Abstract
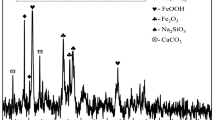
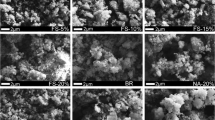
The high alkalinity of bauxite residue and its sustained release impose major limitation on its reuse and ecological disposal. It has been confirmed from sustained rehabilitation that gypsum can effectively reduce the alkalinity of bauxite residue by continuously releasing Ca2+ to react with carbonate and hydroxide. However, the combined bauxite residue with high calcium content exhibits stubborn alkalinity for most alkaline reduction methods employing cations to consume carbonate. In this study, we have aimed to address this knowledge gap by investigating the dose–response relationship in the alkaline reduction induced by ferrous sulfate (FS) neutralization. The pH, exchangeable sodium percentage (ESP), and CO32-/HCO3- of bauxite residue decreased from 10.6, 44.1%, and 42.7/24.5 mg/kg to 8.1, 27.7%, and 0.7/18.0 mg/kg, respectively. Approximately 20–55 days were required for the neutralization reaction to reach equilibrium. The FS induced an increase in free iron oxide (Fed) and amorphous iron oxide (Feo), and partial dissolution of alkaline minerals including calcite, cancrinite, and kaolinite in bauxite residue. Further, addition of FS also affected the kinetic dissolution process of bauxite residue; the acid neutralization capacity of bauxite residue to pH 7 decreased from 0.21 mol H+/kg solid to 0.02 mol H+/kg solid. The results showed FS to be a potential candidate for improving the characteristics of the combined bauxite residue, and guide the FS application for the disposal of the combined bauxite residue.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data related to this publication are made available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Azof FI, Safarian J (2020) Leaching kinetics and mechanism of slag produced from smelting-reduction of bauxite for alumina recovery. Hydrometallurgy 195:105388
Boland DD, Collins RN, Miller CJ, Glover CJ, Waite TD (2014) Effect of solution and solid-phase conditions on the Fe(II)-accelerated transformation of ferrihydrite to lepidocrocite and goethite. Environ Sci Technol 48:5477–5485
Burkle D, De Motte R, Taleb W, Kleppe A, Comyn T, Vargas SM, Neville A, Barker R (2017) In situ SR-XRD study of FeCO3 precipitation kinetics onto carbon steel in CO2-containing environments: The influence of brine pH. Electrochim Acta 255:127–144
Chen CR, Phillips IR, Wei LL, Xu ZH (2010) Behaviour and dynamics of di-ammonium phosphate in bauxite processing residue sand in Western Australia--II. Phosphorus fractions and availability. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17:1110–1118
Chen SC, Zhu Q, Su YY, Xing ZP (2018) Preparation and performance of Fe(II)-akaganeite (β-FeOOH) modified red mud granule filter material. Res Chem Intermediat 44:7583–7593
Chen XY, Zeng YY, Chen ZH, Wang S, Xin CZ, Wang LX, Shi CL, Lu L, Zhang CX (2020) Synthesis and electrochemical property of FeOOH/Graphene oxide composites. Front Chem 8:328
Cusack PB, Courtney R, Healy MG, O’ Donoghue LMT, Ujaczki É (2019) An evaluation of the general composition and critical raw material content of bauxite residue in a storage area over a twelve-year period. J Clean Prod 208:393–401
Di Carlo E, Boullemant A, Courtney R (2019a) A field assessment of bauxite residue rehabilitation strategies. Sci Total Environ 663:915–926
Di Carlo E, Chen CR, Haynes RJ, Phillips IR, Courtney R (2019b) Soil quality and vegetation performance indicators for sustainable rehabilitation of bauxite residue disposal areas: a review. Soil Res 57:419
Di Carlo E, Boullemant A, Courtney R (2020) Ecotoxicological risk assessment of revegetated bauxite residue: implications for future rehabilitation programmes. Sci Total Environ 698:134344
Fourrier C, Luglia M, Hennebert P, Foulon J, Ambrosi JP, Angeletti B, Keller C, Criquet S (2020) Effects of increasing concentrations of unamended and gypsum modified bauxite residues on soil microbial community functions and structure - a mesocosm study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 201:110847
Gräfe M, Klauber C (2011) Bauxite residue issues: IV. Old obstacles and new pathways for in situ residue bioremediation. Hydrometallurgy 108:46–59
