Abstract
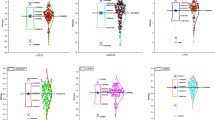
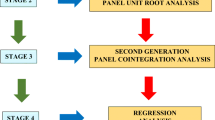
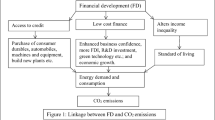
This study explores the role of foreign direct investment (FDI), financial development (FD), and globalization (GLO) in environmental degradation (ED) through the channel of energy consumption (EC) for the selected panel of belt and road initiative (BRI) countries for 1990–2017. The study applies appropriate panel unit root tests, the Westerlund cointegration test, the dynamic seemingly unrelated regression (DSUR) long-run panel estimation approach, and the Dumitrescu–Hurlin panel causality test. Results of panel unit root test ascertain variables are interred either at a level or after first difference and long-run association documents by implementing conventional and error correction. Study findings with DSUR, in the long run, reveal that energy consumption and economic growth expose positive statistically significant association with environmental degradation, implying intensity in energy consumption and aggregate output level shall augment the present state of environmental degradation. While negative statistically significant effects reveal running from FDI, financial development, and globalization to environmental degradation, implying that energy efficiency technology, the scope of green financing through financial development, and cross country effects help the economy reduce environmental consequences with lesser carbon emission. Results of directional causality unveiled feedback hypothesis available in explaining the causality between environmental degradation and energy consumption [ED←➔EC] and FDI and environmental degradation [FDI←➔ED], moreover, unidirectional effects running from financial development, globalization, and economic growth to environmental degradation, i.e., [FD➔ED; GLO➔ED; Y➔ED]. The finding reveals the need to formulate energy policies that promote belt and road (BR) country energy efficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Notes
IEA. World Energy Statistics and Balances. Paris: International Energy Agency; 2017.
Albania, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Bahrain, Belarus, Bangladesh, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Brunei, Cambodia, Colombia, China, Czech Republic, Croatia, Egypt Arab Rep., Ethiopia, Estonia, Georgia, Hungary, Indonesia, India, Iran Iraq, Islamic Rep., Israel, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Rep., Korea Rep., Lebanon, Macedonia, Mongolia, Malaysia, Moldova, Myanmar, Morocco, New Zealand, Nepal, Oman, Panama, Pakistan, Poland, Philippines, Qatar, Russian Federation, Romania, Singapore, Saudi Arabia, Slovak Republic, South Africa, Slovenia, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Tajikistan, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, Ukraine, Vietnam, Yemen Republic.
References
Abidin ISZ, Haseeb M, Azam M, Islam R (2015) Foreign direct investment, financial Development, international trade and energy consumption: panel data evidence from selected ASEAN Countries. Int J Energy Econ Policy 5(3)
Acheampong AO (2018) Economic growth, CO2 emissions and energy consumption: what causes what and where? Energy Econ 74:677–692
Adams S, Klobodu EKM (2018) Financial development and environmental degradation: does political regime matter? J Clean Prod 197:1472–1479
Adamu TM, Haq IU, Shafiq M (2019) Analyzing the impact of energy, export variety, and FDI on environmental degradation in the context of environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: a case study of India. Energies 12(6):1076
Adebayo TS, Kirikkaleli D (2021) Impact of renewable energy consumption, globalization, and technological innovation on environmental degradation in Japan: application of wavelet tools. Environment, Development and Sustainability
Ahmed Z and Le HP (2020) "Linking information communication technology, trade globalization index, and CO2 emissions: evidence from advanced panel techniques." Environ Sci Pollut Res: 1-12.
