Abstract
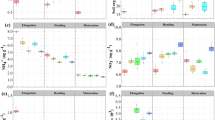
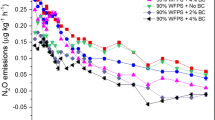
Biochar application to soil is currently widely advocated for a variety of reasons related to sustainability. However, the synergistic effects of biochar combined with mineral or organic fertilizer on soil N2O emissions, NH3 volatilization, and plant N uptake are poorly documented. Field plot experiments planted with peanut were conducted under the application of biochar (derived from rice husk and cottonseed husk, 50 t ha−1) with organic or mineral fertilizer. It was found that biochar increased soil nutrient availability and decreased surface soil bulk density, demonstrating that biochar could improve the soil quality especially in the 0–20-cm profile. The total N content of the plant changed little with treatments, but the kernel N concentration increased significantly when biochar was applied with organic fertilizer. Peanut yield increased with biochar amendment while no significant difference was observed in plant biomass, suggesting biochar had a positive effect on belowground biomass. Peanut N uptake was also increased following biochar amendment with either organic or mineral fertilizers. While biochar amendment had no significant effect on soil NH3 volatilization, it did decrease the cumulative N2O emission by 36.3% on average with organic fertilizer, and by 32.6% with mineral fertilizer, respectively (p < 0.05). The copy numbers of 16S rDNA, nifH, nirK, and nirS were not influenced by the application of biochar; however, the copy number of nosZ was significantly increased under biochar plus mineral fertilizer treatment. The results imply that biochar application can suppress N2O emissions, as a result of abiotic factors and enhanced peanut N uptake rather than changes of denitrification genes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agegnehu G, Bass AM, Nelson PN, Muirhead B, Wright G, Bird MI (2015) Biochar and biochar-compost as soil amendments: effects on peanut yield, soil properties and greenhouse gas emissions in tropical North Queensland, Australia. Agric Ecosyst Environ 213:72–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2015.07.027
Baggs EM (2011) Soil microbial sources of nitrous oxide: recent advances in knowledge, emerging challenges and future direction. Curr Opin Env Sust 3(5):321–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2011.08.011
Case SDC, McNamara NP, Reay DS, Whitaker J (2012) The effect of biochar addition on N2O and CO2 emissions from a sandy loam soil – the role of soil aeration. Soil Biol Bioch 51:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.03.017
Case SDC, McNamara NP, Reay DS, Stott AW, Grant HK, Whitaker J (2015) Biochar suppresses N2O emissions while maintaining N availability in a sandy loam soil. Soil Biol Bioch 81:178–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.11.012
Castaldi S, Riondino M, Baronti S, Esposito FR, Marzaioli R, Rutigliano FA, Vaccari FP, Miglietta F (2011) Impact of biochar application to a Mediterranean wheat crop on soil microbial activity and greenhouse gas fluxes. Chemosphere 85(9):1464–1471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.08.031
Cayuela ML, van Zwieten L, Singh BP, Jeffery S, Roig A, Sánchez-Monedero MA (2014) Biochar's role in mitigating soil nitrous oxide emissions: a review and meta-analysis. Agric Ecosyst Environ 191:5–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2013.10.009
Chen A, Lei B, Hu W, Lu Y, Mao Y, Duan Z, Shi Z (2015) Characteristics of ammonia volatilization on rice grown under different nitrogen application rates and its quantitative predictions in Erhai Lake Watershed, China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 101(1):139–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-014-9660-7
Cornelissen G, Rutherford DW, Arp HP, Dörsch P, Kelly CN, Rostad CE (2013) Sorption of pure N2O to biochars and other organic and inorganic materials under anhydrous conditions. Environ Sci Tec 47(14):7704–7712. https://doi.org/10.1021/es400676q
Darby I, CY X, Wallace HM, Joseph S, Pace B, Bai SH (2016) Short-term dynamics of carbon and nitrogen using compost, compost-biochar mixture and organo-mineral biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(11):11267–11278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6336-7
