Abstract
In the present study, we examined the influence of kindergarten component skills on writing outcomes, both concurrently and longitudinally to first grade. Using data from 265 students, we investigated a model of writing development including attention regulation along with students’ reading, spelling, handwriting fluency, and oral language component skills. Results from structural equation modeling demonstrated that a model including attention was better fitting than a model with only language and literacy factors. Attention, a higher-order literacy factor related to reading and spelling proficiency, and automaticity in letter-writing were uniquely and positively related to compositional fluency in kindergarten. Attention and higher-order literacy factor were predictive of both composition quality and fluency in first grade, while oral language showed unique relations with first grade writing quality. Implications for writing development and instruction are discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
A CFA with a single factor “literacy” variable was also conducted resulting in significantly worse fit than either the correlated factor or higher-order factor model.
References
Abbott, R. D., & Berninger, V. W. (1993). Structural equation modeling of relationships among development skills and writing skills in primary- and intermediate-grade writers. Journal of Educational Psychology, 85, 478–508. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.85.3.478.
Abbott, R. D., Berninger, V. W., & Fayol, M. (2010). Longitudinal relationships of levels of language in writing and between writing and reading in grades 1 to 7. Journal of Educational Psychology, 102(2), 281–298. doi:10.1037/a0019318.
Al Otaiba, S., Connor, C. M., Folsom, J. S., Greulich, L., Meadows, J., & Li, Z. (2011). Assessment data-informed guidance to individualize kindergarten reading instruction: Findings from a cluster-randomized control field trial. Elementary School Journal, 111, 535–560. doi:10.1086/659031.
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Asparouhov, T. (2006). General multi-level modeling with sampling weights. Communications in Statistics: Theory and Methods, 35, 439–460.
Barkley, R. (1996). Linkages between attention and executive functions. In G. R. Lyon & N. Krasnegor (Eds.), Attention, memory, and executive functions (pp. 307–326). Baltimore, MD: Brookes.
Bereiter, C., & Scardamalia, M. (1987). The psychology of written composition. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Berninger, V. W., Abbott, R. D., Abbott, S. P., Graham, S., & Richards, T. (2002). Writing and reading: Connections between language by hand and language by eye. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 35, 39–56. doi:10.1177/002221940203500104.
Berninger, V. W., Abbott, R., Jones, J., Wolf, B., Gould, L., Anderson-Youngstrom, M., et al. (2006). Early development of language by hand: Composing, reading, listening, and speaking connections; three letter-writing modes; and fast mapping in spelling. Developmental Neuropsychology, 29(1), 61–92. doi:10.1207/s15326942dn2901_5.
Berninger, V. W., & Rutberg, J. (1992). Relationship of finger function to beginning writing: Application to diagnosis of writing disabilities. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 34, 155–172. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8749.1992.tb14993.x.
Berninger, V. W., & Winn, W. D. (2006). Implications of advancements in brain research and technology for writing development, writing instruction, and educational evolution. In C. A. MacArthur, S. Graham, & J. Fitzgerald (Eds.), Handbook of Writing Research (pp. 96–114). New York, NY: The Guilford Press.
Blair, C. (2002). School readiness: Integrating cognition and emotion in a neurobiological conceptualization of children’s functioning at school entry. American Psychologist, 57(2), 111–127. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.57.2.111.
Byrne, B., & Fielding-Barnsley, R. (1993). Evaluation of a program to teach phonemic Awareness to young children: A one year follow up. Journal of Educational Psychology, 85, 104–111. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.85.1.104.
Byrne, B., Wadsworth, S., Corley, R., Samuelsson, S., Quain, P., DeFries, J., et al. (2005). Longitudinal twin study of early literacy development: Preschool and kindergarten phases. Scientific Studies of Reading, 9, 219–235. doi:10.1207/s1532799xssr0903_3.
Chenault, B., Thomson, J., Abbott, R. D., & Berninger, V. W. (2006). Effects of prior attention training on child dyslexics’ response to composition instruction. Developmental Neuropsychology, 29(1), 243–260. doi:10.1207/s15326942dn2901_12.
Common Core State Standards Initiative. (2010). Common core state standards for English language arts and literacy in history/social studies, science, and technical subjects. Retrieved from http://www.corestandards.org/assets/CCSSI_ELA%20Standards.pdf.
Duncan, G. J., Dowsett, C. J., Claessens, A., Magnuson, K., Huston, A. C., Klebanov, P., et al. (2007). School readiness and later achievement. Developmental Psychology, 43, 1428–1446. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.43.6.1428.
Ehri, L. C. (2000). Learning to read and learning to spell: Two sides of a coin. Topics in Language Disorders, 20, 19–36. doi:10.1006/ceps.1999.1002.
Fitzgerald, J., & Shanahan, T. (2000). Reading and writing relations and their development. Educational Psychologist, 35, 39–50. doi:10.1207/S15326985EP3501_5.
Graham, S., Berninger, V. W., Abbott, R. D., Abbott, S. P., & Whitaker, D. (1997). Role of mechanics in composing of elementary school students: A new methodological approach. Journal of Educational Psychology, 89, 170–182. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.89.1.170.
