Abstract
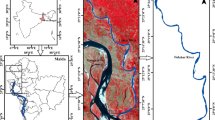
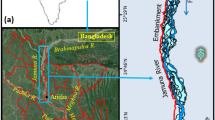
This study has been carried out to analyze and report the river bank erosion hazard due to morphometric change of the Ganga River (also called Ganges in English) in the upstream of Farakka Barrage up to Rajmahal. Morphometric parameters, such as, Sinuosity, Braidedness Index, and percentage of the island area to the total river reach area were measured for the year of 1955, 1977, 1990, 2001, 2003, and 2005 from LANDSAT and IRS satellite images. The analysis shows that there is a drastic increase in all of those parameters over the period of time. This study has found that bank failure is because of certain factors like soil stratification of the river bank, presence of hard rocky area (Rajmahal), high load of sediment and difficulty of dredging and construction of Farakka Barrage as an obstruction to the natural river flow. For the increasing sinuosity, the river has been engulfing the large areas of left bank every year. The victims are mostly Manikchak and Kaliachak-II blocks of Malda district, with a loss of around 1,670 ha agricultural land since 1977. Temporal shift measurements for the river reach between Farakka and Rajmahal has been done with help of 22 cross-sections in this reach. Erosion impact area has also been estimated to emphasize the devastating nature of the hazard.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee M (1999) A report on the impact of Farakka Barrage on the human fabric, On behalf of South Asian network on dams, rivers and people (SANDRP). http://www.sandrp.in/dams/impact_frka_wcd.pdf. Accessed on 12.2.2008
Banerjee SN, Chakroborty P (1983) Some observations on recent trends of shifting of the Ganga between Rajmahal and Ahiron. J Geol Soc India 24:318–321
Brice JC (1960) Index for description of channel braiding. Geol Soc Am Bull 85:581–586
Census of India (2001) Provisional population totals, West Bengal, Table—4. Maldah District (06). Government of West Bengal. http://web.cmc.net.in/wbcensus/DataTables/02/Table4_6.htm. Retrieved 2011-07-21
Das JD, Saraf AK (2007) Technical note: remote sensing in the mapping of the Brahmaputra/Jamuna river channel patterns and its relation to various landforms and tectonic environment. Int J Remote Sens 28(16):3619–3631
Das JD, Dutta T, Saraf AK (2007) Remote sensing and GIS application in change detection of the Barak river channel, N.E. India. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 35(4):301–312
Gurnell AM, Downward SR, Jones R (1994) Channel planform change on the River Dee meanders, 1976–1992. Regul Rivers Res Manag 9:187–200
Hickin EJ (1983) River channel changes: retrospect and prospect. Spec Publ Int As Sedimentol 6:61–83
Hickin EJ, Nanson GC (1984) Lateral migration rates of river bends. J Hydraul Eng Am Soc Civil Eng 110(11):1557–1567
Hickin EJ (1974) The development of meanders in natural river channels. Am J Sci 274:414–442
Howard AD, Keetch ME, Vincent L (1970) Topological and geometrical properties of braided streams. Water Resour Res 20:1674–1688
Howard AD (1992) Modelling channel migration and floodplain development in meandering streams. In: Carling PA, Petts GE (eds) Lowland floodplain rivers. Wiley, Chichester, pp 1–42
Howard AD (1996) Modelling channel evolution and floodplain morphology. In: Anderson MG, Walling DE, Bates PD (eds) Floodplain processes. Wiley, Chichester, pp 15–62
Iqbal S (2010) Flood and erosion induced population displacements: a socio-economic case study in the Gangetic riverine tract at Malda district, West Bengal, India. J Hum Ecol 30(3):201–211
Kansky KJ (1963) Structure of transportation networks: relationships between network geometry and regional characteristics. University of Chicago Department of Geography research paper no. 84. University of Chicago, Chicago
Kent WR, Malcom SP, Muller DR, Saunders DA, Ghose CN (2002) 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the Rajmahal Basalts, India, and their relationship to the Kerguelen Plateau. J Petrol 43(7):1141–1153
Kent WR, Saunders AD, Kempton PD, Ghose CN (1997) Rajmahal basalts, eastern India: mantle sources and melt distribution at a volcanic rifted margin. In: Mahoney JJ, Coffin MF (eds) Large igneous provinces: continental, oceanic and planetary flood volcanism, geophysical monograph, American geophysical union 100, pp 145–182
Keshkar G et al (1996) Report of experts committee for bank erosion problem of river Ganga-Padma in the districts of Malda and Murshidabad. Plan Comm Gov India 1–71
Kotoky P, Bezbaruah D, Baruah J, Sarma JN (2005) Nature of bank erosion along the Brahmaputra river channel, Assam, India. Curr Sci 88(4):634–640
Lawler DM (1993) The measurement of river bank erosion and lateral channel change: a review. Earth Surf Process Landf 18:777–821
Leopold LB, Wolman MG, Miller JP (1964) Fluvial processes in geomorphology. W.H. Freeman and Co., San Francisco
Mani P, Kumar R, Chatterjee C (2003) Erosion study of a part of Majuli River-Island using remote sensing data. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 31(1):12–18
Kummu M, Lu XX, Rasphone A, Juha S, Jorma K (2008) Riverbank changes along the Mekong River: remote sensing detection in the Vientiane–Nong Khai area. Quat Int 186(1):100–112
