Abstract
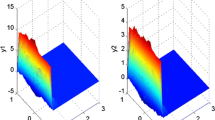
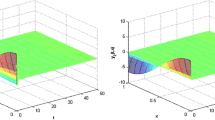
In this paper, we focus on the global existence–uniqueness and input-to-state stability of the mild solution of impulsive reaction–diffusion neural networks with infinite distributed delays. First, the model of the impulsive reaction–diffusion neural networks with infinite distributed delays is reformulated in terms of an abstract impulsive functional differential equation in Hilbert space and the local existence–uniqueness of the mild solution on impulsive time interval is proven by the Picard sequence and semigroup theory. Then, the diffusion–dependent conditions for the global existence–uniqueness and input-to-state stability are established by the vector Lyapunov function and M-matrix where the infinite distributed delays are handled by a novel vector inequality. It shows that the ISS properties can be retained for the destabilizing impulses if there are no too short intervals between the impulses. Finally, three numerical examples verify the effectiveness of the theoretical results and that the reaction–diffusion benefits the input-to-state stability of the neural-network system.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, C.K.: Passive learning and input-to-state stability of switched Hopfield neural networks with time-delay. Inform. Sci. 180(23), 4582–4594 (2010)
Ali, M.S., Narayanan, G., Shekher, V., Alsaedi, A., Ahmad, B.: Global Mittag-Leffler stability analysis of impulsive fractional-order complex-valued BAM neural networks with time varying delays. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 83, 105088 (2020)
Berman, A., Plemmons, R.J.: Nonnegative Matrices in the Mathematical Sciences. SIAM, Philadelphia (1994)
Cao, J., Stamov, G., Stamova, I., Simeonov, S.: Almost periodicity in impulsive fractional-order reaction-diffusion neural networks with time-varying delays. IEEE Trans. Cybern. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.2967625
Chen, W.H., Luo, S., Zheng, W.X.: Impulsive synchronization of reaction-diffusion neural networks with mixed delays and its application to image encryption. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 27(12), 2696–2710 (2016)
He, Y., Ji, M.D., Zhang, C.K., Wu, M.: Global exponential stability of neural networks with time-varying delay based on free-matrix-based integral inequality. Neural Netw. 77, 80–86 (2016)
Hu, J., Sui, G., Lv, X., Li, X.: Fixed-time control of delayed neural networks with impulsive perturbations. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control 23(6), 904–920 (2018)
Jiang, B., Lu, J., Li, X., Qiu, J.: Input/output-to-state stability of nonlinear impulsive delay systems based on a new impulsive inequality. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 29, 6164–6178 (2019)
Li, X., Cao, J.: Delay-independent exponential stability of stochastic Cohen–Grossberg neural networks with time-varying delays and reaction-diffusion terms. Nonlinear Dyn. 50(1–2), 363–371 (2007)
Li, X., O’Regan, D., Akca, H.: Global exponential stabilization of impulsive neural networks with unbounded continuously distributed delays. IMA J. Appl. Math. 80(1), 85–99 (2015)
Li, X., Shen, J., Rakkiyappan, R.: Persistent impulsive effects on stability of functional differential equations with finite or infinite delay. Appl. Math. Comput. 329, 14–22 (2018)
Li, X., Yang, X., Huang, T.: Persistence of delayed cooperative models: impulsive control method. Appl. Math. Comput. 342, 130–146 (2019)
Liu, L., Cao, J., Qian, C.: \(p\)th moment exponential input-to-state stability of delayed recurrent neural networks with Markovian switching via vector Lyapunov function. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(7), 3152–3163 (2018)
Liu, Y., Xu, Y., Ma, J.: Synchronization and spatial patterns in a light-dependent neural network. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 89, 105297 (2020)
Lu, J.G.: Global exponential stability and periodicity of reaction-diffusion delayed recurrent neural networks with Dirichlet boundary conditions. Chaos Solitons Fractals 35(1), 116–125 (2008)
Ma, J., Tang, J.: A review for dynamics in neuron and neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(3), 1569–1578 (2017)
Ma, Q., Shi, G., Xu, S., Zou, Y.: Stability analysis for delayed genetic regulatory networks with reaction-diffusion terms. Neural Comput. Appl. 20(4), 507–516 (2011)
Ma, Q., Xu, S., Zou, Y., Shi, G.: Synchronization of stochastic chaotic neural networks with reaction-diffusion terms. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(3), 2183–2196 (2012)
Pan, J., Liu, X., Zhong, S.: Stability criteria for impulsive reaction-diffusion Cohen–Grossberg neural networks with time-varying delays. Math. Comput. Model. 51(9–10), 1037–1050 (2010)
Pazy, A.: Semigroups of Linear Operators and Applications to Partial Differential Equations. Springer, New York (1983)
Qi, X., Bao, H., Cao, J.: Exponential input-to-state stability of quaternion-valued neural networks with time delay. Appl. Math. Comput. 358, 382–393 (2019)
Sheng, Y., Zeng, Z.: Impulsive synchronization of stochastic reaction-diffusion neural networks with mixed time delays. Neural Netw. 103, 83–93 (2018)
