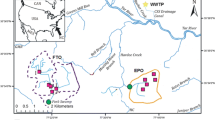
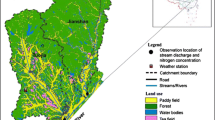
Abstract
Nitrogen inputs to coastal watersheds have been linked to eutrophication. However, the role that domestic sources of wastewater play in contributing nitrogen to coastal watersheds is not well known in the southeastern USA. In a yearlong study (2011–2012), nitrogen concentrations were compared in watersheds served by septic systems and a centralized sewer system in the Coastal Plain of North Carolina. Surface and groundwater samples from septic systems and sewer watersheds were analyzed for total dissolved nitrogen (TDN), total nitrogen, and nitrogen and oxygen isotopes in nitrate. Groundwater beneath the drainfield and adjacent to streams had median concentrations of TDN at 5.9 and 4.4 mg/L, respectively. Additionally, median groundwater-transported loads of TDN to the stream from septic systems sites (0.6 kg-TDN/year) were significantly greater than sites in sewer watersheds (0.2 kg-TDN/year). Isotopic analyses revealed that effluent from septic systems was the primary source of nitrate in watersheds served by septic systems, while fertilizer and/or soil organic matter were dominant sources of nitrate in sewer watersheds. Nitrogen exported from septic systems contributed to elevated nitrogen concentrations in groundwater and streams throughout the watershed, whereas nitrogen exports from sewers were focused at a single point source and affected surface water concentrations. Based on watershed TDN exports from septic systems minus TDN exports from sewers watersheds, it was estimated that septic systems contributed 1.6 kg TDN/ha/year to watershed exports of TDN. Overall, septic systems and sewers contributed to elevated nitrogen loading and should be considered in nutrient-sensitive watershed management.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TDN:
-
Total dissolved nitrogen
- TN:
-
Total nitrogen
References
Alameddine, I., Qian, S. S., & Reckhow, K. H. (2011). A Bayesian changepoint—threshold model to examine the effect of TMDL implementation on the flow-nitrogen concentration relationship in the Neuse River basin. Water Research, 45, 51–62.
Andres, A. S., & Sims, J. T. (2013). Assessing potential impacts of a wastewater rapid infiltration basin system on groundwater quality: a Delaware case study. Journal of Environmental Quality, 42, 391–404.
ArandaCirerol, N., Comín, F., & Herrera-Silveira, J. (2011). Nitrogen and phosphorus budgets for the Yucatán littoral: an approach for groundwater management. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 172, 493–505.
Aravena, R., & Robertson, W. D. (1998). Use of multiple isotope tracers to evaluate denitrification in ground water: study of nitrate from a large-flux septic system plume. Ground Water, 36, 975–982.
Becher, K. D., Schnoebelen, D. J., & Akers, K. K. B. (2000). Nutrients discharged to the Mississippi river from eastern Iowa watersheds. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 36(1), 161–173.
Bouwer, H., & Rice, R. C. (1976). A slug test for determining hydraulic conductivity of unconfined aquifers with completely or partially penetrating wells. Water Resources Research, 12(3), 423–428.
Bowen, J. L., & Valiela, I. (2001). The ecological effects of urbanization of coastal watersheds: historical increases in nitrogen loads and eutrophication of Waquoit Bay estuaries. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 58(8), 1489–1500.
Bowen, J. L., Kroeger, K. D., Tomasky, G., Pabich, W. J., Cole, M. L., Carmichael, R. H., & Valiela, I. (2007). A review of land-sea coupling by groundwater discharge of nitrogen to New England estuaries: mechanisms and effects. Applied Geochemistry, 22(1), 175–191.
Burkholder, J. M., Dickey, D. A., Kinder, C. A., Reed, R. E., Mallin, M. A., McIver, M. R., Cahoon, L. B., Melia, G., Brownie, C., Smith, J., Deamer, N., Springer, J., Glasgow, H. B., & Toms, D. (2006). Comprehensive trend analysis of nutrients and related variables in a large eutrophic estuary: a decadal study of anthropogenic and climatic influences. Limnology and Oceanography, 51, 463–487.
Carlile, B. L., Cogger, C. G., Steinbeck, S. J. (1981). Movement and fate of septic tank effluent in soils of the North Carolina coastal plain, part I. Department of Soil Science, NCSU–Sanitation Branch, North Carolina Division of Health Services.
Casciotti, K. L., Sigman, D. M., Galanter Hastings, M., Böhlke, J. K., & Hilkert, A. (2002). Measurement of the oxygen isotopic composition of nitrate in seawater and freshwater using the denitrifier method. Analytical Chemistry, 74(19), 4905–4912.
