Abstract
Purpose
Urinary bladder may encounter several pathologic conditions that could lead to loss of its function. Tissue engineering using electrospun PLLA scaffolds is a promising approach to reconstructing or replacing the problematic bladder.
Methods
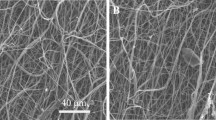
PLLA nanofibrous scaffolds were prepared utilizing single-nozzle electrospinning. The morphology and distribution of fiber diameters were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Human bladder smooth muscle cells (hBSMCs) were isolated from biopsies and characterized by immunocytochemistry (ICC). Then, the cells were seeded on the PLLA nanofibers and Alamar Blue assay proved the biocompatibility of prepared scaffolds. Cell attachment on the nanofibers and also cell morphology over fibrous scaffolds were observed by SEM.
Results
The results indicated that electrospun PLLA scaffold provides proper conditions for hBSMCs to interact and attach efficiently to the fibers. Alamar Blue assay showed the compatibility of the obtained electrospun scaffolds with hBSMCs. Also, it was observed that the cells could achieve highly elongated morphology and their native aligned direction besides each other on the random electrospun scaffolds and in the absence of supporting aligned nanofibers.
Conclusion
Electrospun PLLA scaffold efficiently supports the hBSMCs growth and alignment and also has proper cell compatibility. This scaffold would be promising in urinary bladder tissue engineering.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atala A (2011) Tissue engineering of human bladder. Br Med Bull 97(1):81–104
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A (2011) Cancer statistics, 2011. CA Cancer J Clin 61(4):212–236
Petrovic V, Stankovic J, Stefanovic V (2011) Tissue engineering of the urinary bladder: current concepts and future perspectives. Sci World J 11:1479–1488
McDougal WS (1992) Metabolic complications of urinary intestinal diversion. J Urol 147:1199–1208
Kaefer M, Hendren WH, Bauer SB, Goldenblatt P, Peters CA, Atala A, Retik AB (1998) Reservoir calculi: a comparison of reservoirs constructed from stomach and other enteric segments. J Urol 160(6):2187–2190
Kaefer M, Tobin MS, Hendren WH, Bauer SB, Peters CA, Atala A, Colodny AH, Mandell J, Retik AB (1997) Continent urinary diversion: the Children’s Hospital experience. J Urol 157(4):1394–1399
Filmer RB, Spencer JR (1990) Malignancies in bladder augmentations and intestinal conduits. J Urol 143(4):671–678
Zhang Y, Kropp BP, Moore P, Cowan R, Furness PD, Kolligian ME, Frey P, Cheng EY (2000) Coculture of bladder urothelial and smooth muscle cells on small intestinal submucosa: potential applications for tissue engineering technology. J Urol 164(3):928–935
Zhang Y, Frimberger D, Cheng EY, Hk Lin, Kropp BP (2006) Challenges in a larger bladder replacement with cell-seeded and unseeded small intestinal submucosa grafts in a subtotal cystectomy model. BJU Int 98(5):1100–1105
Kajbafzadeh A-M, Payabvash S, Salmasi AH, Sadeghi Z, Elmi A, Vejdani K, Tavangar SM, Tajik P, Mahjoub F (2007) Time-dependent neovasculogenesis and regeneration of different bladder wall components in the bladder acellular matrix graft in rats. J Surg Res 139(2):189–202
Atala A, Vacanti J, Peters C, Mandell J, Retik A, Freeman M (1992) Formation of urothelial structures in vivo from dissociated cells attached to biodegradable polymer scaffolds in vitro. J Urol 148:658–662
Hoque ME, San WY, Wei F, Li S, Huang M-H, Vert M, Hutmacher DW (2009) Processing of polycaprolactone and polycaprolactone-based copolymers into 3D scaffolds, and their cellular responses. Tissue Eng Part A 15(10):3013–3024
Xu F, Wang Y, Jiang X, Tan H, Li H, Wang K-J (2012) Effects of different biomaterials: comparing the bladder smooth muscle cells on waterborne polyurethane or poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid membranes. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 28(1):10–15
Beachley V, Wen X (2010) Polymer nanofibrous structures: fabrication, biofunctionalization, and cell interactions. Prog Polym Sci 35(7):868–892
Sun B, Long YZ, Zhang HD, Li MM, Duvail JL, Jiang XY, Yin HL (2014) Advances in three-dimensional nanofibrous macrostructures via electrospinning. Prog Polym Sci 39(5):862–890
Najafi-Taher R, Derakhshan MA, Faridi-Majidi R, Amani A (2015) Preparation of ascorbic acid/PVA-chitosan electrospun mat: a core/shell transdermal delivery system. RSC Adv 5:50462–50469
Arvand M, Mirzaei E, Derakhshan MA, Kharrazi S, Sadroddiny E, Babapour M, Faridi-Majidi R (2015) Fabrication of antibacterial silver nanoparticle-modified chitosan fibers using Eucalyptus extract as a reducing agent. J Appl Polym Sci. doi:10.1002/app.42133
Wei G, Li C, Fu Q, Xu Y, Li H (2015) Preparation of PCL/silk fibroin/collagen electrospun fiber for urethral reconstruction. Int Urol Nephrol 47(1):95–99
