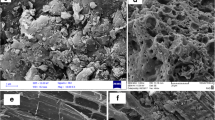
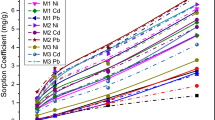
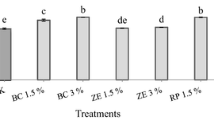
Abstract
Clayey soils have been used as liners at the base of waste deposits due to their geotechnical characteristics and capacity to adsorb metallic cations. However, a number of soils may not possess all required properties to ensure contaminant retention and therefore require additives. This study investigated whether the addition of commercial peat to a tropical residual soil (from the Ribeira Valley, Brazil) could improve its lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd) adsorption capacity for its use as a liner in mining waste disposal. Pure soil and 10 and 20% soil-peat mixtures were compared. The application of peat increased the organic matter (OM) content (from 9 g kg−1 in soil to 58 g kg−1 in the 20% soil-peat mixture) and the cationic exchange capacity (CEC) (from 41.4 mmolc dm−3 in soil to 143.1 mmolc dm−3 in the 20% soil-peat mixture). Batch equilibrium test results revealed that the maximum Pb adsorption capacity of 623.6 μg g−1 also increased (to 1089.1 and 1270.0 μg g−1 in the 10 and 20% soil-peat mixtures, respectively). The soil Cd adsorption capacity of 261.2 μg g−1 increased to 304.0 and 631.3 μg g−1, respectively, with increasing peat proportions. The results suggest that peat can improve soil liner performance in waste deposits. Soil-peat mixtures are alternatives for minimizing potentially toxic metal contamination with available and low-cost materials.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alleoni, L. R. F., Mello, J. W. V., & Rocha, W. S. D. (2016). Eletroquímica, adsorção e troca iônica no solo. In V. F. Melo & L. R. F. Alleoni (Eds.), Química e Mineralogia do Solo Parte II – Aplicações (pp. 70–126). Viçosa: Sociedade Brasileira de Ciência do Solo.
Alloway, B. J. (1995). Heavy metals in soils. London: Blackie Academic & Professional.
Almeida, A. F. (2015). Evaluation of clay materials from Corumbataí formation to use in compressed liners (CCL). MSc Dissertation: University of São Paulo. São Carlos. 162 p.
Alvarez, P. J. J., & Illman, W. A. (2005). Bioremediation and natural attenuation: process, fundamentals and mathematical models. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons.
Arab, P. B. (2011). Cu2+ transport in composite liners made with compacted soil (CCL) and geosynthetic clay liner (GCL). MSc Dissertation: University of São Paulo. São Carlos. 115p.
Araújo, H. A. S (2015). Estudo da adsorção de Pb, Zn e Cd por material inconsolidado transportado da região do Vale do Ribeira (SP). Monography: Universidade de São Paulo. São Carlos. 81p.
Araújo, W. A., & Sobrinho, N. M. B. (2000). Influência das propriedades físicas e químicas de solos intemperizados na adsorção de chumbo, cobre e zinco. Floresta & Ambiente, 7(1), 167–180.
Azevedo, I. C. (2017). Emprego de SIG na avaliação da alteração gerada por atividades de extração de areia e rochas carbonáticas na região do Vale do Ribeira (PR/SP). MSc Dissertation: University of São Paulo. São Carlos.
Azeez, J. O., Hassan, A. O., & Olowoboko, T. B. (2018). Differential sorption behavior of cadmium, lead, zinc, and copper in some tropical soils and their environmental implications. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 49(14), 1707–1718. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2018.1474908.
Bartczak, P., Norman, M., Klapiszewski, L., Karwanska, N., Kawalec, M., Baczynska, M., Wysokowski, M., Zdarta, J., Ciesielczyk, F., & Jesionowki, T. (2018). Removal of nickel(II) and lead(II) ions from aqueous solution using peat as a low-cost adsorbent: a kinect and equilibrium study. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 11(8), 1209–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.07.018.