Cole, M. L., Kroeger, K. D., Mcclelland, J. W., & Valiela, I. (2006). Effects of watershed land use on nitrogen concentrations and δ15nitrogen in groundwater. Biogeochemistry, 77, 199–215.
Conley, D. J., Paerl, H. W., Howarth, R. W., Boesch, D. F., Seitzinger, S. P., Havens, K. E., Lancelot, C., & Likens, G. E. (2009). Controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus. Science, 323, 1014–1015.
Corbett, D. R., Dillon, K., Burnett, W., & Schaefer, G. (2002). The spatial variability of nitrogen and phosphorus concentration in a sand aquifer influenced by onsite sewage treatment and disposal systems: a case study on St. George Island, Florida. Environmental Pollution, 117(2), 337–345.
Core Team, R. (2013). A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation.
Desimone, L. A., & Howes, B. L. (1996). Denitrification and nitrogen transport in a coastal aquifer receiving wastewater discharge. Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 1152–1162.
Diaz, R. J. (2002). Hypoxia and anoxia as global phenomena. In: Thurston, R. V. (Ed.), Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Fish Physiology, Toxicology, and Water Quality. 22–26 Jan 2001. La Paz, Baja, Mexico. Ecosystems Research Division: Athens, GA.
Dugdale, R. C., & Goering, J. J. (1967). Uptake of new and regenerated forms of nitrogen in primary productivity. Limnology and Oceanography, 12, 196–206.
EEG. (2012). Water quality restoration for meeting house branch: plan and implementation. Pamlico-Tar River Foundation. Ecosystem Enhancement Grant. Submitted 30 Oct 2012.
Ferrell, G. M., & Grimes, B. H. (2014). Effects of centralized and onsite wastewater treatment on the occurrence of traditional and emerging contaminants in streams. Journal of Environmental Health, 76(6), 18–27.
Garcia, S. N., Clubbs, R. L., Stanley, J. K., Scheffe, B., Yelderman, J. C., Jr., & Brooks, B. W. (2013). Comparative analysis of effluent water quality from a municipal treatment plant and two on-site wastewater treatment systems. Chemosphere, 92, 38–44.
Geza, M., & McCray, J. E. (2010). Model evaluation of potential impacts of on-site wastewater systems on phosphorus in Turkey Creek watershed. Journal of Environmental Quality, 39, 1636–1646.
Glibert, P. M. (1988). Primary productivity and pelagic nitrogen cycling. In T. H. Blackburn & J. Sorensen (Eds.), Nitrogen cycling in coastal marine environments (pp. 3–31). New York: Wiley.
Granger, J., & Sigman, D. M. (2009). Removal of nitrite with sulfamic acid for nitrate N and O isotope analysis with the denitrifier method. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 23(23), 3753–3762.
Hardison, E. C., O’Driscoll, M. A., DeLoatch, J. P., Howard, R. J., & Brinson, M. M. (2009). Urban land use, channel incision, and water table decline along coastal plain streams, North Carolina. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 45(4), 1032–1046.
Harlin, M. M. (1993). Changes in major plant groups following nutrient enrichment. In A. J. McComb (Ed.), Eutrophic shallow estuaries and lagoons (pp. 173–187). Boca Raton: CRC Press, Inc.
Harman, J., Robertson, W. D., Cherry, J. A., & Zanini, L. (1996). Impacts on a sand aquifer from an old septic system: nitrate and phosphate. Groundwater, 34(6), 1105–1114.
Heath, R. C. (1983). Basic ground-water hydrology. US Geological Survey, Water Supply Paper 2220.
Heathwaite, L., Sharpley, A., & Gburek, W. (2000). A conceptual approach for integrating phosphorus and nitrogen management at watershed scales. Journal of Environmental Quality, 29, 158–166.
Hecky, R. E., & Kilham, P. (1988). Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in freshwater and marine environments: a review of recent evidence on the effects of enrichment. Limnology and Oceanography, 33, 796–822.
Howarth, R., & Marino, R. (2006). Nitrogen as the limiting nutrient for eutrophication in coastal and marine ecosystems: evolving views over three decades. Limnology and Oceanography, 51, 364–376.
Howarth, R., Boyer, E., Pabich, W., & Galloway, J. (2002). Nitrogen use in the United States from 1961–2000 and potential future trends. Ambio, 31, 88–96.
Humphrey, C. P., O’Driscoll, M. A., & Zarate, M. A. (2010). Controls on groundwater nitrogen contributions from on-site wastewater systems in coastal North Carolina. Water Science and Technology, 62(6), 1448–1455.
Humphrey, C. P., O’Driscoll, M. A., & Armstrong, M. C. (2012). Onsite wastewater system nitrogen loading to groundwater in the Newport River watershed, North Carolina. Environment and Natural Resources Research, 2(4), 70–79.
