Abstract
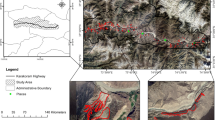
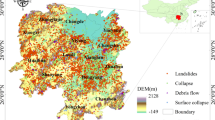
Jiuzhaigou, located in the transitional area between the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau and the Sichuan Basin, is highly prone to geological hazards (e.g., rock fall, landslide, and debris flow). High-performance-based hazard prediction models, therefore, are urgently required to prevent related hazards and manage potential emergencies. Current researches mainly focus on susceptibility of single hazard but ignore that different types of geological hazards might occur simultaneously under a complex environment. Here, we firstly built a multi-geohazard inventory from 2000 to 2015 based on a geographical information system and used satellite data in Google earth and then chose twelve conditioning factors and three machine learning methods—random forest, support vector machine, and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost)—to generate rock fall, landslide, and debris flow susceptibility maps. The results show that debris flow models presented the best prediction capabilities [area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC 0.95)], followed by rock fall (AUC 0.94) and landslide (AUC 0.85). Additionally, XGBoost outperformed the other two methods with the highest AUC of 0.93. All three methods with AUC values larger than 0.84 suggest that these models have fairly good performance to assess geological hazards susceptibility. Finally, evolution index was constructed based on a joint probability of these three hazard models to predict the evolution tendency of 35 unstable slopes in Jiuzhaigou. The results show that these unstable slopes are likely to evolve into debris flows with a probability of 46%, followed by landslides (43%) and rock falls (29%). Higher susceptibility areas for geohazards were mainly located in the southeast and middle of Jiuzhaigou, implying geohazards prevention and mitigation measures should be taken there in near future.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boser BE (2008) A training algorithm for optimal margin classifiers. Proc Annu ACM Workshop Comput Learn Theory 5:144–152. https://doi.org/10.1145/130385.130401
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32
Cao J, Zhang Z, Wang C, Liu J, Zhang L (2019) Susceptibility assessment of landslides triggered by earthquakes in the Western Sichuan Plateau. CATENA 175:63–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.12.013
Chen T, Guestrin C (2016) Xgboost: a scalable tree boosting system. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 785–794. ACM
Chen W, Xie X, Wang J et al (2017) A comparative study of logistic model tree, random forest, and classification and regression tree models for spatial prediction of landslide susceptibility. CATENA 151:147–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.11.032
Cheng S, Zhang S, Li L, Zhang D (2018) Water quality monitoring method based on TLD 3D fish tracking and XGBoost. Math Probl Eng 7:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5604740
Chuang YC, Shiu YS (2018) Relationship between landslides and mountain development-integrating geospatial statistics and a new long-term database. Sci Total Environ 622–623:1265–1276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.039
Corominas J et al (2013) Recommendations for the quantitative analysis of landslide risk. Bull Eng Geol Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-013-0538-8
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-vector networks. Mach Learn 20:273–297
Dickson ME, Perry GLW (2016) Identifying the controls on coastal cliff landslides using machine-learning approaches. Environ Modell Softw 76:117–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.10.029
Dragićević S, Lai T, Balram S (2015) GIS-based multicriteria evaluation with multiscale analysis to characterize urban landslide susceptibility in data-scarce environments. Habitat Int 45:114–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2014.06.031
Fabbri AG, Chung CJF, Cendrero A, Remondo J (2003) Is prediction of future landslides possible with a GIS? Nat Hazards 30:487–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.-2014.06.031
Ge Y, Dou W, Gu Z et al (2013) Assessment of social vulnerability to natural hazards in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 27:1899–1908. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-013-0725-y
Goetz JN, Brenning A, Petschko H, Leopold P (2015) Evaluating machine learning and statistical prediction techniques for landslide susceptibility modeling. Comput Geosci 81:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2015.04.007
Gorsevski PV, Gessler PE, Boll J, Elliot WJ, Foltz RB (2006) Spatially and temporally distributed modeling of landslide susceptibility. Geomorphology 80:178–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.02.011
Guha-Sapir D, Vos F, Below R, Ponserre S (2012) Annual disaster statistical review 2011: the numbers and trends. Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED). https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.10378.88001
Gutiérrez F, Parise M, De Waele J, Jourde H (2014) A review on natural and human-induced geohazards and impacts in karst. Earth Sci Rev 138:61–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.08.002
Ho TK (1998) The random subspace method for constructing decision forests. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal 20:832–844. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.709601
Hong H, Pourghasemi HR, Pourtaghi ZS (2016) Landslide susceptibility assessment in Lianhua County (China): a comparison between a random forest data mining technique and bivariate and multivariate statistical models. Geomorphology 259:105–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.02.012
Huang Y, Zhao L (2018) Review on landslide susceptibility mapping using support vector machines. CATENA 165:520–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.03.003
Kamp U, Growley BJ, Khattak GA, Owen LA (2008) GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping for the 2005 Kashmir earthquake region. Geomorphology 101:631–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.03.003
Kim HG, Lee DK, Park C, Ahn Y, Kil S-H, Sung S, Biging GS (2018) Estimating landslide susceptibility areas considering the uncertainty inherent in modeling methods. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 32:2987–3019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-018-1609-y
