Abstract
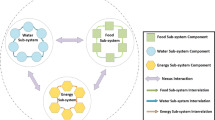
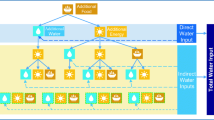
Since essential nexus variables were not considered in the energy subsystem, this study focused on the role of energy in the Water, Energy, and Food nexus (WEF nexus) system. The energy subsystem interacts with water and food on the supply and demand sides. The WEF nexus-based energy model has not been reviewed recently. This study provides a systematic review of 459 articles regarding energy simulation modeling issues relating to the WEF nexus system. The keyword (“energy” AND “simulation” AND “nexus”) as well as “water” OR “food” OR “climate” OR “land” OR “carbon” OR “environment” is used for searching WEF nexus documents for energy simulation. The review highlighted that the energy subsystem is modeled online (One-way) and offline (Two-way), and the energy simulation struggles to represent its system boundary with the water and food subsystems in different spatial scales (household to global). The energy subsystem of the WEF nexus did not address return flow from cooling towers and crop energy consumption comprehensively. In the research, the supply and demand section of the energy subsystem demonstrated that a comprehensive simulation model for energy can be developed using the nexus system approach. The energy subsystem’s supply, primarily power plants, interacts with the water subsystem, and the energy generation policy is based on water use. The WEF nexus system assesses renewable energy effects to reduce tradeoffs. In addition, energy demand is related to energy consumption, so the energy consumption for each crop can be calculated and explained the appropriate cultivation pattern based on it.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data are unavailable and can be presented upon the request of the readers.
References
Abdel-Aal M, Haltas I, Varga L (2020) Modelling the diffusion and operation of anaerobic digestions in Great Britain under future scenarios within the scope of water-energy-food nexus. J Clean Prod 253:119897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119897
Afshar A, Soleimanian E, Akbari Variani H, et al (2022) The conceptual framework to determine interrelations and interactions for holistic Water, Energy, and Food Nexus. Environ Dev Sustain 24:10119–10140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01858-3
Amin A, Dogan E (2021) The role of economic policy uncertainty in the energy-environment nexus for China: Evidence from the novel dynamic simulations method. J Environ Manage 292:112865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112865
Amjath-Babu TS, Sharma B, Brouwer R et al (2019) Integrated modelling of the impacts of hydropower projects on the water-food-energy nexus in a transboundary Himalayan River basin. Appl Energy 239:494–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.01.147
Araujo HFP de, Machado CCC, Pareyn FGC, et al (2021) A sustainable agricultural landscape model for tropical drylands. Land use policy 100:104913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104913
Araya N, Ramírez Y, Cisternas LA, Kraslawski A (2021) Use of real options to enhance water-energy nexus in mine tailings management. Appl Energy 303:117626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.117626
Azizi H, Nejatian N (2022) Evaluation of the climate change impact on the intensity and return period for drought indices of SPI and SPEI (study area: Varamin plain). Water Supply 22(4):4373–4386. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2022.056
Bakhshianlamouki E, Masia S, Karimi P et al (2020) A system dynamics model to quantify the impacts of restoration measures on the water-energy-food nexus in the Urmia Lake Basin, Iran. Sci Total Environ 708:134874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134874
Basheer M, Elagib NA (2018) Sensitivity of water-energy nexus to dam operation: a water-energy productivity concept. Sci Total Environ 616–617:918–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.228
Booth A (2016) Searching for qualitative research for inclusion in systematic reviews: a structured methodological review. Syst Rev 5:74. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0249-x
Casazza M, Xue J, Du S, Liu G, Ulgiati S (2021) Simulations of scenarios for urban household water and energy consumption. PLOS ONE 16(4):e0249781. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0249781
Chang Y, Li G, Yao Y, et al (2016) Quantifying the Water-Energy-Food Nexus: Current Status and Trends. Energies (Basel) 9(2):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9020065
Chen J, Zhou Z, Chen L, Ding T (2020a) Optimization of regional water-energy-food systems based on interval number multi-objective programming: a case study of ordos, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207508
Chen X, Zheng Y, Xu B, et al (2020b) Balancing competing interests in the Mekong River Basin via the operation of cascade hydropower reservoirs in China: Insights from system modeling. J Clean Prod 254:119967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.119967
Chowdhury AFMK, Dang TD, Nguyen HTT, et al (2021) The Greater Mekong’s Climate-Water-Energy Nexus: How ENSO-Triggered Regional Droughts Affect Power Supply and CO2 Emissions. Earths Future 9(3): e2020EF001814. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020EF001814
D’Odorico P, Davis KF, Rosa L et al (2018) The global food-energy-water nexus. Rev Geophys 56:456–531. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017RG000591
Duan C, Chen B (2020) Driving factors of water-energy nexus in China. Appl Energy 257:113984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113984
Endo A, Yamada M, Miyashita Y et al (2020) Dynamics of water–energy–food nexus methodology, methods, and tools. Curr Opin Environ Sci Health 13:46–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coesh.2019.10.004
Ferraz de Campos É, Pereira EB, van Oel P, et al (2021) Hybrid power generation for increasing water and energy securities during drought: Exploring local and regional effects in a semi-arid basin. J Environ Manage 294:112989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112989