Humphrey, C. P., O’Driscoll, M. A., Deal, N., Lindbo, D., Zarate-Bermudez, M. A., & Thieme, S. (2013). On-site wastewater system nitrogen contributions to groundwater in coastal North Carolina. Journal of Environmental Health, 76(5), 16–22.
Iverson, G. (2013). A comparison of watershed nitrogen loading and watershed nitrogen exports from on-site wastewater treatment systems and centralized sewer systems in the North Carolina Coastal Plain. M.S. Thesis, East Carolina Univ., Greenville, NC.
Jetten, M. S. M., van Niftrik, L., Strous, M., Kartal, B., Keltjens, J. T., & Op den Camp, H. J. M. (2009). Biochemistry and molecular biology of anammox bacteria. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 44(2–3), 65–84.
Jha, M. K., Wolter, C. F., Schilling, K. E., & Gassman, P. W. (2010). Assessment of total maximum daily load implementation strategies for nitrate impairment of the Raccoon River, Iowa. Journal of Environmental Quality, 39, 1317–1327.
Jin, Z., Chen, Y., Wang, F., & Ogura, N. (2004). Detection of nitrate sources in urban groundwater by isotopic and chemical indicators, Hangzhou City, China. Environmental Geology, 45, 1017–1024.
Kendall, C., & McDonnell, J. J. (1998). Isotope tracers in catchment hydrology. Elsevier Science B.V.
Kroeger, K. D., Cole, M. L., York, J. K., & Valiela, I. (2006). Nitrogen loads to estuaries from wastewater plumes: modeling and isotopic approaches. Groundwater, 44, 188–200.
Mallin, M. A., Paerl, H. W., Rudek, J., & Bates, P. W. (1993). Regulation of estuarine primary production by watershed rainfall and river flow. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 98, 199–203.
Mallin, M. A., McIver, M. R., Wells, H. A., Parsons, D. C., & Johnson, V. L. (2005). Reversal of eutrophication following sewage treatment upgrades in the New River estuary, North Carolina. Estuaries, 28(5), 750–760.
Mason, C. F. (2002). Biology of freshwater pollution (4th ed.). England: Pearson Education Limited.
Meeroff, D. E., Bloetscher, F., Bocca, T., & Morin, F. (2008). Evaluation of water quality impacts of on-site treatment and disposal systems on urban coastal waters. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 192, 11–24.
Meile, C., Porubsky, W. P., Walker, R. L., & Payne, K. (2010). Natural attenuation of nitrogen loading from septic effluents: spatial and environmental controls. Water Research, 44, 1399–1408.
NCDENR. (2005). Nonpoint source pollution reduction report. 2005 Annual NPS Report to U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. North Carolina Department of Environment and Natural Resources, Division of Water Quality, October 2004–September 2005. Available at: http://test.enr.state.nc.us/stormwater/pdfs/2005%20Annual%20319%20Report%20-%20Final.pdf/.
O’Driscoll, M., Humphrey, C., Deal, N., Lindbo, D., & Zarate-Bermudez, M. (2014). Meteorological influences on nitrogen dynamics of a coastal onsite wastewater treatment system. Journal of Environmental Quality. doi:10.2134/jeq2014.05.0227.
Oakley, S. M., Gold, A. J., & Oczkowski, A. J. (2010). Nitrogen control through decentralized wastewater treatment performance and alternative management strategies. Ecological Engineering, 36, 1520–1531.
Oliver, C. W., Radcliffe, D. E., Risse, L. M., Habteselassie, M., Mukundan, R., Jeong, J., & Hoghooghi, N. (2014). Quantifying the contribution of on-site wastewater treatment systems to stream discharge using the SWAT model. Journal of Environmental Quality, 43, 539–548.
Paerl, H. W. (2009). Controlling eutrophication along the freshwater-marine continuum: dual nutrient (N and P) reductions are essential. Estuaries and Coasts, 32, 593–601.
Paerl, H. W., Crocker, K. M., & Prufert, L. E. (1987). Limitation of N2 fixtation in coastal marine waters: relative importance of molybdenum, iron, phosphorus and organic matter availability. Limnology and Oceanography, 32, 525–536.
Philips, J. D. (1989). An evaluation of the factors determining the effectiveness of water quality buffer zones. Journal of Hydrology, 107, 133–145.
Pradhan, S. S., Hoover, M. T., Austin, R. E., & Devine, H. A. (2007). Potential nitrogen contributions from on-site wastewater treatment systems to North Carolina’s river basins and sub-basins. Raleigh: North Carolina Agricultural Research Service Technical Bulletin 324.
Reay, W. G. (2004). Septic tank impacts on groundwater quality and nearshore sediment nutrient flux. Groundwater, 42(7), 1079–1089.
