Abstract
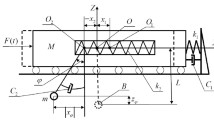
In this paper, we investigate the elastic inverted pendulum with hysteretic nonlinearity (a backlash) in the suspension point. Namely, the problems of stabilization and optimization of such a system are considered. The algorithm (based on the bionic model) which provides the effective procedure for finding of optimal parameters is presented and applied to considered system. The results of numerical simulations, namely the phase portraits and the dynamics of Lyapunov function, are also presented and discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Here it should be noted that although a lot of control algorithms are researched in the system control design, proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller is the most widely used controller structure in the realization of a control system [36]. The advantages of PID controller, which have greatly contributed to its wide acceptance, are its simplicity and sufficient ability to solve many practical control problems.
It should be noted that such an operator is considered on the monotonic inputs. On the piecewise monotonic inputs, this operator can be determined using the semigroup identity [19]
$$\begin{aligned} \varGamma [X(t_{1}),L]Y(t)=\varGamma \left[ \varGamma [X_{0},L] Y(t_{1}),L\right] Y(t). \end{aligned}$$And then, using the special limit construction, such an operator can be redefined on the all continuous functions.
In this paper, we use the following notations: \(a_{x}=\frac{\partial a}{\partial x}\), \(a_{t}=\frac{\partial a}{\partial t}\).
References
Arinstein, A., Gitterman, M.: Inverted spring pendulum driven by a periodic force: linear versus nonlinear analysis. Eur. J. Phys. 29, 385–392 (2008)
Arkhipova, I.M., Luongo, A.: Stabilization via parametric excitation of multi-dof statically unstable systems. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 19, 3913–3926 (2014)
Arkhipova, I.M., Luongo, A., Seyranian, A.P.: Vibrational stabilization of the upright statically unstable position of a double pendulum. J. Sound Vib. 331, 457–469 (2012)
Åström, K.J., Furuta, K.: Swinging up a pendulum by energy control. Automatica 36, 287–295 (2000)
Bloch, A.M., Leonard, N.E., Marsden, J.E.: Controlled lagrangians and the stabilization of mechanical systems. I. The first matching theorem. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 45, 2253–2270 (2000)
Boubaker, O.: The inverted pendulum: a fundamental benchmark in control theory and robotics. In: International Conference on Education and e-Learning Innovations (ICEELI 2012), pp. 1–6 (2012)
Butikov, E.I.: Subharmonic resonances of the parametrically driven pendulum. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 35, 6209 (2002)
Butikov, E.I.: An improved criterion for Kapitza’s pendulum stability. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 44, 295,202 (2011)
Butikov, E.I.: Oscillations of a simple pendulum with extremely large amplitudes. Eur. J. Phys. 33, 1555–1563 (2012)
Chang, L.H., Lee, A.C.: Design of nonlinear controller for bi-axial inverted pendulum system. IET Control Theory Appl. 1, 979–986 (2007)
Chaturvedi, N.A., McClamroch, N.H., Bernstein, D.S.: Stabilization of a 3D axially symmetric pendulum. Automatica 44, 2258–2265 (2008)
Chernous’ko, F.L., Reshmin, S.A.: Time-optimal swing-up feedback control of a pendulum. Nonlinear Dynam. 47, 65–73 (2007)
Dadfarnia, M., Jalili, N., Xian, B., Dawson, D.M.: A Lyapunov-based piezoelectric controller for flexible cartesian robot manipulators. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 126, 347–358 (2004)
Dadios, E.P., Fernandez, P.S., Williams, D.J.: Genetic algorithm on line controller for the flexible inverted pendulum problem. J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform. 10, 155–160 (2006)
Huang, J., Ding, F., Fukuda, T., Matsuno, T.: Modeling and velocity control for a novel narrow vehicle based on mobile wheeled inverted pendulum. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 21, 1607–1617 (2013)
