Abstract
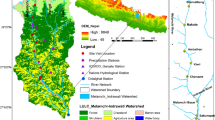
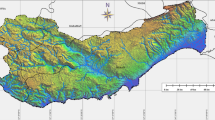
The 4th IPCC report highlights the increased vulnerability of the coastal areas from floods due to sea-level rise (SLR). The existing coastal flood control structures in Bangladesh are not adequate to adapt these changes and new measures are urgently necessary. It is important to determine the impacts of SLR on flooding to analyse the performance of the existing structures and corresponding impact to plan for suitable adaptation and mitigation measures to reduce the impacts of floods on coastal zone. The study aims to develop a comprehensive understanding of the possible effects of SLR on floods in the coastal zone of Bangladesh. A hydrodynamic model, which is a combination of surface and river parts, was utilized for flood simulation. The tool was applied under a range of future scenarios, and results indicate both spatial variability of risk and changes in flood characteristics between now and under SLR. Estimated impact on population, infrastructure and transportation is also exposed. These types of impact estimation would be of value to flood plain management authorities to minimize the socio-economic impact.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
ADB (2005) Southwest area integrated water resources planning and management project in Bangladesh, Asian Development Bank
Agarwala S, Ota T, Ahmed AU, Smith J, Aalst MV (2003) Development and climate change in Bangladesh: focus on coastal flooding and the sundarbans. Organisation for economic co-operation and development (OECD), Paris, 2003
Ali A (1980) Storm surges in the Bay of Bengal and their numerical modeling, SARC Report No. 125/80. Atomic Energy Commission, Dhaka
Ali A (1996) Vulnerability of Bangladesh to climate change and sea level rise through tropical cyclones and storm surges. Bangladesh space research and remote sensing organization (SPARRSO), Dhaka, Bangladesh
Barua DK (1991) The coastline of Bangladesh—an overview of processes and forms. In: Proceedings of the seventh symposium on coastal and ocean management, ASCE, Long Beach, CA, pp 8–12
Bhuiyan MJAN, Dutta D, Gupta AD, Babel MS (2005) Flood simulation and its socio-economic impact analysis in Meghna delta, Bangladesh under climate change conditions. In: International symposium on floods in coastal cities under climate change conditions, June, 2005, Thailand
Blake R, Khanbilvardi R, Rosenzweig C (2000) Climate change impacts on New York City’s water supply system. J Am Water Resour As 36(2): 279–320. ISSN 1093-474X CODEN JWRAF5
Bobba AG (1998) Application of a numerical model to predict freshwater depth in Islands due to climate change: Agatti Island, India. J Environ Hydrol 6:1–13
Choudhury AM (1989) Forecasting and warning system of disaster. A SPARRSO (Bangladesh space research and remote sensing organization) Report, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Choudhury AM, Haque MA, Quadir DA (1997) Consequences of global warming and sea level rise in Bangladesh. Mar Geodesy 20:13–31
Chowdhury MHK, Devsharma SK (1992) Climate change in Bangladesh—a statistical review report on IOC-UNEP. Workshop on impacts of sea level rise due to global warming, NOAMI, 16–19 November, Bangladesh, pp 15
Dutta D, Bhuiyan MJAN (2007) Flood Characteristics under changing climatic conditions in Meghna Delta, Bangladesh. In: 16th IASTED international conference applied simulation and modelling, August 29–31, 2007, Palma de Mallorca, Spain
Dutta D, Nakayama K (2009) Effects of spatial grid resolution on river flow and surface inundation simulation by physically based distributed modelling approach. Hydrol Process 23(4):534–545
Dutta D, Alam MJ, Umeda K, Hayashi M, Hironaka S (2004) Urban flood modeling in Lower Mekong Basin: a physically based distributed modeling approach. In: Proceedings of the international conference on sustainable water resources management in the changing environment of the monsoon region, vol 1, Colombo, Srilanka, pp 407–417