Akhmat G, Zaman K, Shukui T, Irfan D, Khan MM (2014) Does energy consumption contribute to environmental pollutants? Evidence from SAARC countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(9):5940–5951
Al-mulali U, Lee JY (2013) Estimating the impact of the financial development on energy consumption: evidence from the GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) countries. Energy 60:215–221
Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I (2015) The effect of energy consumption, urbanization, trade openness, industrial output, and the political stability on the environmental degradation in the MENA (Middle East and North African) region. Energy 84:382–389
Al-mulali U, Tang CF, Ozturk I (2015) Does financial development reduce environmental degradation? Evidence from a panel study of 129 countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(19):14891–14900
Alam A, Malik IA, Abdullah AB, Hassan A, Awan U, Ali G, Zaman K, Naseem I (2015) Does financial development contribute to SAARC′ S energy demand? From energy crisis to energy reforms. Renew Sust Energ Rev 41:818–829
Alam S, Fatima A, Butt MS (2007) Sustainable development in Pakistan in the context of energy consumption demand and environmental degradation. J Asian Econ 18(5):825–837
Ali MU, Gong Z, Ali MU, Wu X and Yao C (2020a) "Fossil energy consumption, economic development, inward FDI impact on CO2 emissions in Pakistan: testing EKC hypothesis through ARDL model." International Journal of Finance & Economics n/a(n/a).
Ali W, Sadiq F, Kumail T, Li H, Zahid M, Sohag K (2020b) A cointegration analysis of structural change, international tourism and energy consumption on CO2 emission in Pakistan. Curr Issue Tour 23(23):3001–3015
Alsaman AS, Askalany AA, Harby K, Ahmed MS (2017) Performance evaluation of a solar-driven adsorption desalination-cooling system. Energy 128:196–207
Aluko OA, Opoku EEO, Ibrahim M (2021) Investigating the environmental effect of globalization: Insights from selected industrialized countries. J Environ Manag 281:111892
Anser MK, Yousaf Z, Nassani AA, Vo XV, Zaman K (2020) Evaluating ‘natural resource curse’hypothesis under sustainable information technologies: a case study of Saudi Arabia. Res Policy 68:101699
Audi M and Ali A (2018) "Determinants of environmental degradation under the perspective of globalization: a panel analysis of selected MENA nations."
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Driha OM, Shahbaz M, Sinha A (2020) The effects of tourism and globalization over environmental degradation in developed countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(7):7130–7144
Bastola U, Sapkota P (2015) Relationships among energy consumption, pollution emission, and economic growth in Nepal. Energy 80:254–262
Belke A, Dobnik F, Dreger C (2011) Energy consumption and economic growth: new insights into the cointegration relationship. Energy Econ 33(5):782–789
Ben Mbarek M, Saidi K, Rahman MM (2018) Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption, environmental degradation and economic growth in Tunisia. Qual Quant 52(3):1105–1119
Bölük G, Mert M (2014) Fossil & renewable energy consumption, GHGs (greenhouse gases) and economic growth: Evidence from a panel of EU (European Union) countries. Energy 74:439–446
Bozkurt C, Akan Y (2014) Economic growth, CO2 emissions and energy consumption: the Turkish case. Int J Energy Econ Policy 4(3):484
Breitung J (2001) The local power of some unit root tests for panel data. Nonstationary panels, panel cointegration, and dynamic panels, Emerald Group Publishing Limited: 161-177.
