Abstract
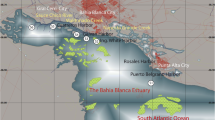
The extent of pollution with organotin compounds was investigated in water, sediment and bivalve mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) from the Northern Adriatic Sea. Butyl-, phenyl- and octyltin species were quantified after extraction and derivatisation by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry in a total of 99 samples from the period from 2000 to 2006. The accuracies of the analytical procedures were checked by spiking of unpolluted water samples and by the analysis of standard reference materials (harbour sediment PACS-2 and mussel tissue ERM-CE 477). Among organotin species analysed in samples butyltins were the predominant. Tributyltin was found to be present in the highest concentrations, suggesting its recent input into the marine environment. Butyltins were detected at all sites surveyed (sum of butyltins was up to 718 ng Sn L−1, 3,552 ng Sn g−1 d.w. and 9,991 ng Sn g−1 d.w. in water, sediment and mussel samples, respectively), phenytins in much lower concentrations (up to 31 ng Sn L−1, 326 ng Sn g−1 d.w. and 442 ng Sn g−1 d.w. in water, sediment and mussel samples) and to a much smaller extent, while octyltins were not detected at any location. The spatial distribution of tributyltin was closely related to boating, with the highest concentrations found in marinas (up to 586 ng Sn L−1 for water samples, 1,995 ng Sn g−1 d.w. for sediment and 6,434 ng Sn g−1 d.w. for mussel samples). The temporal distribution clearly indicates a decrease of organotin pollution at all sites.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abalos, M., Bayona, J. M., Compano, R., Granados, M., Leal, C., & Prat, M. D. (1997). Analytical procedures for the determination of organotin compounds in sediment and biota: a critical review. Journal of Chromatography A, 788, 1–49 doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(97)00733-4.
Aguerre, S., Bancon-Montigny, C., Lespes, G., & Potin-Gautier, M. (2000). Solid phase microextraction (SPME): a new peocedure for the control of butyl- and phenyltin pollution in the environment by GC-FPD. Analyst (London), 125, 263–268. doi:10.1039/a908322g.
Alzieu, C. (1998). Tributyltin: case study of a chronic contaminant in the coastal environment. Ocean and Coastal Management, 40, 23–36, doi:10.1016/S0964-5691(98)00036-2.
Andral, B., Stanisiere, J. Y., Sauzade, D., Damier, E., Thebault, H., Galgani, F., et al. (2004). Monitoring chemical contamination levels in the Mediterranean based on the use of mussel caging. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 704–712 doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.05.008.
Barroso, C. M., Mendo, S., & Moreira, M. H. (2004). Organotin contamination in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis from Portuguese coastal waters. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 48, 1145–1167 doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.03.005.
Barroso, C. M., & Moreira, M. H. (2002). Spatial and temporal changes of TBT pollution along the Portuguese coast: inefficacy of the EEC directive 89/677. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 44, 480–486 doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00260-0.
Bortoli, A., Troncon, A., Dariol, S., Pellizzato, F., & Pavoni, B. (2003). Butyltins and phenyltins in biota and sediments from the Lagoon of Venice. Oceanologia, 45, 7–23.
Boscolo, R., Cacciatore, F., Berto, D., Marin, M. G., & Giani, M. (2004). Contamination of natural and cultured mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) from the northern Adriatic Sea by tributyltin and dibutyltin compounds. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 18, 614–618, doi:10.1002/aoc.647.
Champ, M. A. (2000). A review of organotin regulatory strategies, pending actions, related costs and benefits. The Science of the Total Environment, 258, 21–71 doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00506-4.
Chiavarini, S., Massanisso, P., Nicolai, P., Nobili, R., & Morabito, R. (2003). Butyltins concentration levels and imposex occurrence in snails from the Sicilian coast (Italy). Chemosphere, 50, 311–319 doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00601-X.
Commission Directive 2000/62/EC. (2000). EU Water Framework Directive. Official Journal of the European Communities OJ L, 327.