Robertson, W. D., & Cherry, J. A. (1992). Hydrogeology of an unconfined sand aquifer and its effect on the behavior of nitrogen from a large-flux septic system. Applied Hydrogeology 0, 32–44.
Robertson, W. D., & Cherry, J. A. (1995). In situ denitrification of septic system nitrate using reactive porous media barriers: field trials. Groundwater, 33(1), 99–111.
Robertson, W. D., Cherry, J. A., & Sudicky, E. A. (1991). Ground-water contamination from two small septic systems on sand aquifers. Groundwater, 29(1), 82–92.
Schipper, L. A., Cameron, S. C., & Warneke, S. (2010). Nitrate removal from three different effluents using large-scale denitrification beds. Ecological Engineering, 36, 1552–1557.
Sigman, D. M., Casciotti, K. L., Andreani, M., Barford, C., Galanter, M., & Böhlke, J. K. (2001). A bacterial method for the nitrogen isotopic analysis of nitrate in seawater and freshwater. Analytical Chemistry, 73(17), 4145–4153.
Silva, S. R., Ging, P. B., Lee, R. W., Ebbert, J. C., Tesoriero, A. J., & Inkpen, E. L. (2002). Forensic applications of nitrogen and oxygen isotopes of nitrate in an urban environment. Environmental Forensics, 3, 125–130.
Stow, C. A., Borsuk, M. E., & Stanley, D. W. (2001). Long-term changes in watershed nutrient inputs and riverine exports in the Neuse River, North Carolina. Water Research, 35, 1489–1499.
National Cooperative Soil Survey. (1971). Table 2—evolution of permeability and saturated hydraulic conductivity. In: USDA. (2014). Saturated hydraulic conductivity: water movement concepts and class history. Soil Survey Technical Note 6. Available at: http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/ref/?cid=nrcs142p2_053573/.
USDA. (1974). Pitt County soil survey. United States Department of Agriculture, Soil Conservation Service. Available at: http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_MANUSCRIPTS/north_carolina/pittNC1974/pittNC1974.pdf/ Cited 22 Jul 2014.
Valiela, I., Collins, G., Kremer, J., Lajtha, K., Geist, M., Seely, B., Brawley, J., & Sham, C. H. (1997). Nitrogen loading from coastal watersheds to receiving estuaries: new method and application. Ecological Applications, 7(2), 358–380.
Vellidis, G., Lowrance, R., & Gay, P. (2003). Nutrient transport in a restored riparian wetland. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 711–726.
Vitousek, P. M., Aber, J. D., Howarth, R. W., Likens, G. E., Matson, P. A., Schindler, D. W., Schlesinger, W. H., & Tilman, D. G. (1997). Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: sources and consequences. Ecological Applications, 7(3), 737–750.
Wang, L., Ye, M., Rios, J. F., Fernandes, R., Lee, P. Z., & Hicks, R. W. (2013). Estimation of nitrate load from septic systems to surface water bodies using an ArcGIS-based software. Environmental Earth Sciences, 70(4), 1911–1926.
WestCo. (2008). SmartChem 200 Method 231N-0406C (Rev: July 2008). SM 4500-C1-E. WestCo Scientific Instruments, Inc.
WHO. (1999). Toxic cyanobacteria in water: a guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management. London: World Health Organization. E & EN Spon.
Wilhelm, S. R., Schiff, S. L., & Robertson, W. D. (1996). Biogeochemical evolution of domestic waste water in septic systems: 2. Application of conceptual model in sandy aquifers. Groundwater, 34(5), 853–864.
Withers, P. J. A., Jordan, P., May, L., Jarvie, H. P., & Deal, N. (2014). Do septic tank systems pose a hidden threat to water quality? Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 12, 123–130.
WVDEP. (2014). Discharge measurements. West Virginia Department of Environmental Protection. Available at: http://www.dep.wv.gov/WWE/getinvolved/sos/Pages/SOPflow.aspx/ Cited 23 Aug 2014.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the North Carolina Department of Environment and Natural Resources Water Quality 319 Non-Point Source Pollution Program grant for providing funding necessary to complete this research (Grant 3632). The following are thanked for providing logistical and material support during the project: Environmental Research Laboratory and field technicians at East Carolina University, Colleen Rochelle, Laura McKenna, Jim Watson, John Woods, Mary Hannah Postma, AJ Finley, Katie Supler Del Rosario, Jonathan Harris, Matthew Smith, and Sarah Hardison.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iverson, G., O’Driscoll, M.A., Humphrey, C.P. et al. Wastewater Nitrogen Contributions to Coastal Plain Watersheds, NC, USA. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 325 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2574-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2574-4