Abstract
The syntheses and characterization of fish scale biochar magnetic composites (FSB@Fe3O4) and their applications in the removal of indigo carmine dye from effluents are described. Preparation of the fish scale biochar magnetic composites, FSB@400 °C-Fe3O4, FSB@600 °C-Fe3O4, and FSB@800 °C-Fe3O4, was done following the chemical co-precipitation method. The adsorbents were characterized using peak optical absorbance, functional groups, magnetic strength, surface morphology, particle size, elemental compositions, surface charge, surface area, thermal stability, and crystalline phase, using ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis spec), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM), transmission electron microscopy/scanning electron microscopy (TEM/SEM), energy dispersive X-ray (EDX), point of zero charge pH (pHpzc), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET), thermo-gravimetric analysis (TGA), and powder x-ray diffraction (PXRD) techniques, correspondingly. The potential of magnetic composites for the abstraction of indigo carmine dye from wastewater was determined as a function of the initial concentration of indigo carmine dye, contact time, dye solution pH, adsorbent dosage, and solution temperature. The results demonstrated that the quantity (q) of indigo carmine dye adsorbed onto magnetic composites improved with a rise in initial dye concentration, adsorbent load, and solution temperature. Conversely, lower quantities of adsorbed dye were recorded at higher pH levels. The data fitted a pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The Langmuir isotherm gave the best fit (Langmuir>Freundlich>Redlich-Peterson>Toth>Hill>Sips>Temkin) suggesting a uniformly monolayer adsorption. Adsorption of environmental wastewater samples revealed that all the adsorbents can be used to effectively treat industrial wastewaters. The recycling data established that the adsorbents could be used for five consecutive cycles without significant loss of adsorption capacities.
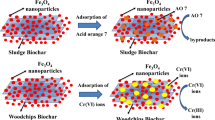
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not available.
References
Achieng GO, Shikuku VO (2020) Adsorption of copper ions from water onto fish scales derived biochar: isothermal perspectives. J. Mater Environ Sci 11:1816–1827
Achieng’ GO, Kowenje CO, Lalah JO, Ojwach SO (2019) Preparation, characterization of fish scales biochar and their applications in the removal of anionic indigo carmine dye from aqueous solutions. Water Sci Technol 80:2218–2231. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.040
Ali SFA, Gad ES (2020) Investigation of an adsorbent based on novel starch/chitosan nanocomposite in extraction of indigo carmine dye from aqueous solutions. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 10:5556–5563. https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC103.556563
Allen SJ, Gan Q, Matthews R, Johnson PA (2003) Comparison of optimized isotherm models for basic dye adsorption by kudzu. Bioresour Technol 88:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00281-X
Almoisheer N, Alseroury F, Kumar R, Aslam M, Barakat M (2019) Adsorption and anion exchange insight of indigo carmine onto CuAl-LDH/SWCNTs nanocomposite: kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm analysis. RSC Adv 9:560–568. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA09562K
Ansari R, Seyghali B, Mohammad-khah A, Zanjanchi MA (2012) Application of nano surfactant modified biosorbent as an efficient adsorbent for dye removal. Sep Sci Technol 47:1802–1812. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2012.658485
Ayanda OS, Amodu OS, Adubiaro H, Olutona GO, Ebenezer OT, Nelana SM, Naidoo EB (2019) Effectiveness of termite hill as an economic adsorbent for the adsorption of alizarin red dye. J Water Reuse and Des 9:83–93. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2018.026
Azizi SN, Colagar AH, Hafeziyan SM (2012) Removal of Cd(II) from aquatic system using Oscillatoria sp. biosorbent. Sci World J 2012:7. https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/347053
Badeenezhad A, Azhdarpoor A, Bahrami S, Yousefinejad S (2019) Removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions by natural clinoptilolite and clinoptilolite modified by iron oxide nanoparticles. Mol Simul 45:564–571. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927022.2018.1564077
Bagtash M, Zolgharnein J (2017) Hybrid central composite design for simultaneous optimization of removal of methylene blue and alizarin red S from aqueous solutions using Vitis tree leaves. J Chemom 32:13. https://doi.org/10.1002/cem.2960
Bordoloi N, Dey MD, Mukhopadhyay R, Kataki R (2018) Adsorption of methylene blue and rhodamine B by using biochar derived from Pongamia glabra seed cover. Water Sci Technol 77:638–646. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.579
Bouteraa S, Saiah FBD, Hamouda S, Bettahar N (2020) Zn-M-CO3 Layered double hydroxides (M= Fe, Cr, or Al): synthesis, characterization, and removal of aqueous indigo carmine. Bull Chem React Eng Catal 15:43–54. https://doi.org/10.9767/bcrec.15.1.5053.43-54
Chaki S, Malek TJ, Chaudhary M, Tailor J, Deshpande M (2015) Magnetite Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesis by wet chemical reduction and their characterization. Adv Nat Sci: Nanosci and Nanotech 6:6. https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6262/6/3/035009
Chakraborty J, Dey S, Halder U (2016) An eco-friendly bio-sorbent derived from fish (carp) scale: a study of commercial dye removal. Int J Sci Eng Res 7:72–76
Couto SR (2009) Dye removal by immobilised fungi. Biotech Adv 27:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.12.001
Dada A, Adekola F, Odebunmi E (2014) Synthesis and characterization of iron nanoparticles and its ash rice husk supported nanocomposite. Published Proceedings of the 1st African International Conference/Workshop on Applications of Nanotechnology to Energy, Health and Environment, UNN 138-149.
