruded and expanded polystyrene foam surfaces. J Fire Sci. 2014;32(3):193–209.
Quintiere JG, Rangwala AS. A theory for flame extinction based on flame temperature. Fire Mater. 2004;28:387–402.
Huang XJ, Wang QS, Zhang Y, Yin Y, Sun JH. Thickness effect on flame spread characteristics of expanded polystyrene in different environments. J Thermoplast Compos Mater. 2011;25:427–38.
Acknowledgements
This study has been funded by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, Grant. No. 2012CB719702), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51206002), and the open fund of State Key Laboratory of Fire Science (No. HZ2012-KF04). The authors gratefully acknowledge these supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Zhao, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Effects of altitude and sample orientation on heat transfer for flame spread over polystyrene foams. J Therm Anal Calorim 121, 641–650 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4615-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4615-z