Breusch TS, Pagan AR (1980) The Lagrange multiplier test and its applications to model specification in econometrics. Rev Econ Stud 47(1):239–253
Chang S-C (2015a) Effects of financial developments and income on energy consumption. Int Rev Econ Financ 35:28–44
Chang S-C (2015b) Threshold effect of foreign direct investment on environmental degradation. Port Econ J 14(1):75–102
Cheng C, Ren X, Wang Z, Yan C (2019) Heterogeneous impacts of renewable energy and environmental patents on CO2 emission - evidence from the BRIICS. Sci Total Environ 668:1328–1338
Çoban S, Topcu M (2013) The nexus between financial development and energy consumption in the EU: A dynamic panel data analysis. Energy Econ 39:81–88
Dabachi UM, Mahmood S, Ahmad AU, Ismail S, Farouq IS, Jakada AH, Kabiru K (2020) Energy consumption, energy price, energy intensity environmental degradation, and economic growth nexus in african OPEC countries: evidence from simultaneous equations models. J Environ Treat Tech 8(1):403–409
Dogan B, Deger O (2016) How globalization and economic growth affect energy consumption: panel data analysis in the sample of BRIC countries. Int J Energy Econ Policy 6(4)
Dogan E, Aslan A (2017) Exploring the relationship among CO2 emissions, real GDP, energy consumption and tourism in the EU and candidate countries: evidence from panel models robust to heterogeneity and cross-sectional dependence. Renew Sust Energ Rev 77:239–245
Doytch N, Narayan S (2016) Does FDI influence renewable energy consumption? An analysis of sectoral FDI impact on renewable and non-renewable industrial energy consumption. Energy Econ 54:291–301
Dumitrescu E-I, Hurlin C (2012) Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econ Model 29(4):1450–1460
Emre Caglar A (2020) The importance of renewable energy consumption and FDI inflows in reducing environmental degradation: bootstrap ARDL bound test in selected 9 countries. J Clean Prod 264:121663
Eyuboglu K, Uzar U (2021) A new perspective to environmental degradation: the linkages between higher education and CO2 emissions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(1):482–493
Fan L, Pan S, Liu G, Zhou P (2017) Does energy efficiency affect financial performance? Evidence from Chinese energy-intensive firms. J Clean Prod 151:53–59
Farhani S, Solarin SA (2017) Financial development and energy demand in the United States: new evidence from combined cointegration and asymmetric causality tests. Energy 134:1029–1037
Framework I (2015) "Vision and actions on jointly building silk road economic belt and 21st-century maritime silk road."
Furuoka F (2015) Electricity consumption and economic development in Asia: new data and new methods. Asian-Pac Econ Lit 29(1):102–125
Godement F and Kratz A (2015) One Belt, One Road’: China’s great leap outward. European Council on Foreign Relations.
Gómez M, Rodríguez JC (2019) Energy consumption and financial development in NAFTA Countries, 1971–2015. Appl Sci 9(2):302
Gulistan A, Tariq YB, Bashir MF (2020) Dynamic relationship among economic growth, energy, trade openness, tourism, and environmental degradation: fresh global evidence. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(12):13477–13487
Hadri K (2000) Testing for stationarity in heterogeneous panel data. Econ J 3(2):148–161
Han L, Han B, Shi X, Su B, Lv X, Lei X (2018) Energy efficiency convergence across countries in the context of China’s Belt and Road initiative. Appl Energy 213:112–122
Islam F, Shahbaz M, Ahmed AU, Alam MM (2013) Financial development and energy consumption nexus in Malaysia: a multivariate time series analysis. Econ Model 30:435–441
Jelinek JA (2017) Shifting relations in South-East Asia: the changing Philippine-Sino-American foreign relations in the early era of the Duterte administration, Central European University.
Kahouli B (2017) The short and long run causality relationship among economic growth, energy consumption and financial development: evidence from South Mediterranean Countries (SMCs). Energy Econ 68:19–30
Kao C (1999) Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data. J Econ 90(1):1–44
Kaufmann RK, Davidsdottir B, Garnham S, Pauly P (1998) The determinants of atmospheric SO2 concentrations: reconsidering the environmental Kuznets curve. Ecol Econ 25(2):209–220
Kearney A, Policy F (2006) Globalization index. Foreign Policy 157:74–81
Khan MTI, Yaseen MR, Ali Q (2017) Dynamic relationship between financial development, energy consumption, trade and greenhouse gas: comparison of upper middle income countries from Asia, Europe, Africa and America. J Clean Prod 161:567–580
Kivyiro P, Arminen H (2014) Carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, and foreign direct investment: causality analysis for Sub-Saharan Africa. Energy 74:595–606
Kochi I, López PCM (2013) Beyond the environmental Kuznets curve: understanding the determinants of environmental degradation in Mexico. Nóesis Revista de Ciencias Sociales y Humanidades 22(43-1):52–83
Kumar M, Babu MS, Loganathan N and Shahbaz M (2016) "Does financial development intensify energy consumption in Saudi Arabia?".