Dai Z, Meng J, Muhammad N, Liu X, Wang H, He Y, Brookes PC, Xu J (2013) The potential feasibility for soil improvement, based on the properties of biochars pyrolyzed from different feedstocks. J Soils Sediments 13:989–1000. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0698-y
De León-Condés CA, Roa-Morales G, Martínez-Barrera G, Menchaca-Campos C, Bilyeu B, Balderas-Hernández P, Ureña-Núñez F, Toledo-Jaldin HP (2019) Sulfonated and gamma-irradiated waste expanded polystyrene with iron oxide nanoparticles, for removal of indigo carmine dye in textile wastewater. Heliyon 5:e02071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02071
Delgado CL, Wada N, Rosegrant MW, Meijer S, Ahmed M (2003) The future of fish. Issues Trends 2020:6 https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12348/2179. Accessed 26 Sep 2020
Ebrahimian Pirbazari A, Saberikhah E, Ahmad Gorabi N (2016) Fe3O4 nanoparticles loaded onto wheat straw: an efficient adsorbent for basic blue 9 adsorption from aqueous solution. Des Water Treat 57:4110–4121. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.989918
El Haddad M, Slimani R, Mamouni R, Laamari MR, Rafqah S, Lazar S (2013) Evaluation of potential capability of calcined bones on the biosorption removal efficiency of safranin as cationic dye from aqueous solutions. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 44:13–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2012.10.003
Elango G, Govindasamy R (2018) Removal of colour from textile dyeing effluent using temple waste flowers as ecofriendly adsorbent. J Appl Chem 11:19–28. https://doi.org/10.9790/5736-1106011928
Esakkiraj P, Maruthiah T, Nawas PMA, Immanuel G, Palavesam A (2013) Solid-state protease production by Bacillus thuringiensis AP-CMST using trash fish meal as substrate. J Pure Appl Micro 7:1–8
Essandoh M, Garcia RA (2018) Efficient removal of dyes from aqueous solutions using a novel hemoglobin/iron oxide composite. Chemosphere 206:502–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.182
Federation WE, APH Association (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association (APHA), Washington
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Review: insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013
Fraga TJM, de Lima LEM, de Souza ZSB, Carvalho MN, de Luna Freire EMP, Ghislandi MG, da Motta MA (2019) Amino-Fe3O4-functionalized graphene oxide as a novel adsorbent of methylene blue: kinetics, equilibrium, and recyclability aspects. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:28593–28602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.06.068
Freundlich H (1907) Über die adsorption in lösungen. Z Phys Chem 57:385–470. https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-1907-5723
Gholami N, Dadvand Koohi A, Ebrahimian Pirbazari A (2018) Fabrication, characterization, regeneration and application of nanomagnetic Fe3O4@Fish scale as a bio-adsorbent for removal of methylene blue. J Water Environ Nanotech 3:219–234. https://doi.org/10.22090/jwent.2018.03.003
Goncalves AH, Sicilian PH, Alves OC, Cesar D, Henriques CA, Gaspar AB (2020) Synthesis of a magnetic Fe3O4/RGO composite for the rapid photo-Fenton discoloration of indigo carmine dye. Topics Catal pp 13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-020-01277-0.