Gräfe M, Power G, Klauber C (2011) Bauxite residue issues: III. Alkalinity and associated chemistry. Hydrometallurgy 108:60–79
Han YS, Ji SW, Lee PK, Oh C (2017) Bauxite residue neutralization with simultaneous mineral carbonation using atmospheric CO2. J Hazard Mater 326:87–93
Higgins D, Curtin T, Burke I, Courtney R (2016) The potential for constructed wetlands to treat alkaline bauxite-residue leachate: Phragmites australis growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:24305–24315
Higgins D, Curtin T, Burke I, Courtney R (2018) The potential for constructed wetland mechanisms to treat alkaline bauxite residue leachate: carbonation and precipitate characterisation. Environ Sci Pollu Res 25:29451–29458
Hove M, van Hille RP, Lewis AE (2008) Mechanisms of formation of iron precipitates from ferrous solutions at high and low pH. Chem. Eng. Sci. 63:1626–1635
Hu Y, Liang S, Yang JK, Chen Y, Ye N, Ke Y, Tao SY, Xiao KK, Hu JP, Hou HJ, Fan W, Zhu SY, Zhang YS, Xiao B (2019) Role of Fe species in geopolymer synthesized from alkali-thermal pretreated Fe-rich Bayer red mud. Constr Build Mater 200:398–407
Hua Y, Heal KV, Friesl-Hanl WF (2017) The use of red mud as an immobiliser for metal/metalloid-contaminated soil: A review. J Hazard Mater 325:17–30
Huang PH, Deng SG, Zhang ZY, Wang XL, Chen XD, Yang XS, Yang L (2015) A sustainable process to utilize ferrous sulfate waste from titanium oxide industry by reductive decomposition reaction with pyrite. Thermochimica Acta 620:18–27
Ishikawa T, Takeuchi K, Kandori K, Nakayama T (2005) Transformation of γ-FeOOH to α-FeOOH in acidic solutions containing metal ions. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects. 266:155–159
Jiang J, Xu RK, Zhao AZ (2011) Surface chemical properties and pedogenesis of tropical soils derived from basalts with different ages in Hainan, China. Catena 87:334–340
Ke WS, Zhang XC, Zhu F, Wu H, Zhang YF, Shi Y, Hartley W, Xue SG (2021) Appropriate human intervention stimulates the development of microbial communities and soil formation at a long-term weathered bauxite residue disposal area. J Hazard Mater 405:124689
Khaitan S, Dzombak DA, Lowry GV (2009) Chemistry of the acid neutralization capacity of bauxite residue. Environ Eng Sci 26:873–884
Kong XF, Li M, Xue SG, Hartley W, Chen CR, Wu C, Li XF, Li YW (2017) Acid transformation of bauxite residue: Conversion of its alkaline characteristics. J Hazard Mater 324:382–390
Li XY, Lei ZW, Qu J, Li Z, Zhou XW, Zhang QW (2017) Synthesizing slow-release fertilizers via mechanochemical processing for potentially recycling the waste ferrous sulfate from titanium dioxide production. J. Environ. Manage. 186:120–126
Li XF, Ye YZ, Xue SG, Jiang J, Wu C, Kong XF, Hartley W, Li YW (2018) Leaching optimization and dissolution behavior of alkaline anions in bauxite residue. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28:1248–1255
Li YY, Haynes RJ, Chandrawana I, Zhou YF (2019) Growth of Rhodes grass and leaching of ions from seawater neutralized bauxite residues after amendment with gypsum and organic wastes. J Environ Manage 231:596–604
Liu H, Wei Y, Sun YH, Wei W (2005) Dependence of the mechanism of phase transformation of Fe(III) hydroxide on pH. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects. 252:201–205
Liu WC, Chen XQ, Li WX, Yu YF, Yan K (2014) Environmental assessment, management and utilization of red mud in China. J. Clean. Prod. 84:606–610
Luo JQ, Wang LL, Li QS, Zhang QK, He BY, Wang Y, Qin LP, Li SS (2015) Improvement of hard saline–sodic soils using polymeric aluminum ferric sulfate (PAFS). Soil Tillage Res 149:12–20
Lyu F, Hu YH, Wang L, Sun W (2021) Dealkalization processes of bauxite residue: a comprehensive review. J Hazard Mater 403:123671
Mahdy AM (2011) Comparative Effects of different soil amendments on amelioration of saline-sodic soils. Soil & Water Res 6:205–216
McIntyre NS, Zetaruk DG (2002)X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic studies of iron oxides. Anal Chem 49:1521–1529
Menzies NW, Kopittke PM (2020) Seawater neutralization and gypsum amelioration of bauxite refining residue to produce a plant growth medium. Sci Total Environ 763:143046