Graham, S., Bollinger, A., Booth Olson, C., D’Aoust, C., MacArthur, C., McCutchen, D., et al. (2012a). Teaching elementary school students to be effective writers: A practice guide (NCEE 2012-4058). Washington, DC: National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance, Institute of Education Sciences, US Department of Education. Retrieved from http://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/publications_reviews.aspx#pubsearch.
Graham, S., & Harris, K. R. (2000). The role of self-regulation and transcription skills in writing and writing development. Educational Psychologist, 35, 3–12. doi:10.1207/S15326985EP3501_2.
Graham, S., Harris, K. R., & McKeown, D. (2013). The writing of students with learning disabilities, meta-analysis of self-regulated strategy development writing intervention studies, and future directions: Redux. In L. Swanson, K. R. Harris, & S. Graham (Eds.), Handbook of learning disabilities (2nd ed., pp. 405–438). New York: Guilford Press.
Graham, S., McKeown, D., Kiuhara, S., & Harris, K. R. (2012b). A meta-analysis of writing instruction for students in the elementary grades. Journal of Educational Psychology, 104, 879–896. doi:10.1037/a0029185.
Graham, S., & Perin, D. (2007). A meta-analysis of writing instruction for adolescent students. Journal of Educational Psychology, 99, 445–476. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.99.3.445.
Happaney, K., Zelazo, P. D., & Stuss, D. T. (2004). Development of orbitofrontal function: Current themes and future directions. Brain and Cognition, 55(1), 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.bandc.2004.01.001.
Hooper, S. R., Costa, L., McBee, M., Anderson, K. L., Yerby, D. C., Knuth, S. B., et al. (2011). Concurrent and longitudinal neuropsychological contributors to written language expression in first and second grade students. Reading and Writing, 24, 221–252. doi:10.1007/s11145-010-9263-x.
Hooper, S. R., Swartz, C. W., Wakely, M. B., de Kruif, R. E. L., & Montgomery, J. W. (2002). Executive functions in elementary school children with and without problems in written expression. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 35(1), 57–68. doi:10.1177/002221940203500105.
Jones, D., & Christensen, C. A. (1999). Relationship between automaticity in handwriting and students’ ability to generate written text. Journal of Educational Psychology, 91, 44–49. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.91.1.44.
Juel, C. (1988). Learning to read and write: A longitudinal study of 54 children from first through fourth grades. Journal of Educational Psychology, 80, 437–447. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.80.4.437.
Juel, C., Griffith, P. L., & Gough, P. B. (1986). Acquisition of literacy: A longitudinal study of children in first and second grade. Journal of Educational Psychology, 78, 243–255. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.78.4.243.
Kent, S. C., Wanzek, J., & Al Otaiba, S. (2012). Print reading in general education kindergarten classrooms: What does it look like for students at-risk for reading difficulties? Learning Disabilities Research and Practice, 27(2), 56–65. doi:10.1111/j.1540-5826.2012.00351.x.
Kim, Y.-S., Al Otaiba, S., Folsom, J. S., Folsom, J. S., & Greulich, L. (2013). Language, literacy, attentional behaviors, and instructional quality predictors of written composition for first graders. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 28, 461–469. doi:10.1016/j.ecrsq.2013.01.001.
Kim, Y.-S., Al Otaiba, S., Folsom, J. S., Greulich, L., & Puranik, C. (in press). Evaluating the dimensionality of first grade written composition. Journal of Speech, Hearing, and Language Research.
Kim, Y., Al Otaiba, S., Puranik, C., Folsom, J. S., Greulich, L., & Wagner, R. K. (2011). Componential skills of beginning writing: An exploratory study. Learning and Individual Differences, 21, 517–525. doi:10.1016/j.lindif.2011.06.004.
Kline, R. B. (2011). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Lehto, J. E., Juuiärvi, P., Kooistra, L., & Pulkkinen, L. (2003). Dimensions of executive functioning: Evidence from children. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 21, 59–80. doi:10.1348/026151003321164627.
Lembke, E., Deno, S. L., & Hall, K. (2003). Identifying an indicator of growth in early writing proficiency for elementary school students. Assessment for Effective Intervention, 28, 23–35. doi:10.1177/073724770302800304.
McClelland, M. M., Acock, A. C., Piccinin, A., Rhea, S. A., & Stallings, M. C. (2013). Relations between preschool attention span-persistence and age 25 educational outcomes. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 28(2), 314–324. doi:10.1016/j.ecresq.2012.07.008.
McCutchen, D. (2000). Knowledge, processing, and working memory: Implications for a theory of writing. Educational Psychologist, 35, 13–23. doi:10.1207/S15326985EP3501_3.
McMaster, K. L., Du, X., & Pestursdottir, A. L. (2009). Technical features of curriculum-based measures for beginning writers. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 42, 41–60. doi:10.1177/0022219408326212.
Mehta, P. D., Foorman, B. R., Branum-Martin, L., & Taylor, W. P. (2005). Literacy as a unidimensional multilevel construct: Validation, sources of influence, and implications in a longitudinal study in grades 1 to 4. Scientific Studies of Reading, 9(2), 85–116. doi:10.1207/s1532799xssr0902_1.
