Abstract
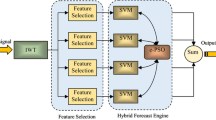
In this paper, a new and efficient hybrid empirical wavelet transform (EWT)-based reduced robust Mexican hat wavelet kernel ridge regression (RMHWK) model is proposed to achieve both point and interval forecasting of solar power in a smart grid scenario. Initially, the actual nonlinear solar power data series was decomposed by the EWT method. A reduced robust kernel ridge regression (RKRR) approach was incorporated that shows a notable decrease in training time without appreciable loss in forecasting accuracy. The reduction in the size of the kernel matrix was achieved by selecting a set of random support vectors from the training data set. For validating the superior performance of the proposed EWT-RMHWK forecasting model, a numerical experimentation implementing a real-time data set of 1 MW solar power plant (Odisha, India) as well as an online historical data set (Florida, USA) was considered and compared with other hybrid models using either empirical mode decomposition- or wavelet decomposition-based RKRR and EWT-ELM, etc. The kernel parameters were optimized with the chaotic water cycle algorithm to boost the performance of the proposed prediction model. Further, the proposed EWT-RKRR method was used to construct prediction interval forecasting with three different confidence levels with 90%, 95%, and 99% for Florida solar power plant using different time horizons of 15 min, 1 h, and 1 day, respectively.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ak, R., Fink, O., & Zio, E. (2015). Two machine learning approaches for short-term wind speed time-series prediction. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 27(8), 1734–1747.
Amini, M. H., Kargarian, A., & Karabasoglu, O. (2016). ARIMA-based decoupled time series forecasting of electric vehicle charging demand for stochastic power system operation. Electric Power Systems Research, 140, 378–390.
Armengot, M., Laparra, V., Gómez-Chova, L., Malo, J., & Camps-Valls, G. (2010). Adaptive kernel ridge regression for image denoising. In 2010 IEEE international workshop on machine learning for signal processing (pp. 432–437). IEEE.
Boroojeni, K. G., Amini, M. H., Nejadpak, A., Iyengar, S. S., Hoseinzadeh, B., & Bak, C. L. (2016, May). A theoretical bilevel control scheme for power networks with large-scale penetration of distributed renewable resources. In 2016 IEEE international conference on electro information technology (EIT) (pp. 0510–0515). IEEE.
Bouzerdoum, M., Mellit, A., & Pavan, A. M. (2013). A hybrid model (SARIMA–SVM) for short-term power forecasting of a small-scale grid-connected photovoltaic plant. Solar Energy, 98, 226–235.
Carriere, T., Vernay, C., Pitaval, S., & Kariniotakis, G. (2019). A novel approach for seamless probabilistic photovoltaic power forecasting covering multiple time frames. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid (early access). https://doi.org/10.1109/tsg.2019.2951288.
Cawley, G. C., & Talbot, N. L. (2002). Reduced rank kernel ridge regression. Neural Processing Letters, 16(3), 293–302.
Chen, X., Dong, Z. Y., Meng, K., Xu, Y., Wong, K. P., & Ngan, H. W. (2012). Electricity price forecasting with extreme learning machine and bootstrapping. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 27(4), 2055–2062.
Chupong, C., & Plangklang, B. (2011). Forecasting power output of PV grid connected system in Thailand without using solar radiation measurement. Energy Procedia, 9, 230–237.
Contreras, J., Espinola, R., Nogales, F. J., & Conejo, A. J. (2003). ARIMA models to predict next-day electricity prices. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 18(3), 1014–1020.
Dai, W., Chen, Q., Chu, F., Ma, X., & Chai, T. (2017). Robust regularized random vector functional link network and its industrial application. IEEE Access, 5, 16162–16172.
David, M., Ramahatana, F., Trombe, P. J., & Lauret, P. (2016). Probabilistic forecasting of the solar irradiance with recursive ARMA and GARCH models. Solar Energy, 133, 55–72.
Deng, W. Y., Ong, Y. S., & Zheng, Q. H. (2016). A fast reduced kernel extreme learning machine. Neural Networks, 76, 29–38.
Foley, A. M., Leahy, P. G., Marvuglia, A., & McKeogh, E. J. (2012). Current methods and advances in forecasting of wind power generation. Renewable Energy, 37(1), 1–8.
Gilles, J. (2013). Empirical wavelet transform. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 61(16), 3999–4010.
Guo, J., Xu, X., Lian, W., & Zhu, H. (2019). A new approach for interval forecasting of photovoltaic power based on generalized weather classification. International Transactions on Electrical Energy Systems, 29(4), e2802.
Guo, Z., Zhao, W., Lu, H., & Wang, J. (2012). Multi-step forecasting for wind speed using a modified EMD-based artificial neural network model. Renewable Energy, 37(1), 241–249.