Gupta VK (2009) Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal–a review. J Environ Manag 90:2313–2342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.11.017
Gupta VK, Jain R, Varshney S (2007) Removal of Reactofix golden yellow 3 RFN from aqueous solution using wheat husk-an agricultural waste. J Hazard Mater 142:443–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.08.048
Han Y, Cao X, Ouyang X, Sohi SP, Chen J (2016) Adsorption kinetics of magnetic biochar derived from peanut hull on removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution: effects of production conditions and particle size. Chemosphere 145:336–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.050
Hessel C, Allegre C, Maisseu M, Charbit F, Moulin P (2007) Guidelines and legislation for dye house effluents. J Environ Manag 83:171–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.02.012
Ho YS, McKay G (2003) Sorption of dyes and copper ions onto biosorbents. Process Biochem 38:1047–1061. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(02)00239-X
Hossain MA, Ngo HH, Guo WS, Nguyen TV (2012) Palm oil fruit shells as biosorbent for copper removal from water and wastewater: experiments and sorption models. Bioresour Technol 113:97–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.11.111
Keypour H, Saremi SG, Noroozi M, Veisi H (2017) Synthesis of magnetically recyclable Fe3O4@[(EtO)3Si–L1H]/Pd(II) nanocatalyst and application in Suzuki and Heck coupling reactions. Appl Organomet Chem 31:7. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.3558
Khenifi A, Bouberka Z, Sekrane F, Kameche M, Derriche Z (2007) Adsorption study of an industrial dye by an organic clay. Adsorp 13:149–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-007-9016-6
Konan ATS, Richard R, Andriantsiferana C, Yao KB, Manero MH (2020) Recovery of borassus palm tree and bamboo waste into activated carbon: application to the phenolic compound removal. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 11:1584–1598
Konicki W, Aleksandrzak M, Moszyński D, Mijowska E (2017) Adsorption of anionic azo-dyes from aqueous solutions onto graphene oxide: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Colloid Interface Sci 496:188–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.02.031
Kulkarni MR, Revanth T, Acharya A, Bhat P (2017) Removal of crystal violet dye from aqueous solution using water hyacinth: equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics study. Resource-Efficient Technol 3:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reffit.2017.01.009
Kumar KV, Kumaran A (2005) Removal of methylene blue by mango seed kernel powder. Biochem Eng J 27:83–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2005.08.004
Langmuir I (1916) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I Solids. J Am Chem Soc 38:2221–2295. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02268a002
Machala L, Tucek J, Zboril R (2011) Polymorphous transformations of nanometric iron (III) oxide: a review. Chem Mater 23:3255–3272. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm200397g
Mahdavi M, Namvar F, Ahmad MB, Mohamad R (2013) Green biosynthesis and characterization of magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using seaweed (Sargassum muticum) aqueous extract. Molecules 18:5954–5964. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18055954
Malek NNA, Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS, Ismail K, Hameed BH (2020) New magnetic Schiff’s base-chitosan-glyoxal/fly ash/Fe3O4 biocomposite for the removal of anionic azo dye: an optimized process. Int J Biol Macromol 146:530–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.020
Miraboutalebi SM, Nikouzad SK, Peydayesh M, Allahgholi N, Vafajoo L, McKayc G (2017) Methylene blue adsorption via maize silk powder: kinetic, equilibrium, thermodynamic studies, and residual error analysis. Proc Safety Environ Prot 106:191–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.01.010
Mtshatsheni KN, Naidoo BE, Ofomaja AE (2020) Characterization of grafted acrylamide onto pine magnetite composite for the removal of methylene blue from wastewater. In Textile Industry and Waste pp 15. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.92114.