O’Connor G, Courtney R (2020) Constructed wetlands for the treatment of bauxite residue leachate: long term field evidence and implications for management. Ecol Eng 158:106076
Phillips IR, Chen C (2010) Surface charge characteristics and sorption properties of bauxite-processing residue sand. Aust J Soil Res 48:77–87
Ren J, Liu JD, Chen J, Liu XL, Li FS, Du P (2017) Effect of ferrous sulfate and nitrohumic acid neutralization on the leaching of metals from a combined bauxite residue. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:9325–9336
Ren J, Chen J, Han L, Wang M, Yang B, Du P, Li FS (2018) Spatial distribution of heavy metals, salinity and alkalinity in soils around bauxite residue disposal area. Sci Total Environ 628–629:1200–1208
Ren J, Chen J, Guo W, Yang B, Qin XP, Du P (2019) Physical, chemical, and surface charge properties of bauxite residue derived from a combined process. J Cent South Univ 26:373–382
Rezaei Rashti M, Esfandbod M, Phillips IR, Chen CR (2019) Aged biochar alters nitrogen pathways in bauxite-processing residue sand: environmental impact and biogeochemical mechanisms. Environ Pollu 247:438–446
Rubinos DA, Spagnoli G (2019) Assessment of red mud as sorptive landfill liner for the retention of arsenic (V). J Environ Manage 232:271–285
Santini TC, Peng YG (2017) Microbial fermentation of organic carbon substrates drives rapid pH neutralization and element removal in bauxite residue leachate. Environ Sci Technol 51:12592–12601
Santini TC, Kerr JL, Warren LA (2015)Microbially-driven strategies for bioremediation of bauxite residue. J Hazard Mater 293:131–157
Santini TC, Malcolm LI, Tyson GW, Warren LA (2016) pH and organic carbon dose rates control microbially driven bioremediation efficacy in alkaline bauxite residue. Environ Sci Technol 50:11164–11173
Snars K, Gilkes RJ (2009) Evaluation of bauxite residues (red muds) of different origins for environmental applications. Appl Clay Sci 46:13–20
Tian T, Ke WS, Zhu F, Wang QL, Ye YZ, Guo Y, Xue SG (2019) Effect of substrate amendment on alkaline minerals and aggregate stability in bauxite residue. J Cent South Univ 26:393–403
Tian T, Cl Z, Zhu F, Yuan SX, Guo Y, Xue SG (2021) Effect of phosphogypsum on saline-alkalinity and aggregate stability of bauxite residue. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 31:1484–1495
Vempati RK, Loeppert RH (1988) Chemistry and mineralogy of Fe-containing oxides and layer silicates in relation to plant available iron. J Plant Nutr 11:1557–1574
Wang L, Sun N, Tang HH, Sun W (2019) A Review on comprehensive utilization of red mud and prospect analysis. Minerals 9:396
Xing BB, Graham N, Yu WZ (2020) Transformation of siderite to goethite by humic acid in the natural environment. Commun Chem 3:38
Xue SG, Zhu F, Kong XF, Wu C, Huang L, Huang N, Hartley W (2016a) A review of the characterization and revegetation of bauxite residues (Red mud). Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:1120–1132
Xue SG, Kong XF, Zhu F, Hartley W, Li XF, Li YW (2016b) Proposal for management and alkalinity transformation of bauxite residue in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:12822–12834
Xue SG, Huang N, Fan JR, Liu Z, Ye Y, He YZ, Hartley W, Zhu F (2020) Evaluation of aggregate formation, stability and pore characteristics of bauxite residue following polymer materials addition. Sci Total Environ 765:142750
Zhu F, Hou JT, Xue SG, Wu C, Wang QL, Hartley W (2017) Vermicompost and gypsum amendments improve aggregate formation in bauxite residue. Land Degrad Dev 28:2109–2120
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41907360 and No. 41501350).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xueqian Ren wrote the original draft, and Jie Ren conceptualized and designed the study. Xi Zhang and Pinpeng Tuo performed the experiment and data analysis. Bin Yang, Juan Chen, Wei Guo commented on and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ioannis A. Katsoyiannis
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, ., Zhang, X., Tuo, P. et al. Neutralization of bauxite residue with high calcium content in abating pH rebound by using ferrous sulfate. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 13167–13176 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16622-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16622-3