Han, Y., Wang, N., Ma, M., Zhou, H., Dai, S., & Zhu, H. (2019). A PV power interval forecasting based on seasonal model and nonparametric estimation algorithm. Solar Energy, 184, 515–526.
Heidari, A. A., Abbaspour, R. A., & Jordehi, A. R. (2017). An efficient chaotic water cycle algorithm for optimization tasks. Neural Computing and Applications, 28(1), 57–85.
Hong, Y. Y., Yu, T. H., & Liu, C. Y. (2013). Hour-ahead wind speed and power forecasting using empirical mode decomposition. Energies, 6(12), 6137–6152.
https://www.nrel.gov/grid/solar-power-data.html, Accessed on 15th January 2019.
Hu, J., & Wang, J. (2015). Short-term wind speed prediction using empirical wavelet transform and Gaussian process regression. Energy, 93, 1456–1466.
Huang, G. B. (2014). An insight into extreme learning machines: Random neurons, random features and kernels. Cognitive Computation, 6(3), 376–390.
Huang, C. M., Chen, S. J., Yang, S. P., & Kuo, C. J. (2015). One-day-ahead hourly forecasting for photovoltaic power generation using an intelligent method with weather-based forecasting models. IET Generation, Transmission and Distribution, 9(14), 1874–1882.
Huang, R., Huang, T., Gadh, R., & Li, N. (2012, November). Solar generation prediction using the ARMA model in a laboratory-level micro-grid. In 2012 IEEE third international conference on smart grid communications (SmartGridComm) (pp. 528–533). IEEE.
Huang, G. B., Wang, D. H., & Lan, Y. (2011a). Extreme learning machines: A survey. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2(2), 107–122.
Huang, G. B., Zhou, H., Ding, X., & Zhang, R. (2011b). Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 42(2), 513–529.
Hwang, J. G., & Ding, A. A. (1997). Prediction intervals for artificial neural networks. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 92(438), 748–757.
Izgi, E., Öztopal, A., Yerli, B., Kaymak, M. K., & Şahin, A. D. (2012). Short–mid-term solar power prediction by using artificial neural networks. Solar Energy, 86(2), 725–733.
Kavasseri, R. G., & Seetharaman, K. (2009). Day-ahead wind speed forecasting using f-ARIMA models. Renewable Energy, 34(5), 1388–1393.
Kavousi-Fard, A., Khosravi, A., & Nahavandi, S. (2015). A new fuzzy-based combined prediction interval for wind power forecasting. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 31(1), 18–26.
Khosravi, A., Nahavandi, S., Creighton, D., & Atiya, A. F. (2010). Lower upper bound estimation method for construction of neural network-based prediction intervals. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 22(3), 337–346.
Khosravi, A., Nahavandi, S., Srinivasan, D., & Khosravi, R. (2014). Constructing optimal prediction intervals by using neural networks and bootstrap method. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 26(8), 1810–1815.
Lee, W., Kim, K., Park, J., Kim, J., & Kim, Y. (2018). Forecasting solar power using long-short term memory and convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access, 6, 73068–73080.
Li, K., Wang, R., Lei, H., Zhang, T., Liu, Y., & Zheng, X. (2018). Interval prediction of solar power using an improved bootstrap method. Solar Energy, 159, 97–112.
Liu, H., Chen, C., Tian, H. Q., & Li, Y. F. (2012). A hybrid model for wind speed prediction using empirical mode decomposition and artificial neural networks. Renewable Energy, 48, 545–556.
Liu, D., Niu, D., Wang, H., & Fan, L. (2014). Short-term wind speed forecasting using wavelet transform and support vector machines optimized by genetic algorithm. Renewable Energy, 62, 592–597.
Liu, H., Tian, H., Liang, X., & Li, Y. (2015). New wind speed forecasting approaches using fast ensemble empirical model decomposition, genetic algorithm, mind evolutionary algorithm and artificial neural networks. Renewable Energy, 83, 1066–1075.
Martín, L., Zarzalejo, L. F., Polo, J., Navarro, A., Marchante, R., & Cony, M. (2010). Prediction of global solar irradiance based on time series analysis: Application to solar thermal power plants energy production planning. Solar Energy, 84(10), 1772–1781.
Naik, J., Satapathy, P., & Dash, P. K. (2018). Short-term wind speed and wind power prediction using hybrid empirical mode decomposition and kernel ridge regression. Applied Soft Computing, 70, 1167–1188.
Ni, Q., Zhuang, S., Sheng, H., Kang, G., & Xiao, J. (2017). An ensemble prediction intervals approach for short-term PV power forecasting. Solar Energy, 155, 1072–1083.