Mushtaq W, Rafiq M, Mushtaq Z, Nadeem F, Abdul H (2019) Wastewater treatment and dye sequestration using potential magnetic composites–a comprehensive review. Int J Chem Biochem Sci 15:74–86
Nia NN, Rahmani M, Kaykhaii M, Sasani M (2017) Evaluation of eucalyptus leaves as an adsorbent for decolourization of methyl violet (2B) dye in contaminated waters: thermodynamic and kinetics model. Model Earth Syst Environ 3:825–829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0338-4
Nnadozie EC, Ajibade PA (2020) Adsorption, kinetic and mechanistic studies of Pb (II) and Cr (VI) ions using APTES functionalized magnetic biochar. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 309:110573–110581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110573
Nnadozie EC, Ajibade PA (2021) Isotherm, kinetics, thermodynamics studies and effects of carbonization temperature on adsorption of indigo carmine (IC) dye using C. odorata biochar. Chem Data Collect 33:100673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cdc.2021.100673
Ogugbue CJ, Sawidis T (2011) Bioremediation and detoxification of synthetic wastewater containing triarylmethane dyes by Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from industrial effluent. Biotechnol Res Int 2011:11. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/967925
Ooi J, Lee LY, Hiew BYZ, Thangalazhy-Gopakumar S, Lim SS, Gan S (2017) Assessment of fish scales waste as a low cost and eco-friendly adsorbent for removal of an azo dye: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Bioresour Technol 245:656–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.153
Othman N, Abd-Kadir A, Zayadi N (2016) Waste fish scale as cost-effective adsorbent in removing zinc and ferum ion in wastewater. J Eng Appl Sci 11:1584–1592
Owens JW (2002) Chemical toxicity indicators for human health: case study for classification of chronic noncancer chemical hazards in life-cycle assessment. Environ Toxicol Chem: An International Journal 21:207–225. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620210129
Panhwar A, Faryal K, Kandhro A, Brohi N, Khanzada S, Ahmed K (2020) Removal of color from textile industry effluent. J Chem, Bio Physic Sci 10:299–304. https://doi.org/10.24214/jcbps.D.10.3.29904
Pati F, Adhikari B, Dhara S (2010) Isolation and characterization of fish scale collagen of higher thermal stability. Bioresour Technol 101:3737–3742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.133
Pattanayak M, Nayak P (2013) Ecofriendly green synthesis of iron nanoparticles from various plants and spices extract. Int J Plant, Anim Environ Sci 3:68–78
Pereira L, Alves M (2012) Dyes-environmental impact and remediation. In Environmental protection strategies for sustainable development. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 111–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-1591-2_4
Pereira PCG, Reimão RV, Pavesi T, Saggioro EM, Moreira JC, Correia FV (2017) Lethal and sub-lethal evaluation of indigo carmine dye and byproducts after TiO2 photocatalysis in the immune system of Eisenia andrei earthworms. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 143:275–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.05.043
Rahmi M, Faid M, ElYachioui M, Berny EH, Fakir M, Ouhssine M (2008) Protein-rich ingredients from fish waste for sheep feeding. Afri J Micro Res 2:73–77. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR
Ramesh TN, Pavagada Sreenivasa V (2015) Removal of indigo carmine dye from aqueous solution using magnesium hydroxide as an adsorbent. J Mater 2015:10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/753057
Ramesh TN, Kirana DV, Mohana Kumari TN, Ashwini A (2013) Adsorption studies of indigo carmine dye by magnesium oxide. Int J of Sci Res 1:495–501
Ramesha GK, Kumara AV, Muralidhara HB, Sampath S (2011) Graphene and graphene oxide as effective adsorbents toward anionic and cationic dyes. J Colloid Interface Sci 361:270–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.05.050
Redlich O, Peterson DL (1959) A useful adsorption isotherm. J Phys Chem 63:1024–1026. https://doi.org/10.1021/j150576a611
Robinson T, Chandran B, Nigam P (2002) Removal of dyes from a synthetic textile dye effluent by biosorption on apple pomace and wheat straw. Water Res 36:2824–2830. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00521-8
Santhi T, Manonmani S, Vasantha VS, Chang YT (2016) A new alternative adsorbent for the removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution. Arab J Chem 9:466–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2011.06.004
Sharma P, Kaur H (2011) Sugarcane bagasse for the removal of erythrosine B and methylene blue from aqueous waste. Appl Water Sci 1:135–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-011-0018-x
Shikuku VO, Achieng GO, Kowenje CO (2020) Removal of dyes from wastewater by adsorption onto low-cost adsorbents. In Impact of Textile Dyes on Public Health and the Environment (pp. 239-257). IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-7998-0311-9.ch011.