Davidson EA (2009) The contribution of manure and fertilizer nitrogen to atmospheric nitrous oxide since 1860. Nat Geosci 2(9):659–662. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo608
Doydora SA, Cabrera ML, Das KC, Gaskin JW, Sonon LS, Miller WP (2011) Release of nitrogen and phosphorus from poultry litter amended with acidified biochar. Int J Environ Res Public Health 8:1491–1502
Fageria NK, Baligar VC, Jones CA (2010) Growth and mineral nutrition of field crops. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/b10160
Freddo A, Cai C, Reid BJ (2012) Environmental contextualisation of potential toxic elements and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in biochar. Environ Pollut 171:18–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.07.009
Gai X, Wang H, Liu J, Zhai L, Liu S, Ren T, Liu H (2014) Effects of feedstock and pyrolysis temperature on biochar adsorption of ammonium and nitrate. PLoS One 9(12):e113888. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0113888
Gai X, Liu H, Zhai L, Tan G, Liu J, Ren T, Wang H (2016) Vegetable yields and soil biochemical properties as influenced by fertilization in Southern China. Appl Soil Ecol 107:170–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.06.001
Güereña DT, Lehmann J, Thies JE, Enders A, Karanja N, Neufeldt H (2015) Partitioning the contributions of biochar properties to enhanced biological nitrogen fixation in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Biol Fert Soil 51:479–491
Harter J, Krause HM, Schuettler S, Ruser R, Fromme M, Scholten T, Kappler A, Behrens S (2014) Linking N2O emissions from biochar-amended soil to the structure and function of the N-cycling microbial community. The ISME journal 8(3):660–674. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2013.160
Howarth RW, Sharpley A, Dan W (2002) Sources of nutrient pollution to coastal waters in the United States: implications for achieving coastal water quality goals. Estuar Coast 25(4):656–676. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02804898
Jones D, Rousk J, Edwards-Jones G, DeLuca T, Murphy D (2012a) Biochar-mediated changes in soil quality and plant growth in a three year field trial. Soil Biol Bioch 45:113–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.10.012
Jones DL, Rousk J, Edwards-Jones G, DeLuca TH, Murphy DV (2012b) Biochar-mediated changes in soil quality and plant growth in a three year field trial. Soil Biol Bioch 45:113–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.10.012
Kammann C, Ippolito J, Hagemann N, Borchard N, Cayuela ML, Estavillo JM, Fuertes-Mendizabal T, Jeffery S, Kern J, Novak J, Rasse D, Saarnio S, Schmidt H-P, Spokas K, Wrage-Mönnig N (2017) Biochar as a tool to reduce the agricultural greenhouse-gas burden – knowns, unknowns and future research needs. J Environ Eng Landsc 25(2):114–139. https://doi.org/10.3846/16486897.2017.1319375
Liu J, You L, Amini M, Obersteiner M, Herrero M, Zehnder AJ, Yang H (2010) A high-resolution assessment on global nitrogen flows in cropland. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(17):8035–8040. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0913658107
Ly P, Duong VQ, Jensen LS, Pandey A, de Neergaard A (2014) Effects of rice straw, biochar and mineral fertiliser on methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions from rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown in a rain-fed lowland rice soil of Cambodia: a pot experiment. Paddy Water Environ 13:465–475
Mandal S, Thangarajan R, Bolan NS, Sarkar B, Khan N, Ok YS, Naidu R (2016) Biochar-induced concomitant decrease in ammonia volatilization and increase in nitrogen use efficiency by wheat. Chemosphere 142:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.04.086
Margesin R, Schinner F (2005) Manual of soil analysis. Springer, Berlin
Mosier A, Kroeze C, Nevison C, Oenema O, Seitzinger S, Ovan C (1998) Closing the global N2O budget: nitrous oxide emissions through the agricultural nitrogen cycle: OECD/IPCC/IEA phase II development of IPCC guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventory methodology. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 52(2/3):225–248. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009740530221
Mukherjee A, Lal R, Zimmerman AR (2014) Effects of biochar and other amendments on the physical properties and greenhouse gas emissions of an artificially degraded soil. Sci Total Environ 487:26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.03.141
