Abstract
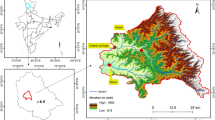
This paper aimed at examining the climate variability and land-use change effects on streamflow and pollutant loadings, namely total suspended sediment (TSS), total nitrogen (T-N), and total phosphorus (T-P), in the Sesan, Sekong, and Srepok (3S) River Basin in the period 1981–2010. The well-calibrated and validated Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) was used for this purpose. Compared to the reference period, climate variability was found to be responsible to a 1.00% increase in streamflow, 2.91% increase in TSS loading, 11.35% increase in T-N loading, and 19.12% reduction in T-P loading for the whole basin. With regard to the effect of land-use change (LUC), streamflow, TSS, T-N, and T-P loadings increased by 0.01%, 3.70%, 10.12%, and 10.94%, respectively. Therefore, the combination of climate variability and LUC showed amplified increases in streamflow (1.03%), TSS loading (7.09%), and T-N loading (25.05%), and a net effect of decreased T-P loading (10.35%). Regarding the Sekong and Srepok River Basins, the streamflow, TSS, T-N and T-P showed stronger responses to climate variability compared to LUC. In case of the Sesan River Basin, LUC had an effect on water quantity and quality more strongly than the climate variability. In general, the findings of this work play an essential role in providing scientific information to effectively support decision makers in developing sustainable water resources management strategies in the study area.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abbaspour KC (2015) SWAT-CUP: SWAT Calibration and Uncertainty Programs - a user manual. Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology, Eawag
Adamson PT, Rutherfurd ID, Peel MC, Conlan IA (2009) The hydrology of the Mekong River. In: Campbell ICBT-TM (ed) The Mekong. Elsevier, San Diego, pp 53–76
Arnold JG, Srinivasan R, Muttiah RS, Williams JR (1998) Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment - Part I: Model development. J Am Water Resour Assoc 34:73–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1998.tb05961.x
Baran E, Guerin E, Nasielski J (2015) Fish, sediment and dams in the Mekong. In: WorldFish, and CGIAR Research Program on Water. Land and Ecosystems (WLE), Penang
Bastia F, Equeenuddin SM (2016) Spatio-temporal variation of water flow and sediment discharge in the Mahanadi River, India. Glob Planet Change 144:51–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2016.07.004
Bieger K, Hörmann G, Fohrer N (2014) Simulation of streamflow and sediment with the soil and water assessment tool in a data scarce catchment in the Three Gorges Region, China. J Environ Qual 43:37–45. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2011.0383
Borrelli P, Robinson DA, Fleischer LR, Lugato E, Ballabio C, Alewell C, Meusburger K, Modugno S, Schütt B, Ferro V, Bagarello V, Oost KV, Montanarella L, Panagos P (2017) An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nat Commun 8:2013. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02142-7
Brath A, Montanari A, Moretti G (2006) Assessing the effect on flood frequency of land use change via hydrological simulation (with uncertainty). J Hydrol 324:141–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.10.001
Brodie JE, Mitchell AW (2005) Nutrients in Australian tropical rivers: changes with agricultural development and implications for receiving environments. Mar Freshw Res 56:279–302
Buda AR, DeWalle DR (2009) Dynamics of stream nitrate sources and flow pathways during stormflows on urban, forest and agricultural watersheds in central Pennsylvania, USA. Hydrol Process 23:3292–3305. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7423
Buytaert W, Célleri R, De Bièvre B et al (2006) Human impact on the hydrology of the Andean páramos. Earth-Science Rev 79:53–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2006.06.002
Constable D (2015a) The Sesan and Sre Pok River Basins. Bangkok, Thailand
Constable D (2015b) Atlas of the 3S Basins. IUCN, Bangkok
de Oliveira VA, de Mello CR, Beskow S, Viola MR, Srinivasan R (2019) Modeling the effects of climate change on hydrology and sediment load in a headwater basin in the Brazilian Cerrado biome. Ecol Eng 133:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.04.021
Delkash M, Al-Faraj FAM, Scholz M (2018) Impacts of anthropogenic land use changes on nutrient concentrations in surface waterbodies: a review. CLEAN - Soil, Air, Water 46:1800051. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201800051
Dijkstra FA, Pendall E, Morgan JA, Blumenthal DM, Carrillo Y, LeCain DR, Follett RF, Williams DG (2012) Climate change alters stoichiometry of phosphorus and nitrogen in a semiarid grassland. New Phytol 196:807–815. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04349.x