Lashof DA, Ahuja DR (1990) Relative contributions of greenhouse gas emissions to global warming. Nature 344(6266):529–531
Lee JW (2013) The contribution of foreign direct investment to clean energy use, carbon emissions and economic growth. Energy Policy 55:483–489
Levin A, Lin C-F, Chu C-SJ (2002) Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J Econ 108(1):1–24
Mahdi Ziaei S (2015) Effects of financial development indicators on energy consumption and CO2 emission of European, East Asian and Oceania countries. Renew Sust Energ Rev 42:752–759
Mark NC, Ogaki M, Sul D (2005) Dynamic seemingly unrelated cointegrating regressions. Rev Econ Stud 72(3):797–820
Menyah K, Nazlioglu S, Wolde-Rufael Y (2014) Financial development, trade openness and economic growth in African countries: new insights from a panel causality approach. Econ Model 37:386–394
Muhammad B, Khan MK, Khan MI, Khan S (2021) Impact of foreign direct investment, natural resources, renewable energy consumption, and economic growth on environmental degradation: evidence from BRICS, developing, developed and global countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(17):21789–21798
Nadeem AM, Ali T, Khan MT, Guo Z (2020) Relationship between inward FDI and environmental degradation for Pakistan: an exploration of pollution haven hypothesis through ARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–19
Naradda Gamage SK, Hewa Kuruppuge R, Haq IU (2017) Energy consumption, tourism development, and environmental degradation in Sri Lanka. Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning, and Policy 12(10):910–916
Nasir M, Ur Rehman F (2011) Environmental Kuznets curve for carbon emissions in Pakistan: An empirical investigation. Energy Policy 39(3):1857–1864
Nazlioglu S, Lebe F, Kayhan S (2011) Nuclear energy consumption and economic growth in OECD countries: cross-sectionally dependent heterogeneous panel causality analysis. Energy Policy 39(10):6615–6621
O'Connell PG (1998) The overvaluation of purchasing power parity. J Int Econ 44(1):1–19
Ozturk I, Acaravci A (2013) The long-run and causal analysis of energy, growth, openness and financial development on carbon emissions in Turkey. Energy Econ 36:262–267
Palit A (2017) India’s economic and strategic perceptions of China’s maritime silk road initiative. Geopolitics 22(2):292–309
Pedroni P (1999) Critical values for cointegration tests in heterogeneous panels with multiple regressors. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 61(S1):653–670
Pedroni P (2001) Purchasing power parity tests in cointegrated panels. Rev Econ Stat 83(4):727–731
Pedroni P (2004) Panel cointegration: asymptotic and finite sample properties of pooled time series tests with an application to the PPP hypothesis. Econometric theory 20(3):597–625
Pesaran MH (2004) "General diagnostic tests for cross section dependence in panels."
Pesaran MH (2006) Estimation and inference in large heterogeneous panels with a multifactor error structure. Econometrica 74(4):967–1012
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Econ 22(2):265–312
Pesaran MH, Shin Y (1998) An autoregressive distributed-lag modelling approach to cointegration analysis. Econometric Society Monographs 31:371–413
Pesaran MH, Ullah A, Yamagata T (2008) A bias-adjusted LM test of error cross-section independence. Econ J 11(1):105–127
Pesaran MH, Yamagata T (2008) Testing slope homogeneity in large panels. J Econ 142(1):50–93
Pohekar SD, Ramachandran M (2004) Application of multi-criteria decision making to sustainable energy planning—a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 8(4):365–381
Qamruzzaman M, Jianguo W (2018) Investigation of the asymmetric relationship between financial innovation, banking sector development, and economic growth. Quant Finance and Econ 2(4):952–980
Qamruzzaman M, Jianguo W (2020) The asymmetric relationship between financial development, trade openness, foreign capital flows, and renewable energy consumption: fresh evidence from panel NARDL investigation. Renew Energy 159:827–842
Qamruzzaman M, Jianguo W, Jahan S and Yingjun Z (2020) "Financial innovation, human capital development, and economic growth of selected South Asian countries: an application of ARDL approach." International Journal of Finance & Economics.
