Abstract
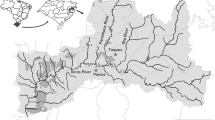
The study monitored the contamination of fish muscle tissue by elements Al, As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Hg, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn at 17 sampling sites, in order to assess the pollution status of the main rivers in Serbia. Of the six commercially important fish species included in the study (pikeperch Sander lucioperca, catfish Silurus glanis, bream Abramis brama, barbel Barbus barbus, chub Squalius cephalus, nase Chondrostoma nasus), the bioconcentration factor (BCF) indicated that benthivore bream and barbel and predatory catfish have the highest tendency toward the accumulation of elements. This study achieved its primary objective and produced a contamination map of Serbia as a basis for further research. The estimated metal pollution index (MPI) showed the Tisa River to be unaffected by direct pollution (with an MPI value of 0.31) and the West Morava and Pek rivers to be affected (with MPI values of 1.92 and 0.73 for the WM1 and WM2 sampling sites and 0.65 for the Pek sampling site). Over the past two decades, Serbia has not expanded its industrial activity, which has resulted in the barely noticeable anthropogenic input of heavy metals in the rivers close to industry, and the main rivers are mostly unaffected and slightly affected. We assumed that pollution by heavy metals in the 1990s was trapped in the sediment, thus showing an increased concentration of elements in the species that live and feed on the bottom. Hg concentrations exceeded the maximum permitted concentrations (MPCs) only in catfish samples (0.62 mg kg−1) from the Danube (D3 sampling site) and barbel (0.78 mg kg−1) from the West Morava (WM1 sampling site), while Cd concentrations exceeded the MPC in catfish samples (0.09 mg kg−1) from the Danube (D1 sampling site) and chub samples (0.1 mg kg−1) from the South Morava (SM2 sampling site). The average concentrations of Pb exceeded the MPC in chub and barbel samples (0.32 and 0.82 mg kg−1, respectively) from the West Morava (WM1 sampling site); chub, barbel, and nase samples (0.35, 0.32, 0.31 mg kg−1, respectively) from the West Morava (WM2 sampling site); chub and barbel samples (0.35 and 0.3 mg kg−1, respectively) from the Ibar; chub samples (0.39 mg kg−1) from the Drina; chub and barbel samples (0.59 and 0.4 mg kg−1, respectively) from the Great Timok; and nase samples (0.33 mg kg−1) from the Pek. These results demonstrate that there is a need for future studies that would involve similar analyses and focus especially on smaller rivers that have been neglected so far.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alibabić V, Vahcić N, Bajramović M (2007) Bioaccumulation of metals in fish of Salmonidae family and the impact of fish meat quality. Environ Monit Assess 131(1–3):349–364
Andres S, Ribeyre F, Tourencq J-N, Boudou A (2000) Interspecific comparison of cadmium and zinc contamination in the organs of four fish species along a polymetallic pollution gradient (Lot River, France). Sci Total Environ 248(1):11–25
Braune B, Muir D, DeMarch B, Gamberg W, Eamer J, Elkin B, Evans M, Grundy S, Hebert C, Johnstone R, Kidd K, Koenig B, Lockhart L, Marshall H, Reimer K, Sanderson J, Shutt L (1999) Spatial and temporal trends of contaminants in Canadian Arctic freshwater and terrestrial ecosystems: a review. Sci Total Environ 230:145–207
Burger J, Gaines KF, Boring CS, Stephens WL, Snodgrass J, Dixon C, McMahon M, Shukla S, Shukla T, Gochfeld M (2002) Metal levels in fish from the Savannah River: potential hazards to fish and other receptors. Environ Res 89(1):85–97
Čelechovská O, Svobodová Z, Žlábek V, Macharáčková B (2007) Distribution of metals in tissues of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Acta Vet Brno 76:S93–S100
Chovanec A, Hofer R, Schiemer F (2003) Fish as bioindicators. Trace metals and other contaminants in the environment 6. In: Markert BA, Breure AM, Zechmeister HG (eds) Bioindicators and biomonitors. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 639–677
Dallinger R, Kautzky H (1985) The importance of contaminated food and uptake of heavy metals by rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri): a field study. Oecologia 67:82–89
Djinovic JM, Popovic AR (2007) In situ influence of coal ash dump on the quality of neighboring surface and ground waters by applying correlation statistic analysis. Fuel 86(1–2):218–226
Dušek L, Svobodová Z, Janoušková D, Vykusová B, Jarkovský J, Šmíd R, Pavliš P (2005) Bioaccumulation of mercury in muscle tissue of fish in the Elbe River (Czech Republic): multispecies monitoring study 1991–1996. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 6(2):256–267
European Commission Regulation (2006) Setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs, Official Journal of the European Union No 1881/2006