Commission Directive 2002/62/EC. (2002) Annex I to Council Directive 76/769/EEC on the approximation of the laws, regulation and administrative provisions of the member States relating to restrictions on the marketing and use of certain dangerous substances and preparations (organostannic compounds). Official Journal of the European Communities L, 183/58.
Conti, M. E., & Cecchetti, G. (2003). A biomonitoring study: trace metals in algae and molluscs from Tyrrhenian costal area. Environmental Research, 93, 99–112 doi:10.1016/S0013-9351(03)00012-4.
Convention, A.F.S. Report 52. (2003). International Convention on the Control of Harmful Anti-fouling Systems on Ships. Treaties tabled in March 2003, 5, 73–81, http://www.aph.gov.au/house/committee/jsct/march2003/report/chap5.pdf.
de Mora, S., Stewart, C., & Phillips, D. (1995). Sources and rate of degradation of tri(n-butyl)tin in marine sediments near Auckland, New Zealand. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 30(1), 50–57, doi:10.1016/0025-326X(94)00178-C.
Devier, M.-H., Augagneur, S., Budzinski, H., Le Menach, K., Mora, P., Narbonne, J.-F., et al. (2005). One-year monitoring survey of organic compounds (PAHs, PCBs, TBT), heavy metals and biomarkers in blue mussels from the Archon Bay, France. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 224, 224–240, doi:10.1039/b409577d.
Diez, S., Abalos, M., & Bayona, J.-M. (2002). Organotin contamination in sediments from the Western Mediterranean enclosures following 10 years of TBT regulation. Water Research, 36, 905–918 doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00305-0.
Diez, S., Lacorte, S., Viana, P., Barcelo, D., & Bayona, J.-M. (2005). Survey of organotin compounds in rivers and costal environments in Portugal 1999–2000. Environmental Pollution, 136, 525–536 doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2004.12.011.
Fent, K. (1996). Ecotoxicology of organotin compounds. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 26(1), 1–117 doi:10.3109/10408449609089891.
Gallina, A., Magno, F., Tallandini, L., Passaler, T., Caravello, G. U., & Pastore, P. (2000). Simple and effective gas chromatographic mass spectrometric procedure for the speciation analysis of organotin compounds in specimens of marine mussels. An evaluation of organotin pollution of the Lagoon of Venice. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 14, 373–378. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0231(20000331)14:6<373::AID-RCM877>3.0.CO;2-N.
Garaventa, F., Pellizzato, F., Faimali, M., Terlizzi, A., Medakovic, D., Geraci, S., et al. (2006). Imposex in Hexaplex trunculus at some sites on the North Mediterranean coast as a base-line for future evaluation of the effectiveness of the total ban on organotin based antifouling paints. Hydrobiologia, 555, 281–287, doi:10.1007/s10750-005-1124-2.
Gomez-Ariza, J. L., Santos, M. M., Morales, E., Giraldez, I., Sanches-Rodas, D., Vieira, N., et al. (2006). Organotin contamination in the Atlantic Ocean off the Iberian Peninsula in relation to shipping. Chemosphere, 64, 1100–1108 doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.11.068.
Hoch, M. (2001). Organotin compounds in the environment—an overview. Applied Geochemistry, 16, 719–743, doi:10.1016/S0883-2927(00)00067-6.
Ko, M. M. C., Bradley, G. C., Neller, A. H., & Broom, M. J. (1995). Tributyltin contamination of marine sediments of Hong-Kong. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 31(4–12), 249–253.
Laughlin, R. B., Guard, H. E., & Coleman, W. M. (1989). Tributyltin in seawater: speciation and octanol–water partition coefficient. Environmental Science & Technology, 20, 201–204, doi:10.1021/es00144a016.
Michel, P., Averty, B., Andral, B., Chiffoleau, J.-F., & Galgani, F. (2001). Tributyltin along the coast of Corsica (Western Mediterranean): a persistent problem. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42(11), 1128–1132 doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00101-1.