Qamruzzaman M, Wei J (2018) Financial innovation, stock market development, and economic growth: an application of ARDL model. Int J Financ Stud 6(3):69
Qamruzzaman M, Wei J (2019) Do financial inclusion, stock market development attract foreign capital flows in developing economy: a panel data investigation. Quant Financ Econ 3:88–108
Rahman MM (2020) Environmental degradation: the role of electricity consumption, economic growth and globalisation. J Environ Manag 253:109742
Rahman MM, Kashem MA (2017) Carbon emissions, energy consumption and industrial growth in Bangladesh: empirical evidence from ARDL cointegration and Granger causality analysis. Energy Policy 110:600–608
Rahman ZU, Ahmad M (2019) Modeling the relationship between gross capital formation and CO2 (a)symmetrically in the case of Pakistan: an empirical analysis through NARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(8):8111–8124
Raza SA, Shah N, Sharif A (2019) Time frequency relationship between energy consumption, economic growth and environmental degradation in the United States: evidence from transportation sector. Energy 173:706–720
Rehman MU, Rashid M (2017) Energy consumption to environmental degradation, the growth appetite in SAARC nations. Renew Energy 111:284–294
Rjoub H, Odugbesan JA, Adebayo TS, Wong W-K (2021) Sustainability of the moderating role of financial development in the determinants of environmental degradation: evidence from Turkey. Sustainability 13(4):1844
Saboori B, Sulaiman J (2013) Environmental degradation, economic growth and energy consumption: evidence of the environmental Kuznets curve in Malaysia. Energy Policy 60:892–905
Sadorsky P (2010) The impact of financial development on energy consumption in emerging economies. Energy Policy 38(5):2528–2535
Sadorsky P (2011) Financial development and energy consumption in Central and Eastern European frontier economies. Energy Policy 39(2):999–1006
Saud S, Baloch MA, Lodhi RN (2018) The nexus between energy consumption and financial development: estimating the role of globalization in Next-11 countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(19):18651–18661
Saud S, Chen S, Danish, Haseeb A (2019a) Impact of financial development and economic growth on environmental quality: an empirical analysis from Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(3):2253–2269
Saud S, Chen S, Haseeb A (2019b) Impact of financial development and economic growth on environmental quality: an empirical analysis from Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(3):2253–2269
Sehrawat M, Giri A, Mohapatra G (2015) The impact of financial development, economic growth and energy consumption on environmental degradation. An International Journal, Management of Environmental Quality
Shahbaz M, Hye QMA, Tiwari AK, Leitão NC (2013a) Economic growth, energy consumption, financial development, international trade and CO2 emissions in Indonesia. Renew Sust Energ Rev 25:109–121
Shahbaz M, Khan S, Ali A, Bhattacharya M (2017a) The impact of globalization on CO2 emissions in China. Singap Econ Rev 62(04):929–957
Shahbaz M, Khan S, Tahir MI (2013b) The dynamic links between energy consumption, economic growth, financial development and trade in China: fresh evidence from multivariate framework analysis. Energy Econ 40:8–21
Shahbaz M, Mallick H, Mahalik MK, Sadorsky P (2016) The role of globalization on the recent evolution of energy demand in India: implications for sustainable development. Energy Econ 55:52–68
Shahbaz M, Nasir MA, Roubaud D (2018) Environmental degradation in France: the effects of FDI, financial development, and energy innovations. Energy Econ 74:843–857
Shahbaz M, Van Hoang TH, Mahalik MK, Roubaud D (2017b) Energy consumption, financial development and economic growth in India: new evidence from a nonlinear and asymmetric analysis. Energy Econ 63:199–212
Sirin SM (2017) Foreign direct investments (FDIs) in Turkish power sector: a discussion on investments, opportunities and risks. Renew Sust Energ Rev 78:1367–1377
Solarin SA, Shahbaz M, Mahmood H, Arouri M (2013) Does financial development reduce CO2 emissions in Malaysian economy? A time series analysis. Econ Model 35:145–152
Sun H, Mohsin M, Alharthi M, Abbas Q (2020) Measuring environmental sustainability performance of South Asia. J Clean Prod 251:119519
Tamazian A, Bhaskara Rao B (2010) Do economic, financial and institutional developments matter for environmental degradation? Evidence from transitional economies. Energy Econ 32(1):137–145
