Abstract
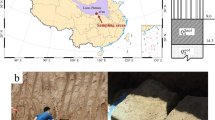
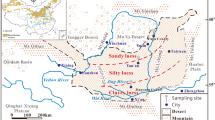
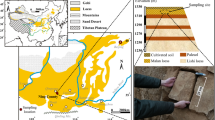
Water pollution has changed the physical and mechanical properties of Xiashu loess, which has become an important factor in the frequent occurrence of Xiashu loess landslides. In order to understand the mechanism of Xiashu loess landslide in acid or alkali environment, a large number of Xiashu loess samples were collected in Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province. X-ray diffraction, energy-dispersive analysis of X-ray, compression test, direct shear test, and scanning electron microscope test (SEM) were used to analyze physical properties, mechanical properties, and microstructure of acid–alkali-contaminated Xiashu loess. The results show that the newly formed insoluble (slightly soluble) substances in the alkalization Xiashu loess increase its density and decrease the void ratio and water content. In sulfuric acid solution, the minerals in Xiashu loess mainly suffer dissolution reactions, which leads to decrease in soil density and increase in void ratio and water content. In the SEM image, the surface of acidified Xiashu loess soil particles is rough and uneven, while the surface of alkalized Xiashu loess soil particles is smooth and flat. This is an important reason that the internal friction angle of acidified Xiashu loess is significantly higher than that of alkalized Xiashu loess.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen YY, Li XS, Han ZY, Yang SY, Wang YB, Yang DY (2008) Chemical weathering intensity and element migration features of the Xiashu loess profile in Zhenjiang Jiangsu Province. J Geogr Sci 18(3):341–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-008-0341-9
Chen HE, Jiang YL, Gao Y, Yuan XQ (2019) Structural characteristics and its influencing factors of typical loess. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78:4893–4905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1431-2
Gao YB, Liu JD, Wang YY (2018) Plasticity and its relationship with mechanical properties of a remolded silty clay contaminated by several acids and bases. Chin J Geotech Eng 40(11):2103–2109. https://doi.org/10.11779/CJGE201811017 (in Chinese)
Han AM, Xiao JH, Qiao CY, Ding CY (2013) Experiments on Micro and Macro Behaviors of Nanjing Xiashu Soil Under Triaxial Compression. J Jilin Univ (Earth Sci Edn) 43(6):1897–1903. https://doi.org/10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.2013.06.016 (in Chinese)
Li P, Shao SJ (2020) Can X-ray computed tomography (CT) be used to determine the pore-size distribution of intact loess? Environ Earth Sci 79:29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8777-z
Li XS, Han ZY, Lu HY, Chen YY, Li Y, Yuan XK, Zhou YW, Jiang MY, Lv CJ (2018) Onset of Xiashu loess deposition in southern China by 0.9Ma and its implications for regional aridification. Sci China Earth Sci 61(3):256–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-017-9134-2
Li P, Shao SJ, Vanapalli SK (2020a) Characterizing and modeling the pore-size distribution evolution of a compacted loess during consolidation and shearing. J Soil Sediment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02621-3
Li XA, Hong B, Wang L, Li LC, Sun JQ (2020b) Microanisotropy and preferred orientation of grains and aggregates (POGA) of the Malan loess in Yan’an, China: a profile study. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:1893–1907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01674-0
Liu HL, Zhu CP, Zhang XL (2008) Fundamental physical properties of soil polluted by acid and alkali in laboratory. Chinese J Geotech Eng 30(8):1213–1217 (in Chinese)
Liu H, Zhang SC, Niu FJ, Shao ZS, Niu ZL, Lu J (2019) Experimental study on one-dimensional compression characteristics of Q3 loess contaminated by acid or alkali solutions. Rock Soil Mech 40(S1):210–216. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2018.1659 (in Chinese)
Liu H, He JT, Zhao Q, Wang TX, Guo CY (2020) Experimental study on the evolution rules of micro-permeability characteristics of acid-contaminated original loess. Rock Soil Mech 41(3):765–772. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2019.0875 (in Chinese)
Lu HJ, Li JX, Wang WW, Wang CH (2015) Cracking and water seepage of Xiashu loess used as landfill cover under wetting–drying cycles. Environ Earth Sci 74:7441–7450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4729-4
Meng J, Li XA (2019) Effects of carbonate on the structure and properties of loess and the corresponding mechanism: an experimental study of the Malan loess, Xi’an area, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78:4965–4976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-01457-z
