Abstract
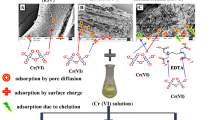
Current study deals with the comparative assessment for efficient adsorption of Cr(VI) from simulated wastewater using raw (NPP), phosphoric acid-activated (PPP) and sulphuric acid-activated (SPP) Pongamia pinnata shells. Physico-chemical alterations of the adsorbent were characterised by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), zeta-potential analysis, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and total pore analysis using Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET). Parameters influencing the efficient biosorption of Cr(VI) species viz. initial pH of Cr(VI) solution, dosage of biosorbent, biosorbent-Cr(VI) contact period, initial concentration of Cr(VI) ions and reaction temperature were optimised. Various two-parameter and three-parameter isotherm models, kinetic models and thermodynamic studies were performed using equilibrium data. Langmuir adsorption capacity for NPP (raw biomass), PPP (phosphoric acid-activated biomass) and SPP (sulphuric acid-activated biomass) was found to be 96.2, 152 and 192 mg/g, respectively. All the biosorbents gave best fit for pseudo-second-order model. Thermodynamic studies suggest spontaneous and endothermic interaction with increased degree of randomness. Effect of co-existing cations and anions on Cr(VI) biosorption onto the biosorbents implied that minimal competition and the biosorption capacity of the biosorbents for Cr(VI) species remained unaffected. Regeneration studies suggest that activated biosorbents can be used up to three times with continuous desorption.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendjeffal H, Djebli A, Mamine H, Metidji T, Dahak M, Rebbani N, Bouhedja Y (2018) Effect of the chelating agents on bio-sorption of hexavalent chromium using Agave sisalana fibers. Chin J Chem Eng 26:984–992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2017.10.016
Bhatnagar A, Hogland W, Marques M, Sillanpää M (2013) An overview of the modification methods of activated carbon for its water treatment applications. Chem Eng J 219:499–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.12.038
Bhaumik M, Agarwal S, Gupta VK, Maity A (2016) Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using polypyrrole wrapped oxidized MWCNTs nanocomposites adsorbent. J Colloid Interface Sci 470:257–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.02.054
Chojnacka K (2010) Biosorption and bioaccumulation – the prospects for practical applications. Environ Int 36:299–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2009.12.001
Costa M (2003) Potential hazards of hexavalent chromate in our drinking water. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 188:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0041-008X(03)00011-5
Deng S, Bai R (2004) Removal of trivalent and hexavalent chromium with aminated polyacrylonitrile fibers: performance and mechanisms. Water Res 38:2424–2432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.02.024
Dong L, Liang J, Li Y, Hunang S, Wei Y, Bai X, Jin Z, Zhang M, Qu J (2018) Effect of coexisting ions on Cr(VI) adsorption onto surfactant modified Auricularia auricula spent substrate in aqueous solution. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 166:390–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.097
Enniya I, Rghioui L, Jourani A (2018) Adsorption of hexavalent chromium in aqueous solution on activated carbon prepared from apple peels. Sustain Chem Pharm 7:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2017.11.003
Gerçel Ö, Gerçel HF (2007) Adsorption of lead(II) ions from aqueous solutions by activated carbon prepared from biomass plant material of Euphorbia rigida. Chem Eng J 132:289–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.01.010
Gupta VK, Agarwal S, Saleh TA (2011) Chromium removal by combining the magnetic properties of iron oxide with adsorption properties of carbon nanotubes. Water Res 45:2207–2212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.01.012
Gupta VK, Agarwal S, Bharti AK, Sadegh H (2017) Adsorption mechanism of functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes for advanced Cu (II) removal. J Mol Liq 230:667–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.01.083
Han R, Wang Y, Han P, Shi J, Yang J, Lu Y (2006) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by chaff in batch mode. J Hazard Mater 137:550–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.02.029
Karagöz S, Tay T, Ucar S, Erdem M (2008) Activated carbons from waste biomass by sulfuric acid activation and their use on methylene blue adsorption. Bioresour Technol 99:6214–6222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.12.019
Nakagawa Y, Molina-Sabio M, Rodríguez-Reinoso F (2007) Modification of the porous structure along the preparation of activated carbon monoliths with H3PO4 and ZnCl2. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 103:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2007.01.029
Nakkeeran E, Patra C, Shahnaz T, Rangabhashiyam S, Selvaraju N (2018) Continuous biosorption assessment for the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions using Strychnos nux vomica fruit shell. Bioresour Technol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2018.09.001
Owalude SO, Tella AC (2016) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by adsorption on modified groundnut hull. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 5:377–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjbas.2016.11.005
Patra C, Medisetti RMN, Pakshirajan K, Narayanasamy S (2019) Assessment of raw, acid-modified and chelated biomass for sequestration of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using Sterculia villosa Roxb. shells. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:23625–23637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05582-4
Peng S-H, Wang R, Yang L-Z, He L, He X, Liu X (2018) Biosorption of copper, zinc, cadmium and chromium ions from aqueous solution by natural foxtail millet shell. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 165:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.08.084
Rakhunde R, Deshpande L, Juneja HD (2012) Chemical speciation of chromium in water: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42:776–810. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2010.534029
Sadegh H, Ali GAM, Makhlouf ASH, Chong KF, Alharbi NS, Agarwal S, Gupta VK (2018) MWCNTs-Fe3O4 nanocomposite for Hg(II) high adsorption efficiency. J Mol Liq 258:345–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.03.012
Scott PT, Pregelj L, Chen N, Hadler JS, Djordjevic MA, Gresshoff PM (2008) Pongamia pinnata: an untapped resource for the biofuels industry of the future. BioEnergy Research 1:2–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-008-9003-0
Song X, Liu H, Cheng L, Qu Y (2010) Surface modification of coconut-based activated carbon by liquid-phase oxidation and its effects on lead ion adsorption. Desalination 255:78–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.01.011
Sun Y, Yue Q, Gao B, Gao Y, Li Q, Wang Y (2013) Adsorption of hexavalent chromium on Arundo donax Linn activated carbon amine-crosslinked copolymer. Chem Eng J 217:240–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.121
Sun Y, Yue Q, Mao Y, Gao B, Gao Y, Huang L (2014) Enhanced adsorption of chromium onto activated carbon by microwave-assisted H3PO4 mixed with Fe/Al/Mn activation. J Hazard Mater 265:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.11.057
Tobin JM, Cooper DG, Neufeld RJ (1984) Uptake of metal ions by Rhizopus arrhizus biomass. Appl Environ Microbiol 47:821–824
Toles CA, Marshall WE, Johns MM (1999) Surface functional groups on acid-activated nutshell carbons. Carbon 37(8):1207–1214. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(98)00315-7
Xie R, Wang H, Chen Y, Jiang W (2013) Walnut shell-based activated carbon with excellent copper (II) adsorption and lower chromium (VI) removal prepared by acid–base modification. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 32(3):688–696. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.11686
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering, Indian Institute of Technology-Guwahati for providing the research grounds and facilities. The authors also acknowledge the facilities provided by the Central Instrumentation Facility (CIF), Indian Institute of Technology-Guwahati.
Funding
The IITG Start-up Research Grant (Grant No. BSBESUGIITG01213xSEN001) provided funding for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 29 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patra, C., Shahnaz, T., Subbiah, S. et al. Comparative assessment of raw and acid-activated preparations of novel Pongamia pinnata shells for adsorption of hexavalent chromium from simulated wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 14836–14851 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07979-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07979-y