Ferroukhi et al. (2015) Renewable Energy in the Water, Energy & Food Nexus. In: International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2015/IRENA_Water_Energy_Food_Nexus_2015.pdf. Accessed 20 Nov 2022
Garcia DJ, You F (2016) The water-energy-food nexus and process systems engineering: a new focus. Comput Chem Eng 91:49–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMPCHEMENG.2016.03.003
Gozini H, Zahraie B, Ravar Z (2021) System dynamics modeling of water–energy nexus for resource-saving policy assessment. Int J Environ Res 15:349–367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-021-00321-5
Handayani K, Filatova T, Krozer Y, Anugrah P (2020) Seeking for a climate change mitigation and adaptation nexus: Analysis of a long-term power system expansion. Appl Energy 262:114485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.114485
Heidari A, Watkins D Jr, Mayer A et al (2021) Spatially variable hydrologic impact and biomass production trade-offs associated with Eucalyptus (E. grandis) cultivation for biofuel production in Entre Rios, Argentina. GCB Bioenergy 13:823–837. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcbb.12815
Hernandez EA, Uddameri V, Singaraju S (2014) Combined optimization of a wind farm and a well field for wind-enabled groundwater production. Environ Earth Sci 71:2687–2699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2907-9
Huang D, Li G, Sun C, Liu Q (2020) Exploring interactions in the local water-energy-food nexus (WEF-Nexus) using a simultaneous equations model. Sci Total Environ 703:135034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135034
Hussien WA, Memon FA, Savic DA (2017) An integrated model to evaluate water-energy-food nexus at a household scale. Environ Model Softw 93:366–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2017.03.034
IEA (2010) World Energy Outlook 2010. IEA, Paris. https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2010. License: CC BY 4.0. Accessed 29 May 2022
IEA (2017) Water-Energy Nexus. IEA, Paris. https://www.iea.org/reports/water-energy-nexus. License: CC BY 4.0. Accessed 4 Jul 2022
Jääskeläinen J, Veijalainen N, Syri S et al (2018) Energy security impacts of a severe drought on the future Finnish energy system. J Environ Manage 217:542–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.03.017
Karki R, You YH (2020) A solution to a fractional order semi linear equation using variational method. Math Appl Sci Eng 1:275–285. https://doi.org/10.5206/mase/9413
Keyhanpour MJ, Musavi Jahromi SH, Ebrahimi H (2021) System dynamics model of sustainable water resources management using the Nexus Water-Food-Energy approach. Ain Shams Eng J 12:1267–1281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2020.07.029
Khalkhali M, Westphal K, Mo W (2018) The water-energy nexus at water supply and its implications on the integrated water and energy management. Sci Total Environ 636:1257–1267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.408
Kulp SA, Strauss BH (2019) New elevation data triple estimates of global vulnerability to sea-level rise and coastal flooding. Nat Commun 10:4844. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12808-z
Laspidou CS, Mellios NK, Spyropoulou AE et al (2020) Systems thinking on the resource nexus: modeling and visualisation tools to identify critical interlinkages for resilient and sustainable societies and institutions. Sci Total Environ 717:137264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137264
Lee S-H, Choi J-Y, Hur S-O, et al (2020) Food-centric interlinkages in agricultural food-energy-water nexus under climate change and irrigation management. Resour Conserv Recycl 163:105099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105099
Li G, Wang Y, Huang D, Yang H (2017) Water-energy-food nexus in urban sustainable development: an agent-based model. Int J Crowd Sc 1:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCS-08-2017-0014
Li G, Huang D, Sun C, Li Y (2019) Developing interpretive structural modeling based on factor analysis for the water-energy-food nexus conundrum. Sci Total Environ 651:309–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.188
Li X, Li YP, Huang GH, et al (2021) A multi-scenario input-output economy-energy-environment nexus management model for Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration. J Clean Prod 317:128402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128402
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med 6:e1000100
Liu F, Tait S, Schellart A, et al (2020) Reducing carbon emissions by integrating urban water systems and renewable energy sources at a community scale. Renew Sust Energ Rev 123:109767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.109767
Lv J, Li YP, Huang GH, et al (2020) Quantifying the impact of water availability on China’s energy system under uncertainties: A perceptive of energy-water nexus. Renew Sust Energ Rev 134:110321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110321
Mahdavian SM, Ahmadpour Borazjani M, Mohammadi H et al (2022) Assessment of food-energy-environmental pollution nexus in Iran: the nonlinear approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19280-1
Manthrithilake H, Liyanagama BS (2012) Simulation model for participatory decision making: water allocation policy implementation in Sri Lanka. Water Int 37:478–491. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508060.2012.708602
Markantonis V, Reynaud A, Karabulut A, et al (2019) Can the Implementation of the Water-Energy-Food Nexus Support Economic Growth in the Mediterranean Region? The Current Status and the Way Forward. Front Environ Sci 7:00084. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2019.00084
Martinez-Hernandez E, Leach M, Yang A (2017) Understanding water-energy-food and ecosystem interactions using the nexus simulation tool NexSym. Appl Energy 206:1009–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.09.022