Kornejady A, Heidari K, Nakhavali M (2015) Assessment of landslide susceptibility, semi-quantitative risk and management in the Ilam dam basin, Ilam, Iran. Environ Resour Res 3:85–109. https://doi.org/10.22069/ijerr.2015.2563
Kornejady A, Ownegh M, Bahremand A (2017) Landslide susceptibility assessment using maximum entropy model with two different data sampling methods. CATENA 152:144–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.01.010
Li W, Zhang Q, Liu C, Xue Q (2006) Tourism’s impacts on natural resources: a positive case from China. Environ Manag 38:572–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/-s00267-004-0299-z
Marjanović M, Kovačević M, Bajat B, Voženílek V (2011) Landslide susceptibility assessment using SVM machine learning algorithm. Eng Geol 123:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.09.006
Mokhtari M, Abedian S (2019) Spatial prediction of landslide susceptibility in Taleghan basin, Iran. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 33:1297–1325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-019-01696-w
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A et al (2011) Scikit-learn: machine learning in python. J Mach Learn Res 12:2825–2830
Pourghasemi HR, Rahmati O (2018) Prediction of the landslide susceptibility: which algorithm, which precision? CATENA 162:177–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.-2017.11.022
Pourghasemi HR, Pradhan B, Gokceoglu C (2012) Application of fuzzy logic and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) to landslide susceptibility mapping at Haraz watershed, Iran. Nat Hazards 63:965–996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0217-2
Pradhan B (2013) A comparative study on the predictive ability of the decision tree, support vector machine and neuro-fuzzy models in landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS. Comput Geosci 51:350–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2012.08.023
Qiao X, Du J, Lugli S, Ren J, Xiao W, Chen P, Tang Y (2016) Are climate warming and enhanced atmospheric deposition of sulfur and nitrogen threatening tufa landscapes in Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve, Sichuan, China? Sci Total Environ 562:724–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.073
Swets JA (1988) Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science 240(4857):1285–1293. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3287615
Tehrany MS, Pradhan B, Jebur MN (2015) Flood susceptibility analysis and its verification using a novel ensemble support vector machine and frequency ratio method. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 29:1149–1165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-015-1021-9
Tien Bui D, Tuan TA, Klempe H, Pradhan B, Revhaug I (2015) Spatial prediction models for shallow landslide hazards: a comparative assessment of the efficacy of support vector machines, artificial neural networks, kernel logistic regression, and logistic model tree. Landslides 13:361–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0557-6
Trigila A, Iadanza C, Esposito C, Scarascia-Mugnozza G (2015) Comparison of Logistic Regression and Random Forests techniques for shallow landslide susceptibility assessment in Giampilieri (NE Sicily, Italy). Geomorphology 249:119–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.06.001
Vapnik VN (1999) An overview of statistical learning theory. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10:988–999. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.788640
Vapnik VN (2000) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-2440-0
Wang LJ, Guo M, Sawada K, Lin J, Zhang J (2015) Landslide susceptibility mapping in Mizunami City, Japan: a comparison between logistic regression, bivariate statistical analysis and multivariate adaptive regression spline models. CATENA 135:271–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.08.007
Westen CJV, Castellanos E, Kuriakose SL (2008) Spatial data for landslide susceptibility, hazard, and vulnerability assessment: an overview. Eng Geol 102:112–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.03.010
Wu CH, Peng C, Li YS, Ayala IA, Chao H, Yi SJ (2018) Seismogenic fault and topography control on the spatial patterns of landslides triggered by the 2017 Jiuzhaigou earthquake. J Mt Sci 15:793–807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-017-4761-9
Yang J, Song C, Yang Y, Xu C, Guo F, Xie L (2019) New method for landslide susceptibility mapping supported by spatial logistic regression and GeoDetector: a case study of Duwen Highway Basin, Sichuan Province, China. Geomorphology 324:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.09.019
Yao X, Tham LG, Dai FC (2008) Landslide susceptibility mapping based on Support Vector Machine: a case study on natural slopes of Hong Kong, China. Geomorphology 101:572–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.02.011
Youssef AM, Pourghasemi HR, Pourtaghi ZS, Al-Katheeri MM (2015) Landslide susceptibility mapping using random forest, boosted regression tree, classification and regression tree, and general linear models and comparison of their performance at Wadi Tayyah Basin, Asir Region, Saudi Arabia. Landslides 13:839–856. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0614-1
Zhu X, Xu Q, Tang M, Nie W, Ma S, Xu Z (2017) Comparison of two optimized machine learning models for predicting displacement of rainfall-induced landslide: a case study in Sichuan Province, China. Eng Geol 218:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/-j.enggeo.2017.01.022
Zou Q, Zhou J, Zhou C, Song L, Guo J (2013) Comprehensive flood risk assessment based on set pair analysis-variable fuzzy sets model and fuzzy AHP. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 27(2):525–546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-012-0598-5
Acknowledgements
The study is financially supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC1502505), and Jiuzhaigou Post-Disaster Restoration and Reconstruction Program Research on Restoration and Protection of World Natural Heritage.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, J., Zhang, Z., Du, J. et al. Multi-geohazards susceptibility mapping based on machine learning—a case study in Jiuzhaigou, China. Nat Hazards 102, 851–871 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-03927-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-03927-8