Abstract
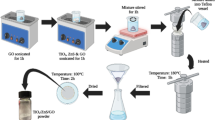
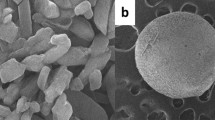
To overcome the titanium oxide limitations, Fe2O3- and Fe3O4-modified TiO2 (3:1) nanoparticles were synthesized by a humid and solid path, respectively. These nanoparticles were embedded in sodium alginate biopolymer to prepare beads with efficient adsorption and photocatalytic behaviors in cationic dye degradation under both UV and visible irradiations. Operating conditions were investigated such as initial methylene blue (MB) concentration and contact time to evaluate their impact on the process. The bead recycling was also scrutinized. We have come to the conclusion that Fe2O3-modified TiO2-Alg displayed superiorities, including expanded responsive wavelength range in the visible region (up to 700 nm), narrower band gap (1.79 eV), and better efficiency for MB removal in terms of adsorption capacities and photocatalytic effectiveness under both UV and visible irradiations. Furthermore, these beads can be effortlessly recovered from the reaction medium after the photocatalytic process and reused up to 5 cycles without any noteworthy decline in their initial properties.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Abbas N, Shao GN, Haider MS, Imran SM, Soo S, Taik H (2016) Sol–gel synthesis of TiO2-Fe2O3 systems: effects of Fe2O3 content and their photocatalytic properties. J Ind Eng Chem 39:112–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.05.015
Ahmed MA, El-katori EE, Gharni ZH (2013) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye using Fe2O3/TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by sol – gel method. J Alloys Compd 553:19–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.10.038
Chen X, Mao SS (2007) Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications and applications. Chem Rev 107:2891–2959. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr0500535
Hong C-S, Wang Y, Bush B (1998) Kinetics and products of the TiO2, photocatalytic degradation of 2-chlorobiphenyl in water. Chemosphere 36:1653–1667
Chkirida S, Bouhfid R, Zari N, Achour R, Qaiss el Kacem A (2020) Effect of iron doped titanium oxide encapsulated in alginate on photocatalytic activity for the removal of dye pollutants. RSC Adv 10:22311–22317. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA02898C
Chládková B, Evgenidou E, Kvítek L, Panáček A, Zbořil R, Kovář P, Lambropoulou D (2015) Adsorption and photocatalysis of nanocrystalline TiO2 particles for Reactive Red 195 removal: effect of humic acids, anions and scavengers. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16514–16524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4806-y
Curcio MS, Oliveira MP, Waldman WR, Sánchez B, Canela MC (2015) TiO2 sol-gel for formaldehyde photodegradation using polymeric support: photocatalysis efficiency versus material stability. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:800–809. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2683-4
Fujishima AKH (1972) Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238:37–38
Giri SK, Das NN (2013) Iron oxide/titania photocatalysts derived from TiO2.nH2O coated ferric hydr(oxide ) precursors: characterizations and visible light photocatalytic activity. Powder Technol 239:193–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2013.02.004
Guettaı N, Amar HA (2005) Photocatalytic oxidation of methyl orange in presence of titanium dioxide in aqueous suspension. Part II: kinetics study. Desalination 185:439–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.04.049
HO Y-S (2004) Citation review of Lagergren kinetic rate equation on adsorption reactions. Scientometrics 59:171–177
Ibrahim U, Halim A (2008) Photochemistry reviews heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants over titanium dioxide: a review of fundamentals, progress and problems. J Photochem Photobiol C 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2007.12.003
Irshad R, Tahir K, Li B, Ahmad A, Siddiqui AR, Nazir S (2017) Antibacterial activity of biochemically capped iron oxide nanoparticles: a view towards green chemistry. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 170:241–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.04.020
Kalikeri S, Kamath N, Gadgil DJ, Shetty Kodialbail V (2018) Visible light-induced photocatalytic degradation of Reactive Blue-19 over highly efficient polyaniline-TiO2 nanocomposite: a comparative study with solar and UV photocatalysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:3731–3744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0663-1
Largitte L, Pasquier R (2016) A review of the kinetics adsorption models and their application to the adsorption of lead by an activated carbon. Chem Eng Res Des 109:495–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2016.02.006