Dutta D, Alam J, Umeda K, Hayashi M, Hironaka S (2007) A two-dimensional hydrodynamic model for flood inundation simulation: a case study in the lower Mekong river basin. Hydrol Process 21:1223–1237. doi:10.1002/hyp.6682
Ericksen NJ, Ahmad QK, Chowdhury AR (1997) Socio-economic implications of climate change in Bangladesh. Briefing document no. 4. Bangladesh Unnayan Parishad: pp 1–37
ESCAP (1991) Manual of comprehensive flood loss prevention and management. Economic and social commission for Asia and the Pacific, Bangkok. Report, pp 65–84
FFWC (2010) Annual flood report 2010. Flood Forecasting & Warning Centre, Bangladesh Water Development Board, Bangladesh
Frank NL, Husain SA (1971) Bull Am Meteor Soc 52, pp 438
IPCC (2007) Climate change impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. Fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Karim MF (2000) Floodplain zoning for the Ganges River in Bangladesh. M.Engineering Thesis, Asian Institute of Technology, Thailand. Thesis No. WM-99-13
Karim MF, Mimura N (2008) Impacts of climate change and sea level rise on cyclonic storm surge floods in Bangladesh. Glob Environ Change 18:490–500. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2008.05.002
Karmaker S, Shrestha ML (2000) Recent climate change in Bangladesh. SMRC Report No. 4. SAARC Meteorological Research Centre (SMRC), Dhaka, p 43
Liakath MA (2002) An integrated approach for the improvement of flood control and drainage schemes in the Coastal Belt of Bangladesh. PhD dissertation, Wageningen University & International Institute for Infrastructural, Hydraulic and Environmental Engineering
Miah MM (1988) Flood in Bangladesh. Academic Publishers, Dhaka
Mirza MQ, Warrick RA, Ericksen NJ, Kenny GJ (1998) Trends and persistence in precipitation in the Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna River Basins. J Hydrol Sci 43(6):845–858. doi:10.1080/02626669809492182
Mitra AP (2003) Climate in South Asia and water resources. In: Proceedings of workshop on climate change and water resources in South Asia, The Asia Pacific Network for Global Change Research, Kathmandu, 2003, pp 1–20
Ninno CD, Dorosh PA, Smith LC, Roy DK (2001) The 1998 floods in Bangladesh: disaster impacts, household coping strategies, and response. International Flood Policy Research Institute. Research Report 122
Quadir DA, Shresta ML, Khan TMA, Nazlee F, Rahman M, Mannan AM (2001) The dynamic changes of climate in Bangladesh and the adjacent regions in association with global warming. In: International Conference of Mechanical Engineering, BUET, 26–28 December, 2001, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Quadir DA, Rahman A, Osman S, Saha GC, Bhattacharjee SR (2002) Final Report on Initial National Communication in Response to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), Department of Environment, Government of Bangladesh
SMRC (2000a) The vulnerability assessment of the SAARC coastal region due to sea level rise: Bangladesh case. SMRC Publication No. 3. SAARC Meteorological Research Centre. Dhaka, July 2000
SMRC (2000b) Recent climatic changes in Bangladesh. SMRC Publication No. 4. SAARC Meteorological Research Centre. Dhaka, September 2000
Tingsanchali T, Karim MF (2005) Flood hazard and risk analysis in the southwest region of Bangladesh. Hydrol Process 19:2055–2069
Watson RT (2001) Climate change 2001: synthesis report. Intergovernmental Panel on climate Change, Third Assessment Report of IPCC, UNEP
WB (2000) Bangladesh: climate change & sustainable development. World Bank Report No 21104 BD. Dhaka, October 2000
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Asia Pacific Network for Global Change Research (APN) for funding and the Asian Institute of Technology (AIT), Thailand, and Monash University, Australia, for support and facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhuiyan, M.J.A.N., Dutta, D. Analysis of flood vulnerability and assessment of the impacts in coastal zones of Bangladesh due to potential sea-level rise. Nat Hazards 61, 729–743 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-011-0059-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-011-0059-3