Abstract
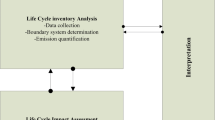
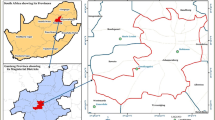
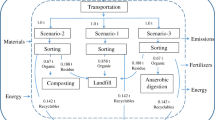
The aim of this paper is to apply life cycle assessment in the waste management sector, in order to compare the environmental performance of different waste management methods. The methods that are studied are: landfilling, aerobic and anaerobic biological treatment, incineration and recycling, focusing on mass and energy balances and the environmental performance of each applied scenario. The Peloponnese Region in Greece was selected as a case for the application of this methodology and more specifically its largest municipalities, where a significant amount of waste is presented. The conducted LCA study proves the necessity of the adoption of an integrated waste management system and indicates its principal objectives by measuring environmental impacts. Thermal scenario contributes significant to the mitigation on the Greenhouse Gases. On the other hand, separation at source and recycling practices provides significant benefits to the abiotic depletion impact.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AU:
-
Administrative unit
- LCA:
-
Life cycle assessment
- LCT:
-
Life cycle thinking
- MBT:
-
Mechanical biological treatment
- MRF:
-
Material recycling facility
- MSW:
-
Municipal solid waste
- NPV:
-
Net present value
- RDF:
-
Refuse-derived fuel
- SETAC:
-
Society for Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry
- WtE:
-
Waste to energy
- WTS:
-
Waste transfer station
References
Abeliotis K (2011) Life cycle assessment in municipal solid waste management, integrated waste management, vol. 1. In: Sunil Kumar (ed), ISBN: 978-953-307-469-6, InTech. http://www.intechopen.com/articles/show/title/life-cycle-assessment-in-municipal-solid-waste-management. Accessed 05 April 2012
Abeliotis K, Kalogeropoulos A, Lasaridi K (2012) Life cycle assessment of the MBT plant in Ano Liossia, Athens, Greece. Waste Manag 32:213–219
Assamoi B, Lawryshyn Y (2011) The environmental comparison of landfilling vs. incineration of MSW accounting for waste diversion. Waste Management 32(5):1019–1030
Aye L, Widjaya E (2006) Environmental and economic analyses of waste disposal options for traditional markets in Indonesia. Waste Manag 26(10):1180–1191
den Boer J, Boer den E, Jager J (2007) LCA-IWM: a decision support tool for sustainability assessment of waste management systems. Waste Manag 27:1032–1045
Borghi D, Gallo A, Borghi M (2009) A survey of life cycle approaches in waste management. Int J Life Cycle Assess 14:597–610
Buttol P, Masoni P, Bonoli A, Goldoni S, Belladonna V, Cavazzuti C (2007) LCA of integrated MSW management systems: case study of the Bologna District. Waste Manag 27(8):1059–1070
Chen D, Christensen TH (2010) Life-cycle assessment (EASEWASTE) of two municipal solid waste incineration technologies in China. Waste Manag Res 28(6):508–519
Cleary J (2009) Life cycle assessments of municipal solid waste management systems: a comparative analysis of selected peer-reviewed literature, review article. Environ Int 35:1256–1266
Consonni S, Giugliano M, Grosso M (2005) Alternative strategies for energy recovery from municipal solid waste. Part A: mass and energy balances. Waste Manag 25(2):123–135
De Feo G, Malvano C (2009) The use of LCA in selecting the best MSW management system. Waste Manag 29:1901–1915
Di Maria F, Fantozzi F (2004) Life cycle assessment of waste to energy micropyrolysis system: case study for an Italian town. Int J of Energ Res 28:449–461
Di Maria F, Sordi A, Micale C (2012) Energy production from mechanical biological treatment and composting plants exploiting solid anaerobic digestion batch: an Italian case study. Energy Convers Manag 56:112–120
Emery A, Davies A, Griffiths A, Williams K (2007) Environmental and economic modeling: a case study of municipal solid waste management scenarios in Wales. Resour Conserv Recycl 49:244–263
Eriksson O, Carlsson Reich M, Frostell B, Björklund A, Assefa G, Sundqvist J-O, Granath J, Baky A, Thyselius L (2005) Municipal solid waste management from a systems perspective. J Clean Prod 13(3):241–252
European Parliament and Council (1999) Directive on the landfill of waste (1999/31/EC)
European Parliament and Council (2000) Directive on the incineration of waste (2000/76/EC)
European Parliament and Council (2004) Directive on packaging and packaging waste (2004/12/EC)
Finnveden G, Johansson J, Lind P, Moberg A (2005) Life cycle assessment of energy from solid waste—part 1: general methodology and results. J Clean Prod 13:213–229
Fricke K, Santen H, Wallman R (2002) Comparison of selected aerobic and anaerobic procedures for MSW treatment. Waste Manag 25:799–810
Fricke K, Santen H, Wallmann R (2005) Comparison of selected aerobic and anaerobic procedures for MSW treatment. Waste Manag 25:799–810
