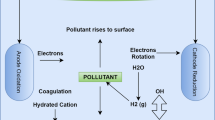
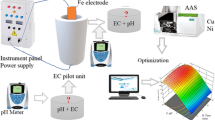
Abstract
In the present paper, the performance of electrocoagulation (EC) for the treatability of mixed metals (chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), lead (Pb), nickel (Ni), and zinc (Zn)) from metal plating industrial wastewater (EPW) has been investigated. The study mainly focused on the affecting parameters of EC process, such as electrode material, initial pH, distance between electrodes, electrode size, and applied voltage. The pH 8 is observed to be the best for metal removal. Fe–Fe electrode pair with 1-cm inter-electrode distance and electrode surface area of 40 cm2 at an applied voltage of 8 V is observed to more efficient in the metal removal. Experiments have shown that the maximum removal percentage of the metals like Cr, Ni, Zn, Cu, and Pb are reported to be 96.2, 96.4, 99.9, 98, and 99.5 %, respectively, at a reaction time of 30 min. Under optimum conditions, the energy consumption is observed to be 51.40 kWh/m3. The method is observed to be very effective in the removal of metals from electroplating effluent.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas HS, Abdulmajeed BA, Salman AB (2014) Electrochemical removal of cadmium from simulated wastewater using a smooth rotating cylinder electrode. Desalin Water Treat. doi:10.1080/19443994.2014.903520
Abdurrahman A, Orhan Taner C, Erhan D, Mehmet K (2013) A comparative study of electrocoagulation and electro-Fenton for treatment of wastewater from liquid organic fertilizer plant. Sep Purif Technol. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2013.03.036
Akbal SC (2011a) Copper, chromium and nickel removal from metal plating wastewater by electrocoagulation. Desalination. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2010.11.001
Akbal SC (2011b) Treatment of metal plating wastewater by electrocoagulation. Environ Prog Sustain Energy. doi:10.1002/ep.10546
Akbal SC (2013) Comparison of electrocoagulation and chemical coagulation for heavy metal removal. Chem Eng Technol. doi:10.1002/ceat.201000091
Anissa A, Fersi C, Ali MBS, Dhahbi M (2009) Treatment of textile wastewater by a hybrid electrocoagulation/nanofiltration process. J Hazard Mater. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.112
Arash D, Gholami M, Joneidi A, Mahmoodi NM (2011) Dye removal, energy consumption and operating cost of electrocoagulation of textile wastewater as a clean process. Clean Soil Air Water. doi:10.1002/clen.201000233
Arroyo MG, Perez-Herranz V, Montanes MT, Garcia-Anton J, Guinon JL (2009) Effect of pH and chloride concentration on the removal of hexavalent chromium in a batch electrocoagulation reactor. J Hazard Mater. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.089
Ashok KC, Sharma AK (2013) Removal of turbidity. COD and BOD from secondarily treated sewage water by electrolytic treatment. Appl Water Sci. doi:10.1007/s13201-012-0066-x
Ashraf EP, Nikazar M, Arami M (2011) Removal of Co (II) from aqueous solution by electrocoagulation process using aluminum electrodes. Desalination. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2011.05.070
Bazafshan E, Mahvim AH, Nasseri S, Mesdaghinia AR, Vaezi F, Nazmara SH (2006) Removal of cadmium from industrial effluents by electrocoagulation process using iron electrodes, Iran. J Environ Health Sci Eng 3:261–266
Bhagawan D, Poodari S, Kumar GR, Golla S, Anand CH, Banda KS, Himabindu V, Vidyavathi S (2014) Reactivation and recycling of spent carbon using solvent desorption followed by thermal treatment (TR). J Mater Cycles Waste Manag. doi:10.1007/s10163-014-0237-y
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) (2012) Environmental protection rules 2nd amendment. http://cpcb.nic.in/Water_Quality_Criteria.php
Cheng H (2006) Cu(II) removal from lithium bromide refrigerant by chemical precipitation and electrocoagulation. Sep Purif Technol. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2006.03.021
Chih W-LC, Kuo Y-M (2009) Removal of COD from laundry wastewater by electrocoagulation/electroflotation. J Hazard Mater. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.122
Denial R, Anjaneyui Y, Krupdam RJ (2007) Electrocoagulation: a cleaner method for treatment of cr(vi) from electroplating industrial effluents. Indian J Chem Technol 14:240–245
Dermentzis K, Christoforids A, Valsamidou E, Lazaridou A, Kokkinos N (2011a) Removal of hexavalent chromium from electroplating wastewater by electrocoagulation with iron electrodes. Glob Nest J 13:412–418
Dermentzis K, Christoforidis A, Valsamidou E (2011b) Removal of nickel, copper, zinc and chromium from synthetic and industrial wastewater by electrocoagulation. Int J Environ Sci. doi:10.6088/ijessi.00105020001
Fatiha PD, Lekhlif B, Bensaid J, Blais J-F, Belcadi S, El Kacemi K (2008) Decolourization of dye-containing effluent using mineral coagulants produced by electrocoagulation. J Hazard Mater. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.041