Du Plessis A, Harmse T, Ahmed F (2014) Quantifying and predicting the water quality associated with land cover change: a case study of the Blesbok Spruit Catchment, South Africa. Water 6(10):2946–2968. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6102946
Fu Q, Li L, Li M, Li T, Liu D, Hou R, Zhou Z (2018) An interval parameter conditional value-at-risk two-stage stochastic programming model for sustainable regional water allocation under different representative concentration pathways scenarios. J Hydrol 564:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.07.008
Fu Q, Shi R, Li T, Sun Y, Liu D, Cui S, Hou R (2019) Effects of land-use change and climate variability on streamflow in the Woken River basin in Northeast China. River Res Appl 35:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.3397
Han J, Ge W, Hei Z, Cong C, Ma C, Xie M, Liu B, Feng W, Wang F, Jiao J (2020) Agricultural land use and management weaken the soil erosion induced by extreme rainstorms. Agric Ecosyst Environ 301:107047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2020.107047
Hartman P, Carlucci K (2014) Climate change impact and adaptation study for the Lower Mekong Basin: Key final results, Bangkok
Hoang LP, Lauri H, Kummu M, Koponen J, van Vliet MTH, Supit I, Leemans R, Kabat P, Ludwig F (2016) Mekong River flow and hydrological extremes under climate change. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 20:3027–3041. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-20-3027-2016
Khoi DN, Suetsugi T (2014) Impact of climate and land-use changes on hydrological processes and sediment yield—a case study of the Be River catchment, Vietnam. Hydrol Sci J 59:1095–1108. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2013.819433
Khoi DN, Thom VT (2015) Impacts of climate variability and land-use change on hydrology in the period 1981-2009 in the central highlands of vietnam. Glob Nest J 17:870–881
Kondolf GM, Rubin ZK, Minear JT (2014) Dams on the Mekong: cumulative sediment starvation. Water Resour Res 50:5158–5169. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013WR014651
Li Z, Liu W, Zhang X, Zheng F (2009) Impacts of land use change and climate variability on hydrology in an agricultural catchment on the Loess Plateau of China. J Hydrol 377:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.08.007
Liu R, Zhang P, Wang X, Chen Y, Shen Z (2013) Assessment of effects of best management practices on agricultural non-point source pollution in Xiangxi River watershed. Agric Water Manag 117:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2012.10.018
Longyang Q (2019) Assessing the effects of climate change on water quality of plateau deep-water lake - a study case of Hongfeng Lake. Sci Total Environ 647:1518–1530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.031
López-Moreno JI, Vicente-Serrano SM, Moran-Tejeda E, Zabalza J, Lorenzo-Lacruz J, García-Ruiz JM (2011) Impact of climate evolution and land use changes on water yield in the ebro basin. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 15:311–322. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-15-311-2011
Ma X, Xu J, Luo Y, Prasad Aggarwal S, Li J (2009) Response of hydrological processes to land-cover and climate changes in Kejie watershed, south-west China. Hydrol Process 23:1179–1191. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7233
Moriasi DN, Arnold JG, Van Liew MW et al (2007) Model Evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans ASABE 50:885–900
MRC (2005) Overview of the hydrology OF the Mekong Basin. Mekong River Comm, Vientiane
Neitsch AL, Arnold JG, Kiniry JR, Williams JR (2011) Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version 2009. Texas A&M University, Texas
Oeurng C, Sauvage S, Sánchez-Pérez J-M (2010) Temporal variability of nitrate transport through hydrological response during flood events within a large agricultural catchment in south-west France. Sci Total Environ 409:140–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.09.006
Oeurng C, Cochrane TA, Arias ME, Shrestha B, Piman T (2016) Assessment of changes in riverine nitrate in the Sesan, Srepok and Sekong tributaries of the Lower Mekong River Basin. J Hydrol Reg Stud 8:95–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2016.07.004
Op de Hipt F, Diekkrüger B, Steup G et al (2019) Modeling the effect of land use and climate change on water resources and soil erosion in a tropical West African catch-ment (Dano, Burkina Faso) using SHETRAN. Sci Total Environ 653:431–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.351
Pirnia A, Darabi H, Choubin B, Omidvar E, Onyutha C, Haghighi AT (2019) Contribution of climatic variability and human activities to stream flow changes in the Haraz River basin, northern Iran. J Hydro-environment Res 25:12–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2019.05.001
Ranzi R, Le TH, Rulli MC (2012) A RUSLE approach to model suspended sediment load in the Lo river (Vietnam): effects of reservoirs and land use changes. J Hydrol 422–423:17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.12.009