Milivojevič Nemanič, T., Leskovšek, H., Horvat, M., Vrišer, B., & Bolje, A. (2002). Organotin compounds in the marine environment of the Bay of Piran, Northern Adriatic Sea. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 4, 426–430 doi:10.1039/b111582k.
Milivojevič Nemanič, T., Milačič, R., & Ščančar, J. (2007b). Critical evaluation of various extraction procedures for the speciation of organotin compounds in sediments by GC–MS. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 87, 615–625, doi:10.1080/03067310701325026.
Milivojevič Nemanič, T., Ščančar, J., Milačič, R., & Zupančič-Kralj, L. (2007a). Critical evaluation of different extraction procedures for determination of organotin compounds in mussels. Acta Chimica Slovenica, 54, 40–48.
O’Connor, T. P., & Lauenstein, G. G. (2006). Trends in chemical concentrations in mussels and oysters collected along the US coast: update to 2003. Marine Environmental Research, 62, 261–285 doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2006.04.067.
Pellizzato, F., Centanni, E., Marin, M. G., Moschino, V., & Pavoni, B. (2004). Concentrations of organotin compounds and imposex in the gastropod Hexaplex trunculus from the Lagoon of Venice. The Science of the Total Environment, 332, 89–100 doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.03.036.
Rainbow, P. S. (1995). Biomonitoring of heavy metal availability in the marine environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 31, 183–192, doi:10.1016/0025-326X(95)00116-5.
Rodriguez-Gonzalez, P., Encinar, J. R., Alonso, J. I. G., & Sanz-Medel, A. (2002). Determination of butyltin compounds in costal sea-water samples using isotope dilution GC–ICP–MS. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 17, 824–830, doi:10.1039/b204169n.
Roper, J. M., Simmers, J. W., & Cherry, D. S. (2001). Bioaccumulation of butyltins in Dreissene polymorpha at a confined placement facility in Buffalo, New York. Environmental Pollution, 111, 447–452 doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00086-5.
Rüdel, H. (2003). Case study: bioavailability of tin and tin compounds. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 56, 180–189 doi:10.1016/S0147-6513(03)00061-7.
Rüdel, H., Muller, J., Steinhanses, J., & Schroter-Karmani, C. (2007). Retrospective monitoring of organotin compounds in freshwater fish from 1988–2003: results from the German environmental specimen bank. Chemosphere, 66, 1884–1894 doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.08.014.
Sarradin, P. M., Lapaquellerie, Y., Astruc, A., Latouche, C., & Astruc, M. (1995). Long term behaviour and degradation kinetics of tributyltin in marine sediment. The Science of the Total Environment, 170, 59–70 doi:10.1016/0048-9697(95)04561-E.
Ščančar, J., Zuliani, T., Turk, T., & Milačič, R. (2007). Organotin compounds and selected metals in the marine environment of Northern Adriatic Sea. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 127, 271–282 doi:10.1007/s10661-006-9278-6.
Shim, W. J., Hong, S. H., Kim, N. S., Yim, U. H., Li, D., & Oh, J. R. (2005). Assessment of butyl- and phenyltin pollution in the costal environment of Korea using mussels and oysters. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 51, 922–931 doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.07.015.
Uveges, M., Rodriguez-Gonzalez, P., Alonso, J. I. G., Sanz-Medel, A., & Fodor, P. (2007). Isotope dilution analysis mass spectrometry for the routine measurement of butyltin compounds in marine environmental and biological samples. Microchemical Journal, 85, 151–121, doi:10.1016/j.microc.2006.04.003.
van der Oost, R., Beyer, J., & Vermeulen, N. P. E. (2003). Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 13, 57–149, doi:10.1016/S1382-6689(02)00126-6.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministry of Higher Education, Science and Technology of the Republic of Slovenia within the research programme P1-0143 and project J1-6568.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milivojevič Nemanič, T., Milačič, R. & Ščančar, J. A Survey of Organotin Compounds in the Northern Adriatic Sea. Water Air Soil Pollut 196, 211–224 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-008-9770-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-008-9770-4