Mu CM, Wei YX (2019) Experimental study on the weakening of mechanical properties of red clay contaminated by acid and alkali in Guilin area. J Chongqing Univ 42(6):109–118. https://doi.org/10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2019.06.012
Mu QY, Zhou C, Ng CWW (2020) Compression and wetting induced volumetric behavior of loess: macro- and micro-investigations. Transp Geotech 23:100345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2020.100345
Ng CWW, Sadeghi H, Jafarzadeh F, Sadeghi M, Zhou C, Baghbanrezvan S (2020) Effect of microstructure on shear strength and dilatancy of unsaturated loess at high suctions. Can Geotech J 57:221–235. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2018-0592
NSCG (National Standards Compilation Group of People’s Republic of China) (2013) Microbeam analysis—identification of authigenic clay mineral in sedimentary rock menthod by scanning electron microscope and energy dispersive spectrometer (GB/T 17361–2013). China Planning Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
NSCG (National Standards Compilation Group of People’s Republic of China) (2019a) Standard for geotechnical testing method (GB/T 50123–2019). China Planning Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
NSCG (National Standards Compilation Group of People’s Republic of China) (2019b) Testing methods of X-ray diffraction for determining the orientation of crystal materials by rotation (GB/T 37983–2019). China Planning Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Shao GB, Zhang GY, Liu GH, Sun JP (2019) Reinforcement techniques for collapsible loess subgrade with NaOH and Cacl2 solutions. J Phys Conf Ser 1176:052015. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1176/5/052015
Wang XM, Chen SX, Cheng CB (2013) Experimental study on physico-mechanical characteristics of original loess soaked in acid solution. Chinese J Geotech Eng 35(9):1619–1626 (in Chinese)
Wang XY, Lu HY, Zhang HZ, Wu J, Hou XX, Fu Y (2018) Distribution, provenance, and onset of the Xiashu loess in Southeast China with paleoclimatic implications. J Asian Earth Sci 155:180–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.11.022
Wang L, Li XA, Li LC, Hong B, Yao W, Lei HN, Zhang C (2020) Characterization of the collapsible mechanisms of Malan loess on the Chinese loess Plateau and their effects on eroded loess landforms. Hum Ecol Risk Assess. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2020.1721265
Wei TT, Fan W, Yu NY, Wei YN (2019) Three-dimensional microstructure characterization of loess based on a serial sectioning technique. Eng Geol 261:105265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105265
Xia J, Han AM (2009) Cyclic variability in microstructure and physio-mechanical properties of the Xiashu loess–palaeosol sequence in Nanjing, China. Eng Geol 104:263–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.11.00
Xia J, Huang GL, Liu ZT, Chen XM (2007) Cyclic variability in chemical composition and swelling-shrinkage properties of the Xiashu loess Stratum near Nanjing. China Pedosphere 17(5):666–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(07)60080-0
Xue Q, Lu HJ, Zhao Y, Liu L (2014) The metal ions release and microstructure of coal gangue corroded by acid-based chemical solution. Environ Earth Sci 71:3235–3244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2743-y
Zhang WG, Yu LZ, Lu M, Zheng XM, Shi YX (2007) Magnetic properties and geochemistry of the Xiashu loess in the present subtropical area of China, and their implications for pedogenic intensity. Earth Planet Sci Lett 260:86–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2007.05.018
Zhang Y, Hu ZQ, Chen H, Xue T (2018a) Experimental investigation of the behavior of collapsible loess treated with the acid-addition pre-soaking method. KSCE J Civ Eng 22(11):4373–4384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-0170-4
Zhang Y, Hu ZQ, Li L, Xue ZJ (2018b) Improving the structure and mechanical properties of loess by acid solutions—an experimental study. Eng Geol 244:132–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.07.023
Zhang SC, Liu H, Chen WH, Niu FJ, Niu ZL (2020) Strength deterioration model of remolded loess contaminated with acid and alkali solution under freeze-thaw cycles. Bull Eng Geol Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01721-w
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, S., Wang, W., Wei, J. et al. The physical–mechanical properties degradation mechanism and microstructure response of acid–alkali-contaminated Xiashu loess. Nat Hazards 106, 2845–2861 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04570-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04570-7