Lin J, Wang L (2009) Comparison between linear and non-linear forms of pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order adsorption kinetic models for the removal of methylene blue by activated carbon. Front Environ Sci Eng China 3:320–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-009-0030-7
Todorović M, Milonjić SK, Čomor JJ, Gal IJ (2006) Adsorption of radioactive ions Cs , Sr , and Co on natural magnetite and hematite. Sep Sci Technol 27:671–679. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496399208018910
Mohammad A, Saud A, Jawad AH (2019) Box-Behnken design to optimize the synthesis of new crosslinked chitosan-glyoxal/TiO2 nanocomposite: methyl orange adsorption and mechanism studies. Int J Biol Macromol 129:98–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.02.025
Murakami N, Chiyoya T, Tsubota T, Ohno T (2008) Switching redox site of photocatalytic reaction on titanium (IV) oxide particles modified with transition-metal ion controlled by irradiation wavelength. Appl Catal A Gen 348:148–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2008.06.040
Muramatsu Y, Jin Q, Fujishima M, Tada H (2012) Environmental visible-light-activation of TiO2 nanotube array by the molecular iron oxide surface modification. Appl Catal B Environ 119–120:74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.02.012
Nouri L, Hemidouche S, Boudjemaa A, Kaouah F (2020) Elaboration and characterization of photobiocomposite beads , based on titanium (IV) oxide and sodium alginate biopolymer, for basic blue 41 adsorption/photocatalytic degradation. Int J Biol Macromol 151:66–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.159
Rashid J, Barakat MA, Ruzmanova Y, Chianese A (2015) Fe3O4/SiO2/TiO2 nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of 2-chlorophenol in simulated wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:3149–3157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3598-9
Saud A, Jawad AH, Mohammad A (2019) Bioresource technology synthesis of chitosan-ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether/TiO2 nanoparticles for adsorption of reactive orange 16 dye using a response surface methodology approach. Bioresour Technol 293:122071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122071
Sheng Y, Wei Z, Miao H, Yao W, Li H, Zhu Y (2019) Enhanced organic pollutant photodegradation via adsorption/photocatalysis synergy using a 3D g-C3N4/TiO2 free-separation photocatalyst. Chem Eng J 370:287–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.197
Tahir K, Ahmad A, Li B, Ullah A, Nazir S, Ul Z, Khan H, Ullah S (2016) Preparation, characterization and an efficient photocatalytic activity of Au/TiO2 nanocomposite prepared by green deposition method. Mater Lett 178:56–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2016.04.176
Valente PS, Padilha PM, Florentino AO (2006) Studies on the adsorption and kinetics of photodegradation of a model compound for heterogeneous photocatalysis onto TiO2. Chemosphere 64:1128–1133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.11.050
Zaleska A (2008) Doped-TiO2 : a review. Recent Patents Eng 2:157–164. https://doi.org/10.2174/187221208786306289
Zhang X, Pan JH, Du AJ, Xu S, Sun DD (2009) Room-temperature fabrication of anatase TiO2 submicrospheres with nanothornlike shell for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 204:154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2009.03.011
Zheng X, Xu S, Wang Y, Sun X, Gao Y, Gao B (2018) Enhanced degradation of ciprofloxacin by graphitized mesoporous carbon (GMC) -TiO2 nanocomposite: strong synergy of adsorption- photocatalysis and antibiotics degradation mechanism. J Colloid Interface Sci 527:202–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.05.054
Funding
This work was supported by MAScIR (Moroccan Foundation for Advanced Science, Innovation and Research).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Soulaima Chkirida: Conceptualization, data curation, methodology, and writing - original draft; Nadia Zari: writing - review and editing; Redouane Achour: supervision; Abou el Kacem Qaiss: validation and supervision; and Rachid Bouhfid: writing - review and editing, validation, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 17 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chkirida, S., Zari, N., Achour, R. et al. Efficient hybrid bionanocomposites based on iron-modified TiO2 for dye degradation via an adsorption-photocatalysis synergy under UV-Visible irradiations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 14018–14027 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11664-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11664-5