Sheng, Y., Zhang, H., Zeng, Z.: Stability and robust stability of stochastic reaction-diffusion neural networks with infinite discrete and distributed delays. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 50(5), 1721–1732 (2020)
Shuai, B., Zuo, Z., Wang, B., Wang, G.: Scene segmentation with dag-recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(6), 1480–1493 (2018)
Silver, D., Huang, A., Maddison, C.J., Guez, A., Sifre, L., et al.: Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature 529, 484–489 (2016)
Song, X., Man, J., Ahn, C.K., Song, S.: Finite-time dissipative synchronization for Markovian jump generalized inertial neural networks with reaction-diffusion terms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2019.2958419
Song, X., Man, J., Song, S., Ahn, C.K.: Gain-scheduled finite-time synchronization for reaction-diffusion memristive neural networks subject to inconsistent Markov chains. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3009081
Song, X., Wang, M., Song, S., Ahn, C.K.: Sampled-data state estimation of reaction diffusion genetic regulatory networks via space-dividing approaches. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2019.2919532
Sontag, E.D.: Smooth stabilization implies coprime factorization. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 34(4), 435–443 (1989)
Stamova, I.: Global Mittag-Leffler stability and synchronization of impulsive fractional-order neural networks with time-varying delays. Nonlinear Dyn. 77(4), 1251–1260 (2014)
Wang, J.L., Zhang, X.X., Wu, H.N., Huang, T., Wang, Q.: Finite-time passivity and synchronization of coupled reaction-diffusion neural networks with multiple weights. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 49(9), 3385–3397 (2019)
Wang, L., Zhang, R., Wang, Y.: Global exponential stability of reaction-diffusion cellular neural networks with S-type distributed time delays. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 10(2), 1101–1113 (2009)
Wang, X., Wang, H., Li, C., Huang, T.: Synchronization of coupled delayed switched neural networks with impulsive time window. Nonlinear Dyn. 84(3), 1747–1757 (2016)
Wei, T., Lin, P., Wang, Y., Wang, L.: Stability of stochastic impulsive reaction-diffusion neural networks with S-type distributed delays and its application to image encryption. Neural Netw. 116, 35–45 (2019)
Wei, T., Lin, P., Zhu, Q., Wang, L., Wang, Y.: Dynamical behavior of nonautonomous stochastic reaction-diffusion neural-network models. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(5), 1575–1580 (2019)
Wu, K., Li, B., Du, Y., Du, S.: Synchronization for impulsive hybrid-coupled reaction-diffusion neural networks with time-varying delays. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 82, 105031 (2020)
Wu, K.N., Ren, M.Z., Liu, X.Z.: Exponential input-to-state stability of stochastic delay reaction-diffusion neural networks. Neurocomputing 412, 399–405 (2020)
Wu, X., Tang, Y., Zhang, W.: Input-to-state stability of impulsive stochastic delayed systems under linear assumptions. Automatica 66, 195–204 (2016)
Yang, X., Cao, J., Yang, Z.: Synchronization of coupled reaction-diffusion neural networks with time-varying delays via pinning-impulsive controller. SIAM J. Control Optim. 51(5), 3486–3510 (2013)
Yang, Z., Zhou, W., Huang, T.: Exponential input-to-state stability of recurrent neural networks with multiple time-varying delays. Cognit. Neurodyn. 8(1), 47–54 (2014)
Yang, Z., Zhou, W., Huang, T.: Input-to-state stability of delayed reaction-diffusion neural networks with impulsive effects. Neurocomputing 333, 261–272 (2019)
Zhang, X., Han, Y., Wu, L., Wang, Y.: State estimation for delayed genetic regulatory networks with reaction-diffusion terms. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(2), 299–309 (2018)
Zhu, H., Li, P., Li, X., Akca, H.: Input-to-state stability for impulsive switched systems with incommensurate impulsive switching signals. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 80, 104969 (2020)
Zhu, Q., Cao, J., Rakkiyappan, R.: Exponential input-to-state stability of stochastic Cohen–Grossberg neural networks with mixed delays. Nonlinear Dyn. 79(2), 1085–1098 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61673247, 11771014), the Research Fund for Excellent Youth Scholars of Shandong Province (JQ201719), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M672109), the Shandong Province Postdoctoral Innovation Project, and the Serbian Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development (No. 451-03-68/2020-14/200108).
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (avi 31181 KB)
Supplementary material 2 (avi 10336 KB)
Supplementary material 3 (avi 34170 KB)
Supplementary material 4 (avi 31396 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, T., Li, X. & Stojanovic, V. Input-to-state stability of impulsive reaction–diffusion neural networks with infinite distributed delays. Nonlinear Dyn 103, 1733–1755 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06208-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06208-6