Rana, M., Koprinska, I., & Agelidis, V. G. (2015). 2D-interval forecasts for solar power production. Solar Energy, 122, 191–203.
Ren, C., An, N., Wang, J., Li, L., Hu, B., & Shang, D. (2014a). Optimal parameters selection for BP neural network based on particle swarm optimization: A case study of wind speed forecasting. Knowledge-Based Systems, 56, 226–239.
Ren, Y., Suganthan, P. N., & Srikanth, N. (2014b). A novel empirical mode decomposition with support vector regression for wind speed forecasting. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 27(8), 1793–1798.
Shah, R., Mithulananthan, N., Bansal, R. C., & Ramachandaramurthy, V. K. (2015). A review of key power system stability challenges for large-scale PV integration. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 41, 1423–1436.
Shi, J., Lee, W. J., Liu, Y., Yang, Y., & Wang, P. (2012). Forecasting power output of photovoltaic systems based on weather classification and support vector machines. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 48(3), 1064–1069.
Shrivastava, N. A., Khosravi, A., & Panigrahi, B. K. (2015). Prediction interval estimation of electricity prices using PSO-tuned support vector machines. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 11(2), 322–331.
Steffel, S. J., Caroselli, P. R., Dinkel, A. M., Liu, J. Q., Sackey, R. N., & Vadhar, N. R. (2012). Integrating solar generation on the electric distribution grid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 3(2), 878–886.
Tascikaraoglu, A., Uzunoglu, M., & Vural, B. (2012). The assessment of the contribution of short- term wind power predictions to the efficiency of stand-alone hybrid systems. Applied Energy, 94, 156–165.
Torres, J. L., Garcia, A., De Blas, M., & De Francisco, A. (2005). Forecast of hourly average wind speed with ARMA models in Navarre (Spain). Solar Energy, 79(1), 65–77.
Ueckerdt, F., Brecha, R., & Luderer, G. (2015). Analyzing major challenges of wind and solar variability in power systems. Renewable Energy, 81, 1–10.
Van der Meer, D. W., Shepero, M., Svensson, A., Widén, J., & Munkhammar, J. (2018). Probabilistic forecasting of electricity consumption, photovoltaic power generation and net demand of an individual building using Gaussian processes. Applied Energy, 213, 195–207.
Voyant, C., Notton, G., Kalogirou, S., Nivet, M. L., Paoli, C., Motte, F., et al. (2017). Machine learning methods for solar radiation forecasting: A review. Renewable Energy, 105, 569–582.
Wan, C., Lin, J., Song, Y., Xu, Z., & Yang, G. (2016). Probabilistic forecasting of photovoltaic generation: An efficient statistical approach. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 32(3), 2471–2472.
Wan, C., Xu, Z., Wang, Y., Dong, Z. Y., & Wong, K. P. (2013). A hybrid approach for probabilistic forecasting of electricity price. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 5(1), 463–470.
Wang, K., Qi, X., & Liu, H. (2019). A comparison of day-ahead photovoltaic power forecasting models based on deep learning neural network. Applied Energy, 251, 113315.
Yadav, A. K., & Chandel, S. S. (2014). Solar radiation prediction using artificial neural network techniques: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 33, 772–781.
Yang, D., Gu, C., Dong, Z., Jirutitijaroen, P., Chen, N., & Walsh, W. M. (2013). Solar irradiance forecasting using spatial-temporal covariance structures and time-forward kriging. Renewable Energy, 60, 235–245.
Yang, H. T., Huang, C. M., Huang, Y. C., & Pai, Y. S. (2014). A weather-based hybrid method for 1-day ahead hourly forecasting of PV power output. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 5(3), 917–926.
Yona, A., Senjyu, T., Funabashi, T., & Kim, C. H. (2013). Determination method of insolation prediction with fuzzy and applying neural network for long-term ahead PV power output correction. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 4(2), 527–533.
Zhang, R., Dong, Z. Y., Xu, Y., Meng, K., & Wong, K. P. (2013). Short-term load forecasting of Australian National Electricity Market by an ensemble model of extreme learning machine. IET Generation, Transmission and Distribution, 7(4), 391–397.
Zhang, G., Wu, Y., Wong, K. P., Xu, Z., Dong, Z. Y., & Iu, H. H. C. (2014). An advanced approach for construction of optimal wind power prediction intervals. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 30(5), 2706–2715.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dash, P.K., Majumder, I., Nayak, N. et al. Point and Interval Solar Power Forecasting Using Hybrid Empirical Wavelet Transform and Robust Wavelet Kernel Ridge Regression. Nat Resour Res 29, 2813–2841 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09630-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09630-6