Abstract
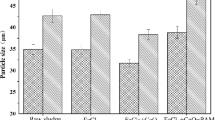
The urban sewage-dewatered sludge (UDSS) containing cationic polyacrylamide is difficult to dewater. FeCl3 was used as conditioner to adjust the UDSS. To investigate the effect and principle, the physicochemical properties of UDSS were evaluated in terms of dewatering equipment, micro electrophoresis, Malvern laser particle size analyzer, nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer, and scanning electron microscopy. Results showed that the network structure of UDSS produced by CPAM still had high negative charge, which locked much water in the flocs and resulted in the poor dewaterability of UDSS. When Fe3+ was added into the UDSS, the inner structure of sludge was destroyed by the charge neutralism and releasing more water. At the same time, because the function of precipitate produced by the hydrolytic action, the inner structure of the sludge was solidified; therefore, the compressibility of UDSS decreased. Finally, the dewaterability of UDSS was improved and the moisture content of filter cakes can be decreased to 55%.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CPAM:
-
cationic polyacrylamide
- CST:
-
capillary suction time
- EPS:
-
extracellular polymeric substances
- LB-EPS:
-
loosely bound EPS
- MC:
-
moisture contents
- PAM:
-
Polyacrylamide
- PN:
-
Protein
- PS:
-
Polysaccharides
- SRF:
-
specific resistance of sludge
- SEM:
-
scanning electron microscopy
- TB-EPS:
-
tightly bound EPS
- USS:
-
urban sewage sludge
- UDSS:
-
urban sewage-dewatered sludge
References
Carrere, H., Dumas, C., Battimelli, A., Batstone, D. J., Delgenes, J. P., Steyer, J. P., & Ferrer, I. (2010). Pretreatment methods to improve sludge anaerobic degradability: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 183, 1–15.
He, C., Chen, C. L., Xu, Z. R., & Wang, J. Y. (2014). Highly efficient secondary dewatering of dewatered sewage sludge using low boiling point solvents. Environmental Technology, 35, 95–103.
Lee, D., & He, P. (2004). Sludge mangement and floc structure. resource & environment, 26–30.
Li, H., Wen, Y., Cao, A., Huang, J., Zhou, Q., & Somasundaran, P. (2012). The influence of additives (Ca2+, Al3+, and Fe3+) on the interaction energy and loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of activated sludge and their flocculation mechanisms. Bioresource Technology, 114, 188–194.
Li, Y. L., Liu, J. W., Chen, J. Y., Shi, Y. F., Mao, W., Liu, H., Li, Y., He, S., & Yang, J. K. (2013). Reuse of dewatered sewage sludge conditioned with skeleton builders as landfill cover material. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 11, 233–240.
Lv, S., Sun, T., Zhou, Q., Liu, J., & Ding, H. (2014). Synthesis of starch-g-p(DMDAAC) using HRP initiation and the correlation of its structure and sludge dewaterability. Carbohydrate Polymers, 103, 285–293.
Niu, M. Q., Zhang, W. J., Wang, D. S., Chen, Y., & Chen, R. L. (2013). Correlation of physicochemical properties and sludge dewaterability under chemical conditioning using inorganic coagulants. Bioresource Technology, 144, 337–343.
Qi, Y., Thapa, K. B., & Hoadley, A. F. A. (2011). Application of filtration aids for improving sludge dewatering properties - a review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 171, 373–384.
Saveyn, H., Pauwels, G., Timmerman, R., & Van der Meeren, P. (2005). Effect of polyelectrolyte conditioning on the enhanced dewatering of activated sludge by application of an electric field during the expression phase. Water Research, 39, 3012–3020.
Vaxelaire, J., & Cezac, P. (2004). Moisture distribution in activated sludges: A review. Water Research, 38, 2214–2229.
Wang, Y., & Zhang, S. (2007). Advances and prospects of dry ing process of surplus sludge. POLLUTION CONTROL TECHNOLOGY, 51-53.
Xia, C., Yue, Q., Song, F., Liu, X., Gao, B., Zhang, T., Li, Q., & Wang, Y. (2014). A study on the deep dewatering of urban dewatered-sewage sludge by aluminum chloride. Desalination and Water Treatment, 1-8.
Zhang, J. Z., Yue, Q. Y., Xia, C., Yang, K. L., Zhao, P., Gao, B. Y., & Yu, H. (2017). The study of Na2SiO3 as conditioner used to deep dewater the urban sewage dewatered sludge by filter press. Separation and Purification Technology, 174, 331–337.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from Tai Shan Scholar Foundation (No.ts201511003), the National High Technology Research and Development Program (863 Program) of China (Grant No.412 2012AA063501).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Zhang Jingzhen and Xia Chao are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Xia, C., Yue, Q. et al. Application of FeCl3 to Adjust Urban Sewage-Dewatered Sludge (UDSS) Containing Cationic Polyacrylamide (CPAM) for Further Dewatering. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 196 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3377-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3377-6