Bosso, S. T., & Enzweiller, J. (2002). Evaluation of heavy metal removal from aqueous solution onto scolecite. Water Research, 36(19), 4795–4800. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00208-7.
Braz, A. M. S., Fernandes, A. R., Ferreira, J. R., & Alleoni, L. R. (2013). Distribution coefficients of potentially toxic elements in soils from the eastern Amazon. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(10), 7231–7242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1723-9.
Bulgariu, L., Bulgariu, D., & Macoveanu, M. (2011). Adsorptive performances of alkaline treated peat for heavy metal removal. Separation Science and Technology, 46(6), 1023–1033. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2010.536192.
Campos, B. G., Cruz, A. C. F., Buruaem, L. M., Rodrigues, A. P. C., Machado, W. T. V., & Abessa, D. M. S. (2016). Using a tiered approach based on ecotoxicological techniques to assess the ecological risks of contamination in a subtropical estuarine protected área. Science of Total Environment, 554, 564–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.124.
Cassiano, A. M. (2001). Estudo da contaminação por metais na Bacia do rio Ribeira de Iguape (SP/PR): Estratégias para a remediação da área de disposição de rejeitos da mina do Rocha. Phd thesis: University of São Paulo. São Carlos. 159p.
Colzato, M., Alleoni, L. R. F., & Kamogawa, M. Y. (2018). Cadmium sorption and extractability in tropical soils with variable charge. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 345–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6666-7.
Couillard, D. (1994). Review: the use of peat in wastewater treatment. Water Research, 28(6), 1261–1274. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(94)90291-7.
Cruz, A. C. F., Gusso-Choueri, P., Araujo, G. S., Campos, B. G., & Abessa, D. M. (2019). Levels of metals and toxicity in sediments from a Ramsar site influenced by former mining activities. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 171, 162–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.088.
Dias, N. M. P., Alleoni, L. R. F., Casagrande, J. C., & Camargo, O. A. (2001). Adsorção de Cádmio em dois latossolos ácricos e um nitossolo. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 25(2), 297–304. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832001000200006.
Egene, C. E., Poucke, R. V., Ok, Y. S., Meers, E., & Tack, F. M. G. (2018). Impact of organic amendments (biochar, compost and peat) on Cd and Zn mobility and solubility in contaminated soil of Campine region after three years. Science of Total Environment, 626, 195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.054.
Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária – EMBRAPA (2017). Teixeira, P. C.; Donagemma, G. K.; Fontana, A. & Teixeira, W. G. Manual de Métodos de Análise de Solo. 3. Ed. Agricultural Research Corporation (EMBRAPA): Brasília.
Eriksson, J. E. (1988). The effects of clay, organic matter and time on adsorption and plant uptake of cadmium added to the soil. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 40, 359–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00163740.
Fontes, M. P. F., & Gomes, P. C. (2003). Simultaneous competitive adsorption of heavy metals by the mineral matrix of tropical soils. Applied Geochemistry, 18, 795–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00188-9.
Fookes, P. G. (1997). Tropical residual soils: a geological society engineering group working party revised report. London: Geological Society.
Franchi, J. G. (2000). Aplicação de turfa na recuperação de solos degradados pela mineração de areia. MSc Dissertation: University of São Paulo. São Paulo. 103p.
Freeze, A. R., & Cherry, J. A. (1979). Groundwater. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall Inc..
Gabas, S. G., Sarkis, J. E. S., & Boscov, M. E. G. (2016). Heavy metal diffusion and retention in a mineral barrier of compacted lateritic soil. Revista Brasileira de Geologia de Engenharia e Ambiental (RBGEA), 4, 9–22.
Giles, C. H., Smith, D., & Huitson, A. (1974). General treatment and classification of the solute adsorption isotherm – I. Theoretical. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 47(3), 755–765.