Ghosh D, Medhi CR, Solanki H (2008) Purkait MK Copper, chromium and nickel removal from metal plating wastewater by electrocoagulation. J Environ Prot Sci 2:25–35
Golder AK, Samanta AN, Ray S (2007a) Removal of trivalent chromium by electrocoagulation. Sep Purif Technol. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2006.06.010
Golder AK, Samanta AN, Ray S (2007b) Trivalent chromium removal by electrocoagulation and characterization of the process sludge. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. doi:10.1002/jctb.1700
Golder AK, Dhaneesh VS, Samanta AN, Subhabrata R (2009) Electrotreatment of industrial copper plating rinse effluent using mild steel and aluminum electrodes. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. doi:10.1002/jctb.2249
Golder AK, Samanta AN, Ray S (2011) Removal of chromium and organic pollutants from industrial chrome tanning effluents by electrocoagulation. Chem Eng Technol. doi:10.1002/ceat.201000236
Ichrak AH, Nafaa A, Lotfi M (2013) Treatment of petroleum refinery sulfidic spent caustic wastes by electrocoagulation. Sep Purif Technol. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2013.01.051
Ilona H, Wolfgang C (2008) Removal of Zn(II), Cu(II), Ni(II), Ag(I) and Cr(VI) present in aqueous solutions by aluminium electrocoagulation. J Hazard Mater. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.068
Kim K, Cui F, Yoon H, Kim M (2013) Treatment of copper wastewater using optimal current electrochemical–coagulation. Environ Technol. doi:10.1080/09593330.2012.696716
Kobya M, Demirbas E, Parlak NU, Yigit S (2010) Treatment of cadmium and nickel electroplating rinse water by electrocoagulation. Environ Technol. doi:10.1080/09593331003713693
Meunier N, Drogui P, Montane C, Hausler R, Mercier G, Blais JF (2006) Comparison between electrocoagulation and chemical precipitation for metals removal from acidic soil leachate. J Hazard Mater. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.02.050
Meyyappan MS, Chiya AB, Velan M (2012) Removal of copper, nickel, and zinc ions from electroplating rinse water. Clean Soil Air Water. doi:10.1002/clen.201000477
Mohd LS, Wahid ZA (2012) Treatment of sewage by electrocoagulation and the effect of high current density. Energy and Environmental Engineering Journal. http://assetedu.org/viewjc.php?id=j1&page_id=18&volume_id=4&content_id=8
Nafaa Adhoum, Monser L, Bellakhal N, Belgaied J-E (2004) Treatment of electroplating wastewater containing Cu2+, Zn2+ and Cr(VI) by electrocoagulation. J Hazard Mater. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.04.018
Ramakrishnan K, Ganesan P, Lakshmi J, Vasudevan S (2013) Removal of copper from water by electrocoagulation process—effect of alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-0855-7
Saeb ES, Javadian HR, Katal R, Seft MV (2013) Removal of oil from biodiesel wastewater by electrocoagulation method. Korean J Chem Eng. doi:10.1007/s11814-012-0162-5
Sepideh S, Moghaddam MRA, Arami M (2013) Improvement of electrocoagulation process on hexavalent chromium removal with the use of polyaluminum chloride as coagulant. Desalin Water Treat. doi:10.1080/19443994.2013.814328
Subramanyan V, Lakshmi J, Ramakrishnan K, Sozhan G (2013) A critical study on the removal of copper by an electrochemically assisted coagulation: equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Asia Pac J Chem Eng. doi:10.1002/apj.1657
Toktam S, Bidhendi GN, Mehrdadi N, Torabian A (2014) Removal of chromium (III) from wastewater by electrocoagulation method. KSCE J Civ Eng. doi:10.1007/s12205-014-0642-8
Vasudevan S, Lakshmi J, Sozhan G (2009) Studies on the removal of iron from drinking water by electrocoagulation—a clean process. Clean Soil Air Water. doi:10.1002/clen.200800175
Visnja RK, Nad K, Mikelic IL, Gustek SF (2013) Treatment of winery wastewater by electrochemical methods and advanced oxidation processes. J Environ Sci Health. doi:10.1080/10934529.2013.797267
YaoXing XYW, Yuan DX, Yan JM (2013) Removal of nickel from aqueous solution using cathodic deposition of nickel hydroxide at a modified electrode. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. doi:10.1002/jctb.4085
Yusuf Y, Ocal E, Koparal AS, Bakır U, Utveren OG (2011) Treatment of dairy industry wastewater by EC and EF processes using hybrid Fe–Al plate electrodes. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. doi:10.1002/jctb.2607
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Environmental Solutions Pvt. Ltd., Hyderabad, India, for providing experimental setup and electroplating industrial effluent.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhagawan, D., Poodari, S., Pothuraju, T. et al. Effect of operational parameters on heavy metal removal by electrocoagulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 14166–14173 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3331-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3331-8