Farkas A, Salánki J, Specziár A (2003) Age- and size-specific patterns of heavy metals in the organs of freshwater fish Abramis brama L. populating a low-contaminated site. Water Res 37(5):959–964
Fernandes C, Fontaínhas-Fernandes A, Cabral D, Salgado MA (2008) Heavy metals in water, sediment and tissues of Liza saliens from Esmoriz-Paramos lagoon, Portugal. Environ Monit Assess 136(1–3):267–275
Food and Agriculture/World Health Organisation (FAO/WHO) (1972) Evaluation of certain food additives and the contaminants mercury, cadmium and lead, WHO Technical Report Series No. 505. WHO, Geneva
Hardisty MW, Karta S, Sainsbury M (1974) Dietary habits and heavy metal concentrations in fish from Severn Estuary and Bristol Channel. Mar Pollut Bull 5:61–63
Has-Schön E, Bogut I, Kralik G, Bogut S, Horvatić J, Cacić I (2008) Heavy metal concentration in fish tissues inhabiting waters of “Buško Blato” reservoir (Bosna and Herzegovina). Environ Monit Assess 144(1–3):15–22
Hutton M (1987) Human health concerns of lead, mercury, cadmium and arsenic. In: Hutchinson TC, Meema KM (eds) Lead, mercury, cadmium and arsenic in the environment. Wiley, Chichester
Jarić I, Višnjić-Jevtić Z, Cvijanović G, Lj J, Skorić S, Lenhardt M (2011) Determination of differential heavy metal and trace element accumulation in liver, gills, intestine and muscle of sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus) from Danube River in Serbia by ICP-OES. Microchem J 98(1):77–81
Jovičić K, Lenhardt M, Višnjić-Jeftić Ž, Đikanović V, Skorić S, Smederevac-Lalić M, Jaćimović M, Gačić Z, Jarić I, Hegediš A (2014) Assessment of fish stocks and elemental pollution in the Danube, Sava and Kolubara Rivers on the Territory of the City of Belgrade. Serbia Acta zool bulg 7:179–184
Jovičić K, Nikolić DM, Višnjić-Jeftić Ž, Đikanović V, Skorić S, Stefanović SM, Lenhardt M, Hegediš A, Krpo-Ćetković J, Jarić I (2015) Mapping differential elemental accumulation in fish tissues: assessment of metal and trace element concentrations in wels catfish (Silurus glanis) from the Danube River by ICP-MS. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(5):3820–3827
Lamas S, Fernández JA, Aboal JR, Carballeira A (2007) Testing the use of juvenile Salmo trutta L. as biomonitors of heavy metal pollution in freshwater. Chemosphere 67(2):221–228
Lau S, Mohammed MA, Yen TC, Su'ut S (1998) Accumulation of heavy metals in fresh water molluscs. Sci Total Environ 214:113-121
Lenhardt M, Jarić I, Višnjić-Jevtić Ž, Skorić S, Gačić Z, Pucar M, Hegediš A (2012) Concentrations of 17 elements in muscle, gills, liver and gonads of five economically important fish species from the Danube River. Knowl Managt Aquatic Ecosyst 407:02
Liu J, Zhang XH, Tran H, Wang DQ, Zhu YN (2011) Heavy metal contamination and risk assessment in water, paddy soil, and rice around an electroplating plant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18(9):1623–1632
McCoy CP, O’Hara TM, Bentt LW, Boyle CR (1995) Liver and kidney concentrations of zinc, copper and cadmium in Channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus): variations due to size, season and health status. Vet Human Toxicol 37:11–15
Nabavi SF, Nabavi SM, Latifi AM, Eslami S, Ebrahimzadeh MA (2012) Determination of trace elements level of pikeperch collected from the Caspian Sea. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88(3):401–405
Official Gazette of RS (2005) Fisheries Law
Official Gazzette of RS (2011) Regulation on quantity of pesticides, metals, metalloids, and other toxic substances, chemotherapeutics, anabolics, and other substances which can be found in food. Official Gazzette of RS No 28/2011
Pawellek F, Frauenstein F, Veizer J (2002) Hydrochemistry and isotope geochemistry of the upper Danube River. Geochim et Cosmochim Acta 66(21):3839–3854
Phillips DJH (ed) (1980) Quantitative aquatic biological indicators. Applied Science Publishers, London
Poleksić V, Lenhardt M, Jarić I, Djordjević D, Gačić Z, Cvijanović G, Rašković B (2010) Liver, gills and skin histopathology and heavy metals content of the Danube sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus Linnaeus, 1758). Environ Toxicol Chem 29:515–521
Prosi F (1981) Heavy metals in aquatic organisms. In: Förstner U, Wittmann GTW (eds) Berlin. Springer, Heidelberg, New York, pp 271–323
Ricart M, Guasch H, Barcelό D, Brix R, Conceiçào MH, Geiszinger A, de Alda MJL, Lόpez-Doval JC, Muñoz I, Postigo C, Romani AM, Villagrasa M, Sabater S (2010) Primary and complex stressors in polluted Mediterranean rivers: pesticide effects on biological communities. J Hydrol 383(1–2):52–61
Sakan S, Sakan N, Đorđević D (2013) Trace element study in Tisa River and Danube alluvial sediment in Serbia. Int J Sediment Res 28(2):234–245