Góes, M. A.; Luz, A. B. & Possa, M. V. (2010). Amostragem. In: Luz, A. B.; Sampaio, J. A.; França, S. C. A. Tratamento de minérios. Rio de Janeiro: CETEM/MCT.
Guimarães, V. (2007). Resíduos de mineração e metalurgia: efeitos poluidores em sedimentos e em espécie biomonitora rio Ribeira de Iguape – SP. Phd thesis: University of São Paulo. São Paulo. 160 p.
Hakanson, L. (1979). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001.
Ho, Y. S., & Mckay, G. (2004). Sorption of copper (II) from aqueous solution by peat. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 158, 77–97. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000044830.63767.a3.
Ho, Y. S., Porter, J. F., & Mckay, G. (2002). Equilibrium isotherm studies for the sorption of divalent metal ions onto peat: copper, nickel and lead single componentes systems. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 141, 1–33. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021304828010.
Holm, P. E., Rootzén, H., Borggaard, O. K., Moberg, J. P., & Christensen, T. H. (2003). Correlation of cadmium distribution coefficients to soil characteristics. Journal Environmental Quality, 32(1), 138–145. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2003.1380.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2011). Trace elements in soils and plants. 4 ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Kasemodel, M. C., Lima, J. Z., Sakamoto, I. K., Varesche, M. B. A., & Rodrigues, V. G. S. (2016). Soil contaminantion assessment for Pb, Zn and Cd in a slag disposal área using the integration of geochemical and microbiological data. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment., 188(12), 698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5708-2.
Kasemodel, M. C. (2017). Avaliação Integrada da Contaminação por Metais Potencialmente tóxicos em Área de Disposição de Resíduo de Mineração de Chumbo – Adrianópolis (PR). Phd thesis: University of São Paulo. São Carlos. 225p.
Kasemodel, M. C., Sakamoto, I. K., Varesche, M. B. A., & Rodrigues, V. G. S. (2019a). Potentially toxic metal contamination and microbial community analysis in an abandoned Pb and Zn mining waste deposit. Science of Total Environment, 675, 367–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.223.
Kasemodel, M. C., Papa, T. B. R., Sígolo, J. B., & Rodrigues, V. G. S. (2019b). Assessment of the mobility, bioaccessibility, and ecological risk of Pb and Zn on a dirt road located in a former mining área – Ribeira Valley – Brazil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(101) 15p). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7238-1.
Kumpiene, J., Lagerkvist, A., & Maurice, C. (2007). Stabilization of Pb- and Cu-contaminated soil using coal fly ash and peat. Environmental Pollution, 145, 365–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.01.037.
Lee, S., Lee, M., Chung, J. W., Park, J. H., Huh, K. Y., & Jun, G. (2013). Immobilization of lead from Pb-contaminated soil amended with peat moss. Journal of Chemistry, 2013, 6p. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/509520.
Lima, J. Z. (2017). Caracterização geológica-geotécnica e estudo da adsorção de Pb, Zn e Cd por turfa e compostos orgânicos. MSc Dissertation: University of São Paulo. São Carlos. 376p.
Lima, J. Z., Raimondi, I. M., Vaz, L. A. A., & Rodrigues, V. G. S. (2016). Caracterização Geológica-Geotécnica da Turfa de Mogi Guaçu (SP). In In Anais do 48° Congresso Brasileiro de Geologia. Porto: Alegre (RS).
Lopes, C. M. (2009). Adsorção individual e competitiva de Cd, Cu, Ni e Zn em solos em função da variação de pH. MSc Dissertation: University of São Paulo. Piracicaba. 100p.
Lubbad, S. H., & Al-Batta, S. N. (2019). Ultrafast remediation of lead-contaminated water applying sphagnum peat moss by dispersive solid-phase extraction. Internatonal Journal of Environmental Studies. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207233.2019.1674582.
Marques, J. P. (2014). Caracterização geológica-geotécnica de solo residual de Eldorado Paulista (SP) para uso como barreira selante (78p). Monography: University of São Paulo. São Carlos.