Fruergaard T, Astrup T (2011) Optimal utilization of waste-to-energy in an LCA perspective. Waste Manag 31:572–582
Gemis® 4.4.2 (2007). Global emission model of integrated systems, Öko-Institut (Institute for Applied Ecology)
Guinée JB, Gorrée M, Heijungs R, Huppes G, Kleijn R, De Koning A, Van Oers L, Wegener Sleeswijk A, Suh S, Udo de Haes HA, De Bruijn H, Huijbregts MAJ, Lindeijer E, Roorda AAH, Van der Ven BL, Weidema BP (2001) Handbook on life cycle assessment; operational guide to the ISO Standards. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Hellenic Law 3851/2010 (FEK 85 Α’/04.06.2010). Accelerating the development of renewable energy sources to deal with climate change and other regulations addressing issues under the authority of the Ministry of Environment, Energy and Climate Change
Hellenic Law 3852/2010 (FEK 87 Α’/07.06.2010). New Architecture of Self-Government and Decentralized Government. The ‘KALLIKRATES’ Program
Hellweg S, Hofstetter TB, Hungerbuhler K (2001) Modeling waste incineration life cycle-inventory analysis in Switzerland. In: Environmental Modeling and Assessment 6. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands
JRC (2007) Environmental assessment of municipal waste management scenarios: part I—data collection and preliminary assessments for life cycle thinking pilot studies, European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Institute for Environment and Sustainability, ISBN: 978-92-79-07449-3, European Communities
Karagiannidis A, Moussiopoulos N (1997) Application of ELECTRE III for the integrated management of municipal solid wastes in the greater Athens area. Eur J Oper Res 97:439–449
Khoo H (2009) Life cycle impact assessment of various conversion technologies. Waste Manag 29:1892–1900
Kirkeby J-T, Birgisdottir H, Hansen T-L, Christensen T-H, Bhander G-S, Mauschild M (2006) Evaluation of environmental impacts from municipal solid waste management in the municipality of Aarhus, Denmark (EASEWASTE). Waste Manag Res 24:16–26
McDougall FR, White PR, Franke M, Hindle P (2001) Integrated solid waste management: a life cycle inventory, 2nd edn. Blackwell, New York. ISBN 0-632-05889-7
Mendes MR, Aramaki T, Hanaki K (2004) Comparison of the environmental impact of incineration and landfilling in Sao Paulo city as determined by LCA. Resour Conserv Recycl 41:47–63
Morf L, Brunner PH (1998) The MSW incinerator as a monitoring tool for waste management. Environ Sci Technol 32(12):1825–1831
Murphy JD, McKeogh E (2004) Technical, economic and environmental analysis of energy production from municipal solid waste. Renew Energy 29(7):1043–1057
Özeler D, Yetis U, Deminer GN (2006) Life cycle assessment of municipal solid waste management methods: Ankara case study. Environ Int 32(3):405–411
Pires A, Martinho G, Ni-Bin C (2011) Solid waste management in European countries: a review of systems analysis techniques. J Environ Manage 92:1033–1050
Rabl A, Spadaro J-V, Zoughaib A (2008) Environmental impacts and costs of solid waste: a comparison of landfill and incineration. Waste Manag Res 26:147–162
Regional Planning (2011) Peloponnese Regional Planning. http://www.perifereia-peloponnisou.gr/
Rimaitytė I, Denafas G, RačysDenafas V (2006) Implementation of life cycle assessment tools for evaluation of municipal waste management scenarios. Environ Res Eng Manag 2(36):68–76
Rodriguez-Iglesias J, Maranon E, Catrillon L, Riestra P, Sastre H (2003) Life cycle analysis of municipal solid waste management possibilities in Asturias, Spain. Waste Manag Res 21:535–548
Shmelev SE, Powell JR (2006) Ecological–economic modeling for strategic regional waste management systems. Ecol Econ 59(1):115–130
Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) (1996) Life cycle assessment and conceptually related programmes. SETAC-Europe Working Group, CRP report, Brussels, Belgium
Tsilemou K, Panagiotakopoulos D (2005) A statistical methodology for generating cost functions for solid waste treatment facilities, in: HELECO 05, Technical Chamber of Greece, 3–6 February 2005, Athens
Weinstein PE (2006) Waste-to-energy as a key component of integrated solid waste management for Santiago, Chile: A cost-benefit analysis, diploma thesis submitted to Earth Resources Engineering, Department of Earth and Environmental Engineering, Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science, Columbia University
Winkler J, Bilitewski B (2007) Comparative evaluation of life cycle assessment models for solid waste management. Waste Manag 27:1021–1031
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antonopoulos, IS., Karagiannidis, A., Tsatsarelis, T. et al. Applying waste management scenarios in the Peloponnese region in Greece: a critical analysis in the frame of life cycle assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 2499–2511 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1139-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1139-y