Kapitza, P.L.: Dynamic stability of a pendulum when its point of suspension vibrates. Soviet Phys. JETP 21, 588–592 (1951)
Kapitza, P.L.: Pendulum with a vibrating suspension. Usp. Fiz. Nauk 44, 7–15 (1951). (in Russian)
Kim, K.D., Kumar, P.: Real-time middleware for networked control systems and application to an unstable system. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 21, 1898–1906 (2013)
Krasnosel’skii, M.A., Pokrovskii, A.V.: Syst. Hysteresis. Springer, Berlin (1989)
Kuwana, Y., Shimoyama, I., Sayama, Y., Miura, H.: Synthesis of pheromone-oriented emergent behavior of a silkworm moth. In: Intelligent Robots and Systems ’96, IROS 96, Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on 3,1722–1729 (1996)
Li, G., Liu, X.: Dynamic characteristic prediction of inverted pendulum under the reduced-gravity space environments. Acta Astronaut. 67, 596–604 (2010)
Lozano, R., Fantoni, I., Block, D.J.: Stabilization of the inverted pendulum around its homoclinic orbit. Syst. Control Lett. 40, 197–204 (2000)
Luo, Z.H., Guo, B.Z.: Shear force feedback control of a single-link flexible robot with a revolute joint. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 42, 53–65 (1997)
Mason, P., Broucke, M., Piccoli, B.: Time optimal swing-up of the planar pendulum. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 53, 1876–1886 (2008)
Mata, G.J., Pestana, E.: Effective hamiltonian and dynamic stability of the inverted pendulum. Eur. J. Phys. 25, 717 (2004)
Mikheev, Y.V., Sobolev, V.A., Fridman, E.M.: Asymptotic analysis of digital control systems. Autom. Rem. Control 49, 1175–1180 (1988)
Pierce-Shimomura, J.T., Morse, T.M., Lockery, S.R.: The fundamental role of pirouettes in Caenorhabditis elegans chemotaxis. J. Neurosci. 19, 9557–9569 (1999)
Reshmin, S.A., Chernous’ko, F.L.: A time-optimal control synthesis for a nonlinear pendulum. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. Int. 46, 9–18 (2007)
Sazhin, S., Shakked, T., Katoshevski, D., Sobolev, V.: Particle grouping in oscillating flows. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluid. 27, 131–149 (2008)
Semenov, M.E., Grachikov, D.V., Mishin, M.Y., Shevlyakova, D.V.: Stabilization and control models of systems with hysteresis nonlinearities. Eur. Res. 20, 523–528 (2012)
Semenov, M.E., Shevlyakova, D.V., Meleshenko, P.A.: Inverted pendulum under hysteretic control: stability zones and periodic solutions. Nonlinear Dyn. 75, 247–256 (2014)
Sieber, J., Krauskopf, B.: Complex balancing motions of an inverted pendulum subject to delayed feedback control. Phys. D 197, 332–345 (2004)
Siuka, A., Schöberl, M.: Applications of energy based control methods for the inverted pendulum on a cart. Robot. Auton. Syst. 57, 1012–1017 (2009)
Stephenson, A.: On an induced stability. Philos. Mag. 15, 233 (1908)
Tang, J., Ren, G.: Modeling and simulation of a flexible inverted pendulum system. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 14(Suppl. 2), 22–26 (2009)
Wang, J.J.: Simulation studies of inverted pendulum based on PID controllers. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 19, 440–449 (2011)
Xu, C., Yu, X.: Mathematical model of elastic inverted pendulum control system. Control Theory Technol. 2, 281–282 (2004)
Yavin, Y.: Control of a rotary inverted pendulum. Appl. Math. Lett. 12, 131–134 (1999)
Yue, J., Zhou, Z., Jiang, J., Liu, Y., Hu, D.: Balancing a simulated inverted pendulum through motor imagery: an EEG-based real-time control paradigm. Neurosci. Lett. 524, 95–100 (2012)
Zhang, Y.X., Han, Z.J., Xu, G.Q.: Expansion of solution of an inverted pendulum system with time delay. Appl. Math. Comput. 217, 6476–6489 (2011)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the RFBR Grant 13-08-00532-a.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Semenov, M.E., Solovyov, A.M. & Meleshenko, P.A. Elastic inverted pendulum with backlash in suspension: stabilization problem. Nonlinear Dyn 82, 677–688 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2186-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2186-y