Marques, J. P. & Rodrigues, V. G. S. (2017). Solo Residual do Vale do Ribeira como Possível Material na Construção de Barreira Selante. In Anais do XVI Congresso Brasileiro de Geoquímica. Búzios (RJ).
Marques, J. P.; Raimondi, I. M.; Lima, J. Z. & Rodrigues, V. G. S. (2019c). Caracsterização de uma mistura de solo residual com turfa visando seu emprego em barreiras selantes. In Anais do IX Congresso Brasileiro de Geotecnia Ambiental (REGEO 2019). São Carlos.
Marques, J. P., Silva, E. A. F., Patinha, C., Kasemodel, M. C., & Rodrigues, V. G. S. (2019b). Adsorption of lead (Pb) in weathered tropical soil (Ribeira Valley region – Brazil). Earth Sciences Research Journal., V23(4), 385–395.
Marques, J. P.; Rodrigues, V. G. S.; Vilar, O. M. & Esquivel, E. R. (2019a). The potential use of residual soil from Ribeira Valley (Brazil) in mitigating metal contamination: a geotechnical characterization. In IAEG/AEG Annual Meeting Proceedings (XIII IAEG Congress). 2, 27-31. San Francisco. 10.1007/978-3-319-93127-2_5.
Mcbride, M. B. (1989). Reactions controlling heavy metal solubility in soils. Advances in Soil Science, 10, 56. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-8847-0_1.
Mohamed, A. O., Paleologos, E. K., Rodrigues, V. G. S., & Singh, D. N. (2018). Fundamentals of geoenvironmental engineering: understanding soil, water, and pollutant interaction and transport. Butterworth-Heineman: Elsevier.
Musso, M. & Pejon, O. J. (2008). Materiais para barreiras de fundo de aterros sanitários do interior do estado de São Paulo. In Anais do 12° Congresso Brasileiro De Geologia De Engenharia E Ambiental. ABGE, 1, 1-13. Porto de Galinhas.
Naymushina, O. & Gaskova, O. (2019). Adsorption of Cu(II) from aqueous solution using raw peat: preliminar results. E3S Web of Conferences, 98, 06010 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20199806010.
Nawab, J., Khan, N., Ahmed, R., Khan, S., Ghani, J., Rahman, Z., Khan, F., Wang, X., Muhammad, J., & Sher, H. (2019). Influence of different organic geo-sorbents on Spinacia oleracea grown in chromite mine-degraded soil: a greenhouse study. Journal of Soils and Sediments., 19, 2417–2432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02260-3.
Oliveira, L. F. C., Lemke-De-Castro, M. L., Rodrigues, C., & Borges, J. D. (2010). Isotermas de sorção de metais pesados em solos do cerrado de Goiás. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental, 14(7), 776–782. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-43662010000700014.
Petroni, S. L. G., Pires, M. A. F., & Munita, C. S. (2000). Adsorção de zinco e cádmio em colunas de turfa. Química Nova, 23(4), 477–481. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-40422000000400009.
Pierangeli, M. A., Guilherme, P., Curi, L. R. G., Silva, N., Oliveira, M. L. N., & Lima, J. M. (2001). Efeito do pH na adsorção-dessorção de chumbo em latossolos brasileiros. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 25(2), 269–277. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832001000200003.
Raij, B. V., Andrade, J. C., Cantarella, H., & Quaggio, J. A. (2001). Análise Química para Avaliação da Fertilidade de Solos Tropicais. Instituto Agronômico de Campinas (IAC): Campinas.
Raimondi, I. M. (2014). Estudo e caracterização geológica e geotécnica de rejeitos de mineração – Adrianópolis (PR) (193 p). MSc Dissertation: University of São Paulo. São Carlos.
Raimondi, I. M.; Lima, J. Z. & Rodrigues, V. G. S. (2019). The characterization of tropical peats for potentially toxic metals adsorption purposes in an abandoned mine area. In IAEG/AEG Annual Meeting Proceedings (IAEG XIII Congress). 2, 129-134. San Francisco. 10.1007/978-3-319-93127-2_19.
