Abstract
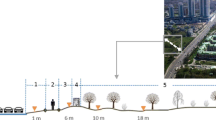
Automobile traffic pollutes roadside environments with a range of contaminants. In this study, we investigate the distribution patterns of different contaminant classes in topsoils across a highway-forest interface north-east of Vienna, Austria, in order to assess spatial pollutant distribution and evaluate the filtering effect of roadside forests. We collected soil samples along transects perpendicular to the highway, and analyzed the soils for road salt residues (Na), total and mobile heavy metals (Pb, Cd, Cu, Zn, Ni, Cr) as well as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Roadside soil pollution was highly heterogeneous. All contaminants followed an exponential-like decrease with distance from the road, reaching background levels at 5 to 10 m from the road curb. Traffic-born heavy metals in the immediate roadside zone tended to be more mobile than heavy metals of predominantly geogenic origin at greater distances from the road; the presence of road salt residues could have contributed to the elevated heavy metal mobility near the road. The forest vegetation acted as filter for PAHs shown by a sharp concentration increase at the forest edge. PAHs are likely transported with airborne soot particles that are scavenged by the wax-coated coniferous needles at our study site.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bäckström, M., Nilsson, U., Håkansson, K., Allard, B., & Karlsson, S. (2003). Speciation of heavy metals in road runoff and roadside total deposition. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 147, 343–366. doi:10.1023/A:1024545916834.
Blum, W. E. H., Spiegel, H., & Wenzel, W. W. (1996). Bodenzustandsinventur (2nd ed.). Vienna: Bundesministerium für Land- und Forstwirtschaft, Bundesministerium für Wissenschaft, Verkehr und Kunst.
Bradl, H. B. (2004). Adsorption of heavy metal ions on soils and soils constituents. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 277, 1–18. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2004.04.005.
Deußner, R., Amon, B., & Zodtl, E. (2004). Entwicklung der Verkehrsmengen und der Emissionen auf wichtigen Straßen in Österreich. Vienna: Österreichisches Institut für Raumplanung.
Dierkes, C., & Geiger, W. F. (1999). Pollution retention capabilities of roadside soils. Water Science and Technology, 39, 201–208. doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(99)00024-4.
Garcia, R., & Millán, E. (1998). Assessment of Cd, Pb and Zn contamination in roadside soils and grasses from Gipuzkoa (Spain). Chemosphere, 37, 1615–1625. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00152-0.
Gocht, T., Werth, C., Razzaque, M., & Grathwohl, P. (2005). Role of carbonaceous particles during accumulation of persistent organic pollutants in rural soils. ACS, Division of Environmental Chemistry—Preprints of Extended Abstracts, 45, 461–466.
Grathwohl, P., Gocht, T., Kleineidam, S., Schmidt, T., & Werth, C. (2005). Role of black carbon (BC) for the accumulation of hydrophobic organic compounds (HOCs) in soils at the catchment scale. ACS, Division of Environmental Chemistry—Preprints of Extended Abstracts, 45, 391–396.
Hjortenkrans, D., Bergbäck, B., & Häggerud, A. (2006). New metal emission patterns in road traffic environments. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 117, 85–98. doi:10.1007/s10661-006-7706-2.
Ho, Y. B., & Tai, K. M. (1988). Elevated levels of lead and other metals in roadside soil and grass and their use to monitor aerial metal depositions in Hong Kong. Environmental Pollution, 49, 37–51. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(88)90012-7.
IUSS Working Group WRB. (2006). World reference base for soil resources 2006, World soil resources rep. 103. (Rome: FAO.)
Johnsen, A. R., De Lipthay, J. R., Reichenberg, F., Sørensen, S. J., Andersen, O., Christensen, P., et al. (2006). Biodegradation, bioaccessibility, and genotoxicity of diffuse polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) pollution at a motorway site. Environmental Science & Technology, 40, 3293–3298. doi:10.1021/es060008u.
Kilbride, C., Poole, J., & Hutchings, T. R. (2006). A comparison of Cu, Pb, As, Cd, Zn, Fe, Ni and Mn determined by acid extraction/ICP-OES and ex situ field portable X-ray fluorescence analyses. Environmental Pollution, 143, 16–23. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.11.013.
Lee, P. -H., Ong, S. K., Golchin, J., & Nelson, G. L. (1999). Extraction method for analysis of PAHs in coal-tar-contaminated soils. Practice Periodical of Hazardous, Toxic, and Radioactive Waste Management, 3, 155–162. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)1090-025X(1999)3:4(155).
Münch, D. (1993). Concentration profiles of arsenic, cadmium, chromium, copper, lead, mercury, nickel, zinc, vanadium and polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in forest soil beside an urban road. The Science of the Total Environment, 138, 47–55. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(93)90404-T.
Nabulo, G., Oryem-Origa, H., & Diamond, M. (2006). Assessment of lead, cadmium, and zinc contamination of roadside soils, surface films, and vegetables in Kampala City, Uganda. Environmental Research, 101, 42–52. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2005.12.016.
Norrström, A. C. (2005). Metal mobility by de-icing salt from an infiltration trench for highway runoff. Applied Geochemistry, 20, 1907–1919. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2005.06.002.
Norrström, A. C., & Jacks, G. (1998). Concentration and fractionation of heavy metals in roadside soils receiving de-icing salts. The Science of the Total Environment, 218, 161–174. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(98)00203-4.
Pagotto, C., Rémy, N., Legret, M., & Le Cloirec, P. (2001). Heavy metal pollution of road dust and roadside soil near a major rural highway. Environmental Technology, 22, 307–319. doi:10.1080/09593332208618280.
Schäfer, J., & Puchelt, H. (1998). Platinum-group-metals (PGM) emitted from automobile catalytic converters and their distribution in roadside soils. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 64, 307–314. doi:10.1016/S0375-6742(98)00040-5.
Unger, H. -J., & Prinz, D. (1997). Bodenbelastung an Straßen mit Schwermetallen und organischen Fremdstoffen. In D. Rosenkranz, G. Bachmann, G. Einsele, & M. Harreß (Eds.), Bodenschutz, ergänzbares Handbuch (pp. 1–65). Berlin: Erich Schmidt.
van Bohemen, H. D., & van de Laak, W. H. J. (2003). The influence of road infrastructure and traffic on soil, water, and air quality. Environmental Management, 31, 50–68. doi:10.1007/s00267-002-2802-8.
Viard, B., Pihan, F., Promeyrat, S., & Pihan, J. -C. (2004). Integrated assessment of heavy metal (Pb, Zn, Cd) highway pollution: bioaccumulation in soil, graminaceae and land snails. Chemosphere, 55, 1349–1359. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.01.003.
Ward, N. I. (1990). Multielement contamination of British motorway environments. The Science of the Total Environment, 93, 393–401. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(90)90130-M.
Wheeler, G. L., & Rolfe, G. L. (1979). The relationship between daily traffic volume and the distribution of lead in roadside soil and vegetation. Environmental Pollution, 18, 265–274. doi:10.1016/0013-9327(79)90022-3.
Zupančič, N. (1999). Lead contamination in the roadside soils of Slovenia. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 21, 37–50. doi:10.1023/A:1006539626650.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zehetner, F., Rosenfellner, U., Mentler, A. et al. Distribution of Road Salt Residues, Heavy Metals and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons across a Highway-Forest Interface. Water Air Soil Pollut 198, 125–132 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-008-9831-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-008-9831-8