Shao G, Guan Y, Zhang D, Yu B, Zhu J (2018) The Impacts of climate variability and land use change on streamflow in the Hailiutu River Basin. Water 10
Someth P et al (2013) Basin profile of the Lower Sekong, Sesan and Srepok (3S) Rivers in Cambodia. Project report: Challenge Program on Water & Food Mekong project MK3. In: Optimizing the management of a cascade of reservoirs at the catchment level. ICEM – International Centre for Environmental Management, Hanoi
Takamatsu M, Kawasaki A, Rogers PP, Malakie JL (2014) Development of a land-use forecast tool for future water resources assessment: case study for the Mekong River 3S Sub-basins. Sustain Sci 9:157–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-013-0225-5
Tan ML, Ibrahim AL, Yusop Z, Duan Z, Ling L (2015) Impacts of land-use and climate variability on hydrological components in the Johor River basin. Malaysia. Hydrol Sci J:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2014.967246
Tan ML, Gassman PW, Srinivasan R, Arnold JG, Yang XY (2019) A review of SWAT studies in Southeast Asia: applications, challenges and future directions. Water 11:914. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050914
Tomer MD, Schilling KE (2009) A simple approach to distinguish land-use and climate-change effects on watershed hydrology. J Hydrol 376:24–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.07.029
Wan R, Cai S, Li H, Yang G, Li Z, Nie X (2014) Inferring land use and land cover impact on stream water quality using a Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach in the Xitiaoxi River Watershed, China. J Environ Manage 133:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.11.035
Wang S, Kang S, Zhang L, Li F (2008) Modelling hydrological response to different land-use and climate change scenarios in the Zamu River basin of northwest China. Hydrol Process 22:2502–2510. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.6846
Wei X, Liu W, Zhou P (2013) Quantifying the relative contributions of forest change and climatic variability to hydrology in large watersheds: a critical review of research methods. Water 5:728–746. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020728
Whitehead PG, Barbour E, Futter MN, Sarkar S, Rodda H, Caesar J, Butterfield D, Jin L, Sinha R, Nicholls R, Salehin M (2015) Impacts of climate change and socio-economic scenarios on flow and water quality of the Ganges{,} Brahmaputra and Meghna (GBM) river systems: low flow and flood statistics. Environ Sci Process Impacts 17:1057–1069. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EM00619D
Wu C, Ji C, Shi B, Wang Y, Gao J, Yang Y, Mu J (2019) The impact of climate change and human activities on streamflow and sediment load in the Pearl River basin. Int J Sediment Res 34:307–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2019.01.002
Yang L, Feng Q, Yin Z, Wen X, Si J, Li C, Deo RC (2017) Identifying separate impacts of climate and land use/cover change on hydrological processes in upper stream of Heihe River, Northwest China. Hydrol Process 31:1100–1112. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.11098
Zhang L, Karthikeyan R, Bai Z, Srinivasan R (2017) Analysis of streamflow responses to climate variability and land use change in the Loess Plateau region of China. CATENA 154:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.02.012
Zhang L, Nan Z, Yu W, Zhao Y, Xu Y (2018) Comparison of baseline period choices for separating climate and land use/land cover change impacts on watershed hydrology using distributed hydrological models. Sci Total Environ 622–623:1016–1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.055
Funding
This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number “105.06-2019.20.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dao Nguyen Khoi: conceptualization; methodology; investigation; formal analysis; writing - review and editing; and paper administration.
Pham Thi Loi: investigation; formal analysis; visualization; writing - original draft; writing - review and editing.
Nguyen Thi Thuy Trang: formal analysis; visualization; writing - review and editing.
Nguyen Dinh Vuong: formal analysis; visualization; writing - review and editing.
Shibo Fang: formal analysis; visualization; writing - review and editing.
Pham Thi Thao Nhi: formal analysis; visualization; writing - original draft; writing - review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khoi, .N., Loi, P.T., Trang, N.T.T. et al. The effects of climate variability and land-use change on streamflow and nutrient loadings in the Sesan, Sekong, and Srepok (3S) River Basin of the Lower Mekong Basin. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 7117–7126 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16235-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16235-w