Moats, L., Foorman, B., & Taylor, P. (2006). How quality of writing instruction impacts high-risk fourth graders’ writing. Reading and Writing, 19(4), 363–391. doi:10.1007/s11145-005-4944-6.
National Commission on Writing. (2004, September). Writing: A ticket to work… Or a Ticket Out. New York, NY: College Entrance Examination Board. Retrieved from: http://www.collegeboard.com/prod_downloads/writingcom/writing-ticket-to-work.pdf.
Newcomer, P. L., & Hamill, D. D. (1997). Test of language development-primary (Vol. 3). Austin, TX: Pro-Ed.
Northwest Regional Educational Laboratory. (2011). 6 + 1 Trait ® Writing. Retrieved from http://educationnorthwest.org/traits.
Puranik, C. S., & Al Otaiba, S. (2012). Examining the contribution of handwriting and spelling to written expression in kindergarten children. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 25, 1523–1546. doi:10.1007/s11145-011-9331-x.
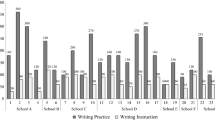
Puranik, C. S., Al Otaiba, S., Sidler, J. F., & Greulich, L. (in press). Exploring the amount and type of writing instruction during language arts instruction in kindergarten classrooms. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal. doi:10.1007/s11145-9441-8.
Puranik, C. S., Lombardino, L. J., & Altmann, L. J. (2007). Writing through retellings: An exploratory study of language-impaired and dyslexic populations. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 20, 251–272. doi:10.1007/s11145-006-9030-1.
Rhoades, B. L., Warren, H. K., Domitrovich, C. E., & Greenberg, M. T. (2011). Examining the link between preschool social-emotional competence and first grade academic achievement: The role of attention skills. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 26(2), 182–191. doi:10.1016/j.ecresq.2010.07.003.
Saez, L., Folsom, J. S., Al Otaiba, S., & Schatschneider, C. (2012). Relations among student attention behaviors, teacher practices, and beginning word reading skill. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 45, 418–432. doi:10.1177/0022219411431243.
Salahu-Din, D., Persky, H., & Miller, J. (2008). The nation’s report card: Writing 2007 (NCES 2008–468). National Center for Education Statistics, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education, Washington, DC.
Shanahan, T. (2006). Relations among oral language, reading, and writing development. In C. A. MacArthur, S. Graham, & J. Fitzgerald (Eds.), Handbook of writing research (pp. 83–95). New York, NY: The Guilford Press.
Shell, D. F., Colvin, C., & Bruning, R. H. (1995). Self-efficacy, attribution, and outcome expectancy mechanisms in reading and writing achievement: Grade-level and achievement-level differences. Journal of Educational Psychology, 87(3), 386–398. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.87.3.386.
Storch, S. A., & Whitehurst, G. J. (2002). Oral language and code-related precursors to reading: Evidence from a longitudinal structural model. Developmental Psychology, 38(6), 934–947. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.38.6.934.
Swanson, J., Shuck, S., Mann, M., Carlson, C., Hartman, K., Sergeant, J., et al. (2006). Categorical and dimensional definitions and evaluations of symptoms of ADHD: The SNAP and SWAN Rating Scales. Unpublished manuscript. University of California Irvine, CA.
Tangel, D. M., & Blachman, B. A. (1992). Effect of phoneme awareness instruction on kindergarten children’s invented spelling. Journal of Reading Behavior, 24, 233–261. doi:10.1080/10862969209547774.
Thomson, J. B., Chenault, B., Abbott, R. D., Raskind, W. H., Richards, R., Aylward, E., et al. (2005). Converging evidence for attentional influences on the orthographic word form in child dyslexics. Journal of Neurolinguistics, 18, 93–126. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroling.2004.11.005.
Torgesen, J. K., Wagner, R. K., & Rashotte, C. A. (1999). Test of word reading efficiency. Austin, TX: Pro-Ed.
Wagner, R. K., Puranik, C. S., Foorman, B., Foster, E., Tschinkel, E., & Kantor, P. T. (2011). Modeling the development of written language. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 24, 203–220. doi:10.1007/s11145-010-9266-7.
Willcutt, E. G., Pennington, B. F., Boada, R., Ogline, J. S., Tunick, R. A., Chhabildas, N. A., et al. (2001). A comparison of the cognitive deficits in reading disability and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 110, 157–172. doi:10.1037/0021-843X.110.1.157.
Woodcock, R. W., McGrew, K. S., & Mather, N. (2001). Woodcock-Johnson III tests of achievement. Itasca, IL: Riverside Publishing.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Grant P50HD052120 from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, and Grant R305B04074 from the Institute of Education Sciences. Dr. Petscher’s time was also supported by Grant R305F100005 from the Institute of Education Sciences. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the National Institutes of Health, or the Institute of Education Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kent, S., Wanzek, J., Petscher, Y. et al. Writing fluency and quality in kindergarten and first grade: the role of attention, reading, transcription, and oral language. Read Writ 27, 1163–1188 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-013-9480-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-013-9480-1