Sips RJ (1948) On the structure of a catalyst surface. J Chem Phys 16:490–495. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1746922
Slimani R, El Ouahabi I, Abidi F, El Haddad M, Regti A, Laamari MR, El Antri S, Lazar S (2014) Calcined eggshells as a new biosorbent to remove basic dye from aqueous solutions: thermodynamics, kinetics, isotherms and error analysis. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45:1578–1587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2013.10.009
Song W, Liu M, Hu R, Tan X, Li J (2014) Water-soluble polyacrylamide coated-Fe3O4 magnetic composites for high-efficient enrichment of U (VI) from radioactive wastewater. Chem Eng J 246:268–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.02.101
Srivastava S (2012) Synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticle from FeCl3 by using polyvinyl alcohol. Int J Physical Soc Sci 2:161–184
Sun P, Hui C, Khan RA, Du J, Zhang Q (2015) Zhao YH (2015) Efficient removal of crystal violet using Fe3O4-coated biochar: the role of the Fe3O4 nanoparticles and modelling study their adsorption behaviour. Sci Rep 5:12. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12638
Temkin MI, Pyzhev V (1940) Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalyst. Acta Phys Chim USSR 12:327–356
Toth J (1971) State equations of the solid-gas interface layer. Acta Chem Acad Hung 69:311–317
Treybal RE (1981) Mass-transfer operations, 3rd ed., McGraw-Hill. Using tree fern as a biosorbent. Process Biochem 40:119–124
Wu N, Liu X, Zhao C, Cui C, Xia A (2016) Effects of particle size on the magnetic and microwave absorption properties of carbon-coated nickel nano-capsules. J Alloys Comp 656:628–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.10.027
Xiu S, Shahbazi A, Li R (2017) Characterization, modification and application of biochar for energy storage and catalysis: a review. Trends Renew Energy 3:86–101. https://doi.org/10.17737/tre.2017.3.1.0033
Xu Y, Wang E (2012) Electrochemical biosensors based on magnetic micro/nanoparticles. Electrochim Acta 84:62–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.03.147
Yadav S, Asthana A, Chakraborty R, Jain B, Singh AK, Carabineiro SAC, Susan MABH (2020) Cationic dye removal using novel magnetic/activated charcoal/β-cyclodextrin/alginate polymer nanocomposite. Nanomater 10:170–189. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010170
Yu X, Tong S, Ge M, Zuo J, Cao C, Song W (2013) One-step synthesis of magnetic composites of cellulose@ iron oxide nanoparticles for arsenic removal. J Mater Chem A 1:959–965. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2TA00315E
Zhang M, Gao B, Varnoosfaderani S, Hebard A, Yao Y, Inyang M (2013) Preparation and characterization of a novel magnetic biochar for arsenic removal. Bioresour Technol 130:457–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.11.132
Zhang J, Zhang P, Zhang S, Zhou Q (2014) Comparative study on the adsorption of tartrazine and indigo carmine onto Maize cob carbon. Sep Sci Technol 49:877–886. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2013.863340
Zhang B, Zeng X, Xu P, Chen J, Xu Y, Luo G, Xu M, Yao H (2016) Using the novel method of nonthermal plasma to add Cl active sites on activated carbon for removal of mercury from flue gas. Environ Sci Technol 50:11837–11843. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b01919
Zhang Q, Cheng Y, Fang C, Chen J, Chen H, Li H, Yao Y (2020) Facile synthesis of porous carbon/Fe3O4 composites derived from waste cellulose acetate by one-step carbothermal method as a recyclable adsorbent for dyes. J Mater Res Technol 9:3384–3393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.01.074
Zheng X, Zheng H, Xiong Z, Zhao R, Liu Y, Zhao C, Zheng C (2020) Novel anionic polyacrylamide-modify-chitosan magnetic composite nanoparticles with excellent adsorption capacity for cationic dyes and pH-independent adsorption capability for metal ions. Chem Eng J 392:123706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123706
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Maseno University, the University of KwaZulu-Natal, and the Technical University of Kenya. Lastly, research financial support from Exceed-Swindon organization.
Funding
GOA received funding from the National Research Foundation (NRF-Kenya) and DAAD-Center of Excellence of International Network on Sustainable Water Management in Developing Countries (exceed-Swindon).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
George O. Achieng’: Investigation, experimental work, validation, software, formalization of analyses, and drafting of the original manuscript. Chrispin O. Kowenje: Conceptualization, supervision, resources, review, and editing of the draft. Joseph O. Lalah: Supervision, resources, review, and editing of the draft. Stephen O. Ojwach: Supervision, resources, review, and editing of the draft, corresponding author.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Santiago V. Luis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary materials contain additional spectral data, micrograph images, kinetic posts, and adsorption data figures.
ESM 1
(DOCX 1749 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Achieng’, G.O., Kowenje, C.O., Lalah, J.O. et al. Synthesis and characterization of FSB@Fe3O4 composites and application in removal of indigo carmine dye from industrial wastewaters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 54876–54890 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14432-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14432-1