Milton EJ, Gilvear DJ, Hooper ID (1995) Investigating change in fluvial systems using remotely sensed data. In: Gurnell A, Petts G (eds) Changing river channels. Wiley, New York, pp 276–301
Mueller J (1968) An introduction to the hydraulic and topographic sinuosity indexes. Ann As Am Geogr 58:371
Mukhopadhyay S (2003) River bank erosion and land degradation, a study of river Ganga, land degradation and desertification. Rawat Publication, New Delhi, pp 366–373
Muller E, Décamps H, Dobson MK (1993) Contribution of space remote sensing to river studies. Freshw Biol 29:301–312
Parua PK (1999) Erosion problems of the river Ganga in the districts of Malda and Murshidabad in West Bengal. Civ Eng Today, ASCE: Calcutta 13(2):3–20
Parua PK (2009) The Ganga water use in the Indian subcontinent. Water Sci Technol Libr 64:391. doi:10.1007/978-90-481-3103-7
Parua PK (2002) Fluvial geomorphology of the river Ganga around Farakka. J Inst Eng 82:193–196
Pati JK, Lal J, Prakash K, Bhusan R (2008) Spatio-temporal shift of western bank of the Ganga river at Allahabad city and its implications. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 36(3):289–297. doi:10.1007/s12524-008-0030-2
Petts GE (1995) Changing river channels: the geographical tradition. In: Gurnell A, Petts G (eds) Changing river channels. Wiley, New York, pp 1–23
Phillip G, Gupta RP, Bhatatcharya AB (1989) Channel migration studies in the middle Ganga basin, India using remote sensing. Int J Remote Sens 10(6):1141–1149
Roey E, Peter A (2008) Defining and measuring braiding intensity. Earth Surf Process Landf 33(14):2121–2138
Rudra K (1996a) Problems of river bank erosion along the Ganga in Murshidabad district of West Bengal. Indian J Geogr Environ 1:25–32
Rudra K (1996b) The Farakka barrage- an interruption to Fluvial regime. Indian J Landsc Syst Ecol Stud 19(2):105–110
Rudra K (2004) The encroaching Ganga and social conflicts: the case of West Bengal. India. Independent Broadcasting Associates, Littleton, p 40. http://www.ibaradio.org/India/ganga/extra/resource/Rudra.pdf. Accessed on 11 Oct 2010
Rudra K (2010) Dynamics of the Ganga in West Bengal, India (1764–2007): implications for science-policy interaction. Quat Int Article (in press). doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2009.10.043
Sen HS (2010) The drying up of River Ganga: an issue of common concern to both India and Bangladesh. Curr Sci 99(6):725–727
Sengupta S (1998) Upper Gondwana stratigraphy and paleobotany of the Rajmahal Hills, Bihar India. Geol Surv India Monogr Paleaontologica Indica 98:180
Showkat I (2010) Flood and erosion induced population displacements: a socio-economic case study in the Gangetic riverine tract at Malda District, West Bengal, India. J Hum Ecol 30(3): 201–211. ©Kamla-Raj
Tangri AK (2000) Application of remote sensing techniques in monitoring the spatial and temporal evolution of fluvio-geomorphic features in Ganga basin with specific reference to their impact on engineering structures. In Sinha R (ed) Proceedings of the workshop on Fluvial geomorphology with special reference to floodplains. Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
Thoma PD, Gupta CS, Bauer EM (2001) Quantifying river bank erosion with scanning laser altimetry. Int Arch Photogramm Remote Sens, Annapolis, MD, 34–3/W4: 169–174
Thoms MC, Walker KF (1992) Channel changes related to low-level weirs on the River Murry, South Australia. In: Carling PA, Petts GE (eds) Lowland floodplain Rivers, geomorphological perspectives. Wiley, New York, pp 235–250
Winterbottom JS, Gilvear JD (2000) A GIS-based approach to mapping probabilities of river bank erosion: regulated River Tummel, Scotland. Regul Rivers Res Manag 16(2):127–140
Yang X (1996) Satellite monitoring of dynamic environmental change of the active Yellow river Delta, China. Int Arch Photogramm Remote Sens 20(7):801–806
Yang X, Damen CJM, Zuidam AR (1999) Satellite remote sensing and GIS for the analysis of channel migration changes in the active Yellow river Delta, China. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 1(2):146–157
http://glcf.umiacs.umd.edu/index.shtml. Accessed on Feb 2006
http://wrmin.nic.in/index3.asp?subsublinkid=714&langid=1&sslid=296. Accessed on 11 Oct 2010
http://wrmin.nic.in/writereaddata/linkimages/anu141200246187.pdf. Accessed on 11 Oct 2010
http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/ams/india/. Accessed on Feb 2006
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gaur,_West_Bengal. Accessed on July 2011
http://malda.nic.in/. Accessed on July 2011
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to V. K. Dadhwal, former Dean, Indian Institute of Remote Sensing (IIRS), Dehradun, Dr. P.S. Roy, current Director, IIRS Dehradun and Department of Irrigation and Waterway, Government of West Bengal for constant support, suggestions and encouragement for completing this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thakur, P.K., Laha, C. & Aggarwal, S.P. River bank erosion hazard study of river Ganga, upstream of Farakka barrage using remote sensing and GIS. Nat Hazards 61, 967–987 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-011-9944-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-011-9944-z