Sakan S, Dević G, Relić D, Anđelković I, Sakan N, Đorđević D (2015) Evaluation of sediment contamination with heavy metals: the importance of determining appropriate background content and suitable element for normalization. Environ Geochem Health 37(1):97–113
Salomons W, Förstner U (1980) Trace metal analysis on polluted sediments: part II: evaluation of environmental impact. Environmental Technology 1(11):506–517
Simić V, Simić S, Stojković Piperac M, Petrović A, Milošević D (2014) Commercial fish species of inland waters: a model for sustainability assessment and management. Sci Total Environ 497–498:642–650
Smederevac-Lalić M, Višnjić-Jeftić Ž, Pucar M, Mićković B, Skorić S, Nikčević M, Hegediš A (2011) Fishing circumstances on the Danube in Serbia. Water Research and Management 1(4):45–49
Smederevac-Lalić M, Pešić R, Cvejić S, Simonović P (2012) Socio-economic features of commercial fishery in the bordering upper Danube River area of Serbia. Environ Monit Assess 184(5):2633–2646
Squadrone S, Prearo M, Brizio P, Gavinelli S, Pellegrino M, Scanzio T, Guarise S, Benedetto A, Abete MC (2013) Heavy metals distribution in muscle, liver, kidney and gill of European catfish (Silurus glanis) from Italian Rivers. Chemosphere 90(2):358–365
Subotić S, Spasić S, Višnjić-Jeftić Z, Hegediš A, Krpo-Ćetković J, Mićković B, Skorić S, Lenhardt M (2013a) Heavy metal and trace element bioaccumulation in target tissues of four edible fish species from the Danube River (Serbia). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 98:196–202
Subotić S, Višnjić Jeftić Ž, Spasić S, Hegediš A, Krpo-Ćetković J, Lenhardt M (2013b) Distribution and accumulation of elements (As, Cu, Fe, Hg, Mn, and Zn) in tissues of fish species from different trophic levels in the Danube River at the confluence with the Sava River (Serbia). Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(8):5309–5317
Sunjog K, Gačić Z, Kolarević S, Višnjić-Jeftić Z, Jarić I, Knežević-Vukčević J, Vuković-Gačić B, Lenhardt M (2012) Heavy metal accumulation and the genotoxicity in barbel (Barbus barbus) as indicators of the Danube River pollution. Sci World J 2012:351074
Teodorović I (2009) Ecotoxicological research and related legislation in Serbia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16(1):S123–S129
Teodorović I, Đukić N, Maletin S, Miljanović B, Jugovac N (2000) Metal pollution index: proposal for freshwater monitoring based on trace metal accumulation in fish. Tiscia 32:55–60
Terra BF, Araújo FG, Calza CF, Lopes RT, Teixeira TP (2008) Heavy metal in tissues of three fish species from different trophic levels in a tropical Brazilian river. Water Air Soil Pollut 187:275–284
Triebskorn R, Telcean I, Casper H, Farkas A, Sandu C, Stan G, Colărescu O, Dori T, Köhler HR (2008) Monitoring pollution in River Mureş, Romania, part II: metal accumulation and histopathology in fish. Environ Monit Assess 141(1–3):177–188
Uchida M, Hirakawa Y, Inoue T (1961) Biochemical studies on Minamata disease IV. Isolation and chemical identification of the mercury compound in the toxic shellfish with special reference to the causal agent of the disease. Kumamoto Medical Journal 14:181–184
Usero J, González-Regalad E, Gracia I (1997) Trace metals in the bivalve molluscs Ruditapes decussatus and Ruditapes philippinarum from the Atlantic Coast of Southern Spain. Environ Int 23(3):291–298
Uysal K, Köse E, Bülbül M, Dönmez M, Erdoğan Y, Koyun M, Ömeroğlu C, Özmal F (2009) The comparison of heavy metal accumulation ratios of some fish species in Enne Dame Lake (Kütahya/Turkey). Environ Monit Assess 157:355–362
van der Schalie WH, Shedd TR, Knechtges PL, Widder MW (2001) Using higher organisms in biologically early warning systems for real time toxicity detection. Biosens Bioelectron 16(7–8):457–465
Visnjic-Jeftic Z, Jaric I, Lj J, Skoric S, Smederevac-Lalic M, Nikcevic M, Lenhardt M (2010) Heavy metal and trace element accumulation in muscle, liver and gills of the Pontic shad (Alosa immaculate, Bennet 1835) from the Danube River (Serbia). Microchem J 95(2):341–344
Yi YJ, Zhang SH (2012) Heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb, Zn) concentrations in seven fish species in relation to fish size and location along the Yangtze River. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19(9):3989–3996
Zrnčić S, Oraić D, Ćaleta M, Mihaljević Ž, Zanella D, Bilandžić N (2013) Biomonitoring of heavy metals in fish from the Danube River. Environ Monit Assess 185(2):1189–1198
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia, Project No. TR31011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milošković, A., Dojčinović, B., Kovačević, S. et al. Spatial monitoring of heavy metals in the inland waters of Serbia: a multispecies approach based on commercial fish. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 9918–9933 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6207-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6207-2