Pereira EIP, Suddick EC, Mansour I, Mukome FND, Parikh SJ, Scow K, Six J (2015) Biochar alters nitrogen transformations but has minimal effects on nitrous oxide emissions in an organically managed lettuce mesocosm. Biol Fert Soil 51(5):573–582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-015-1004-5
Reay DS, Davidson EA, Smith KA, Smith P, Melillo JM, Dentener F, Crutzen PJ (2012) Global agriculture and nitrous oxide emissions. Nat Clim Chang 2(6):410–416. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1458
Rochette P, Angers DA, Chantigny MH, Gasser MO, Macdonald JD, Pelster DE, Bertrand N (2013) NH3 volatilization, soil NH4 + concentration and soil pH following subsurface banding of urea at increasing rates. Can J Soil Sci 93(2):261–268. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjss2012-095
Rondon MA, Lehmann J, Ramírez J, Hurtado M (2006) Biological nitrogen fixation by common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) increases with bio-char additions. Biol Fert Soil 43:699–708
Sun L, Li L, Chen Z, Wang J, Xiong Z (2014) Combined effects of nitrogen deposition and biochar application on emissions of N2O, CO2 and NH3 from agricultural and forest soils. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 60(2):254–265. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2014.885386
Taghizadeh-Toosi A, Clough TJ, Sherlock RR, Condron LM (2012) A wood based low-temperature biochar captures NH3-N generated from ruminant urine-N, retaining its bioavailability. Plant Soil 353(1-2):73–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-1010-9
Tan G, Sun W, Xu Y, Wang H, Xu N (2016) Sorption of mercury (II) and atrazine by biochar, modified biochars and biochar based activated carbon in aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 211:727–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.147
Thomazini A, Spokas K, Hall K, Ippolito J, Lentz R, Novak J (2015) GHG impacts of biochar: predictability for the same biochar. Agric Ecosyst Environ 207:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2015.04.012
Xu HJ, Wang XH, Li H, Yao HY, Su JQ, Zhu YG (2014) Biochar impacts soil microbial community composition and nitrogen cycling in an acidic soil planted with rape. Environ Sci Tec 48(16):9391–9399. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5021058
Xu C-Y, Bai SH, Hao Y, Rachaputi RCN, Xu Z, Wallace HM (2015a) Peanut shell biochar improves soil properties and peanut kernel quality on a red Ferrosol. J Soil Sediment 15(11):2220–2231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1242-z
Xu C-Y, Hosseini-Bai S, Hao Y, Rachaputi RC, Wang H, Xu Z, Wallace H (2015b) Effect of biochar amendment on yield and photosynthesis of peanut on two types of soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:6112–6125
Xu N, Tan G, Wang H, Gai X (2016) Effect of biochar additions to soil on nitrogen leaching, microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Eur J Soil Biol 74:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2016.02.004
Yanai Y, Toyota K, Okazaki M (2007) Effects of charcoal addition on N2O emissions from soil resulting from rewetting air-dried soil in short-term laboratory experiments. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 53(2):181–188. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0765.2007.00123.x
Zhang A, Liu Y, Pan G, Hussain Q, Li L, Zheng J, Zhang X (2011) Effect of biochar amendment on maize yield and greenhouse gas emissions from a soil organic carbon poor calcareous loamy soil from Central China Plain. Plant Soil 351:263–275
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (201303095), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41301311), the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Non-profit Scientific Institution (NO. 1610132016055), and the Newton Fund (Grant Ref: BB/N013484/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hailong Wang
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 250 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, G., Wang, H., Xu, N. et al. Biochar amendment with fertilizers increases peanut N uptake, alleviates soil N2O emissions without affecting NH3 volatilization in field experiments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 8817–8826 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1116-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1116-6