Tamazian A, Chousa JP, Vadlamannati KC (2009) Does higher economic and financial development lead to environmental degradation: evidence from BRIC countries. Energy Policy 37(1):246–253
Tan BW, Tang CF (2016) Examining the causal linkages among domestic investment, FDI, trade, interest rate and economic growth in ASEAN-5 countries. Int J Econ Financ Issues 6(1)
Tang CF, Tan BW (2014) The linkages among energy consumption, economic growth, relative price, foreign direct investment, and financial development in Malaysia. Qual Quant 48(2):781–797
Topcu M, Payne JE (2017) The financial development–energy consumption nexus revisited. Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning, and Policy 12(9):822–830
Usman O, Olanipekun IO, Iorember PT, Abu-Goodman M (2020) Modelling environmental degradation in South Africa: the effects of energy consumption, democracy, and globalization using innovation accounting tests. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(8):8334–8349
Wang S, Ang HM, Tade MO (2007) Volatile organic compounds in indoor environment and photocatalytic oxidation: State of the art. Environ Int 33(5):694–705
Westerlund J (2007) Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxf Bull Econ Stat 69(6):709–748
Westerlund J (2008) Panel cointegration tests of the Fisher effect. J Appl Econ 23(2):193–233
Wolde-Rufael Y (2014) Electricity consumption and economic growth in transition countries: a revisit using bootstrap panel Granger causality analysis. Energy Econ 44:325–330
World Bank (2017) World Development Indicators. World Bank. http://data.worldbank.org/data-catalog/worlddevelopment-indicators
Xu SJ (2012) The impact of financial development on energy consumption in China: based on SYS-GMM estimation. Trans Tech Publ, Advanced Materials Research
Yuan S, Chen Y-P, Qin J-S, Lu W, Zou L, Zhang Q, Wang X, Sun X, Zhou H-C (2016) Linker Installation: Engineering Pore Environment with Precisely Placed Functionalities in Zirconium MOFs. J Am Chem Soc 138(28):8912–8919
Zaman K, Moemen MA-E (2017) Energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions and economic development: evaluating alternative and plausible environmental hypothesis for sustainable growth. Renew Sust Energ Rev 74:1119–1130
Zhang Y-J (2011) The impact of financial development on carbon emissions: an empirical analysis in China. Energy Policy 39(4):2197–2203
Zheng C, Acheampong AK, Shi Z, Mugzech A, Halaly-Basha T, Shaya F, Sun Y, Colova V, Mosquna A, Ophir R, Galbraith DW, Or E (2018) Abscisic acid catabolism enhances dormancy release of grapevine buds. Plant Cell Environ 41(10):2490–2503
Acknowledgements
We want to express our heartfelt gratitude to the esteemed reviewer for his thoughtful suggestions and recommendation during the revision process. Furthermore, we are also grateful to the editor-in-chief for his kindness.
Funding
The study does not receive any financial support from any agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Md Qamruzzaman.; Methodology, Md Qamruzzaman, Jianxin Zhuo; Software, Jianxin Zhuo; Formal Analysis, Md Qamruzzaman, Jianxin Zhuo; Writing—original draft preparation, Md Qamruzzaman, Writing—review and editing, Md Qamruzzaman, Jianxin Zhuo. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Nicholas Apergis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
1. Study gauges the effects of energy consumption, financial development, FDI, and globalization effects on environmental degradation in road and belt countries.
2. The study applies DSUR and panel granger causality test (Dumitrescu and Hurlin 2012).
3. In the long run, energy consumption and economic growth exposed positive association with environmental degradation.
4. Environmental quality can be improved through FDI, financial development, and globalization
5. Study documents feedback hypothesis for environmental degradation and energy consumption and FDI and environmental degradation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuo, J., Qamruzzaman, M. Do financial development, FDI, and globalization intensify environmental degradation through the channel of energy consumption: evidence from belt and road countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 2753–2772 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15796-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15796-0