Baker SC, Atkin N, Gunning PA, Granville N, Wilson K, Wilson D, Southgate J (2006) Characterisation of electrospun polystyrene scaffolds for three-dimensional in vitro biological studies. Biomaterials 27(16):3136–3146
McManus M, Boland E, Sell S, Bowen W, Koo H, Simpson D, Bowlin G (2007) Electrospun nanofibre fibrinogen for urinary tract tissue reconstruction. Biomed Mater 2(4):257
Horst M, Madduri S, Milleret V, Sulser T, Gobet R, Eberli D (2013) A bilayered hybrid microfibrous PLGA—acellular matrix scaffold for hollow organ tissue engineering. Biomaterials 34(5):1537–1545
Del Costantino G, Alberto V, Guido B, Vincenza M, Angelo S, Alessandro Z, Alessandra B, Massimo P (2013) Evaluation of electrospun bioresorbable scaffolds for tissue-engineered urinary bladder augmentation. Biomed Mater 8(4):045013
Sharifiaghdas F, Naji M, Sarhangnejad R, Rajabi-Zeleti S, Mirzadeh H, Zandi M, Saeed M (2014) Comparing supportive properties of poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA), PLGA/collagen and human amniotic membrane for human urothelial and smooth muscle cells engineering. Urol J 11(3):1620–1628
Huang JW, Xu YM, Li ZB, Murphy SV, Zhao W, Liu QQ, Zhu WD, Fu Q, Zhang YP, Song LJ (2015) Tissue performance of bladder following stretched electrospun silk fibroin matrix and bladder acellular matrix implantation in a rabbit model. J Biomed Mater Res A 104(1):9–16
Shakhssalim N, Rasouli J, Moghadasali R, Aghdas FS, Naji M, Soleimani M (2013) Bladder smooth muscle cells interaction and proliferation on PCL/PLLA electrospun nanofibrous scaffold. Int J Artif Organs 36(2):113–120
Ahvaz HH, Soleimani M, Mobasheri H, Bakhshandeh B, Shakhssalim N, Soudi S, Hafizi M, Vasei M, Dodel M (2012) Effective combination of hydrostatic pressure and aligned nanofibrous scaffolds on human bladder smooth muscle cells: implication for bladder tissue engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med 23(9):2281–2290
Gupta B, Revagade N, Hilborn J (2007) Poly (lactic acid) fiber: an overview. Prog Polym Sci 32(4):455–482
Shabani I, Haddadi-Asl V, Seyedjafari E, Soleimani M (2012) Cellular infiltration on nanofibrous scaffolds using a modified electrospinning technique. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 423(1):50–54
Lin C-C, Fu S-J, Lin Y-C, Yang I-K, Gu Y (2014) Chitosan-coated electrospun PLA fibers for rapid mineralization of calcium phosphate. Int J Biol Macromol 68:39–47
Haroosh H, Chaudhary D, Dong Y, Hawkins B (2011) Electrospun PLA: PCL/halloysite nanotube nanocomposites fibers for drug delivery. In: 19th international conference on processing and fabrication of advanced materials (PFAM XIX). The University of Auckland, Auckland, pp 847–858
McCullen SD, Stano KL, Stevens DR, Roberts WA, Monteiro-Riviere NA, Clarke LI, Gorga RE (2007) Development, optimization, and characterization of electrospun poly (lactic acid) nanofibers containing multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J Appl Polym Sci 105(3):1668–1678
Casasola R, Thomas NL, Trybala A, Georgiadou S (2014) Electrospun poly lactic acid (PLA) fibres: effect of different solvent systems on fibre morphology and diameter. Polymer 55(18):4728–4737
Brown AL, Brook-Allred TT, Waddell JE, White J, Werkmeister JA, Ramshaw JA, Bagli DJ, Woodhouse KA (2005) Bladder acellular matrix as a substrate for studying in vitro bladder smooth muscle–urothelial cell interactions. Biomaterials 26(5):529–543
Nivison-Smith L, Weiss AS (2012) Alignment of human vascular smooth muscle cells on parallel electrospun synthetic elastin fibers. J Biomed Mater Res A 100(1):155–161
Wang Y, Shi H, Qiao J, Tian Y, Wu M, Zhang W, Lin Y, Niu Z, Huang Y (2014) Electrospun tubular scaffold with circumferentially aligned nanofibers for regulating smooth muscle cell growth. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(4):2958–2962
Eichhorn SJ, Sampson WW (2005) Statistical geometry of pores and statistics of porous nanofibrous assemblies. J R Soc Interface 2(4):309–318
Jia L, Prabhakaran MP, Qin X, Ramakrishna S (2014) Guiding the orientation of smooth muscle cells on random and aligned polyurethane/collagen nanofibers. J Biomater Appl 29:364–377
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their special gratitude to Dr. Shahram Gooran from TUMS Urology Center at Sina Hospital.
Funding
This research has been supported by Tehran University of Medical Sciences and Health Services (Grant No. 92-02-87-22110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The procedures involving human participants were performed in accordance with the ethical approval of Tehran University of Medical Sciences and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and subsequent amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Derakhshan, M.A., Pourmand, G., Ai, J. et al. Electrospun PLLA nanofiber scaffolds for bladder smooth muscle reconstruction. Int Urol Nephrol 48, 1097–1104 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1259-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1259-2