Rasmussen, G., Fremmersvik, G., & Olsen, R. A. (2002). Treatment of creosote-contaminated groundwater in a peat/sand permeable barrier – a column study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B93, 285–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(02)00056-0.
Rocha, W. S. D., Alleoni, L. R. F., Regitano, J. B., Casagrande, J. C., & Tornisiello, V. L. (2000). Influência do pH na sorção de Imazaquin em um latossolo vermelho acriférrico. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 24(3), 649–655. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832000000300017.
Rodriguez, J. R. (2013). Estudo da viabilidade geológica, geotécnica e geoquímica de solos argilosos como barreiras selantes – Vale do Ribeira (SP). MSc Dissertation: University of São Paulo. São Carlos.
Rúbio, C. L., Araujo, C. R., Buosi, D., Rubio, G. B. G., Alonzo, H. G. A., Ilanes, J. F., Ambrosecchia, M. C., Gianoto, N., & Bueno, P. C. (2008). Avaliação de Risco à Saúde humana por exposição aos resíduos da Plumbum no município de Adrinópolis – PR. In Curitiba: Secretaria de Estado da Saúde do Paraná (SESA). Governo do: Paraná.
Sampaio, L. F. (2011). Avaliação da liberação e toxicidade de metais em escória de fundição: O caso de Plumbum S/A de Adrianópolis (PR). Monografia de Graduação. Escola de Engenharia de São Carlos, Universidade de São Paulo (USP).
Santos, P. S. (1989). Ciência e Tecnologia das Argilas. São Paulo: Edgar Blücher.
Silva, B. De C. M. (2013). Estudo da adsorção de chumbo (PB) por ensaios de equilíbrio em lote em materiais inconsolidados: município de Eldorado Paulista (Vale do Ribeira – SP). MSc Dissertation. University of São Paulo. São Carlos. 210p.
Soares, M. R. & Casagrande, J. C. (2000). Adsorção E Modelos. In Ribeiro, M. R.; Nascimento, C. W. A.; Filho, M. R. R. & Cantalice, J. R. B. Tópicos em ciência do solo. Volume 1. Viçosa: Sociedade Brasileira de Ciência do Solo.
Soares, M. R. (2004). Coeficiente de distribuição (KD) de metais pesados em solos do estado de São Paulo. Phd Thesis. University of São Paulo. Piracicaba. 202p.
Soldatini, G. F., Rifaldi, R., & Levi-Minzi, R. (1976). Pb adsorption by soils. I. Adsorption as measured by the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution., 6, 111–118.
Sposito, G. (1984). The surface chemistry of soils. Oxford: University Press.
Taha, M. R., & Kabir, M. H. (2005). Tropical residual soil as compacted soil liners. Environmental Geology, 47, 375–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-004-1160-7.
Tanaka, K. J. (2018). Caracterização e Avaliação da Capacidade de retenção de cádmio (Cd) em turfa ativada proveniente da Bacia Hidrográfica do Rio Mogi-Guaçu (94p). Monography: University of São Paulo. São Carlos.
United States Environmental Protection Agency – EPA. (1992). Roy, W. R.; Krapac, I. G.; Chou, S. F. J. & griffin, R. A. Batch type procedures for estimating soil adsorption of chemicals. Technical resource document. EPA, Cincinnati, EUA.
World Energy Council (2013). Peat. In: World Energy Council. World energy resources. London: WEC. 468p.
Funding
The authors thank the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) for the provided Master’s degree grants (2016/17894-2 and 2015/02529-4) and research grant (2014/07180-7) and the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) for the offered research productivity grant (305096/2015-0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pelinsom Marques, J., Silvestre Rodrigues, V.G., Monici Raimondi, I. et al. Increase in Pb and Cd Adsorption by the Application of Peat in a Tropical Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 136 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04507-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04507-z