Mitra BK, Sharma D, Zhou X, Dasgupta R (2021) Assessment of the impacts of spatial water resource variability on energy planning in the ganges river basin under climate change scenarios. Sustainability (Switzerland) 13(13):7273. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137273
Molajou A, Afshar A, Khosravi M et al (2021) A new paradigm of water, food, and energy nexus. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13034-1
Molajou A, Pouladi P, Afshar A (2021) Incorporating social system into water-food-energy nexus. Water Resour Manage 35:4561–4580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02967-4
Mounir A, Mascaro G, White DD (2019) A metropolitan scale analysis of the impacts of future electricity mix alternatives on the water-energy nexus. Appl Energy 256:113870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113870
Mounir A, Guan X, Mascaro G (2021) Investigating the value of spatiotemporal resolutions and feedback loops in water-energy nexus modeling. Environ Model Softw 145:105197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2021.105197
Naderi MM, Mirchi A, Bavani ARM, et al (2021) System dynamics simulation of regional water supply and demand using a food-energy-water nexus approach: Application to Qazvin Plain, Iran. J Environ Manage 280:111843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111843
Nouri N, Balali F, Nasiri A et al (2019) Water withdrawal and consumption reduction for electrical energy generation systems. Appl Energy 248:196–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.04.023
Ouyang Y, Cai Y, Xie Y, et al (2021) Multi-scale simulation and dynamic coordination evaluation of water-energy-food and economy for the Pearl River Delta city cluster in China. Ecol Indic 130:108155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108155
Pavičević M, de Felice M, Busch S, et al (2021) Water-energy nexus in African power pools – The Dispa-SET Africa model. Energy 228:120623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120623
Pickering C, Byrne J (2014) The benefits of publishing systematic quantitative literature reviews for PhD candidates and other early-career researchers. High Educ Res Dev 33:534–548. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2013.841651
Popescul D, Radu LD, Păvăloaia VD, Georgescu MR (2020) Psychological Determinants of Investor Motivation in social media-Based Crowdfunding Projects: A Systematic Review. Front Psychol 11:588121. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.588121
Qi Y, Farnoosh A, Lin L, Liu H (2022) Coupling coordination analysis of China’s provincial water-energy-food nexus. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:23303–23313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17036-x
Ravar Z, Zahraie B, Sharifinejad A, et al (2020) System dynamics modeling for assessment of water–food–energy resources security and nexus in Gavkhuni basin in Iran. Ecol Indic 108:105682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105682
Reimer J, Babbar-Sebens M, Rivera SJ (2020) WEST: Water economy simulation tool to predict impacts of economic and environmental shocks. Adv Water Resour 142:103648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2020.103648
Schull VZ, Mehan S, Gitau MW, et al (2021) Construction of critical periods for water resources management and their application in the few nexus. Water (Switzerland) 13(5):718. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13050718
Sharifinejad A, Zahraie B, Majed V et al (2020) Economic analysis of Water-Food-Energy Nexus in Gavkhuni basin in Iran. J Hydro-Environ Res 31:14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2020.03.001
Sharma GD, Shah MI, Shahzad U et al (2021) Exploring the nexus between agriculture and greenhouse gas emissions in BIMSTEC region: the role of renewable energy and human capital as moderators. J Environ Manage 297:113316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113316
Sims REH (2011) “Energy-smart” food for people and climate. In: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). https://www.fao.org/sustainable-food-value-chains/library/details/en/c/266092/. Accessed 29 May 2022
Smith C (2014) World Water Day: Focus on the Water–Energy Nexus. In: United Nations University. https://ourworld.unu.edu/en/world-water-day-focus-on-the-water-energy-nexus. Accessed 20 Nov 2022
Soleimanian E, Afshar A, Molajou A (2022) A review on water simulation models for the WEF Nexus: development perspective. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:79769–79785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19849-w
Stamou A-T, Rutschmann P (2018) Pareto optimization of water resources using the nexus approach. Water Resour Manage 32:5053–5065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-2127-x
Tang B, Wu Y, Yu B, et al (2020) Co-current analysis among electricity-water-carbon for the power sector in China. Sci Total Environ 745:141005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141005
Thompson J, Ganapathysubramanian B, Chen W, et al (2021) Iowa Urban FEWS: Integrating Social and Biophysical Models for Exploration of Urban Food, Energy, and Water Systems. Front Big Data 4:662186. https://doi.org/10.3389/fdata.2021.662186
Toba A-L, Boire L, McJunkin T (2021) Integrated water‐power system resilience analysis in a southeastern idaho irrigation district: Minidoka case study. Sustainability (Switzerland) 13(19):10906. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910906
Tortorella MM, di Leo S, Cosmi C et al (2020) A methodological integrated approach to analyse climate change effects in agri-food sector: the TIMES water-energy-food module. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17217703
United Nations (2019) The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2019. In: United Nations. https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2019/The-Sustainable-Development-Goals-Report-2019.pdf. Accessed 28 Jun 2021
United Nations Report (2019) The United Nations world water development report 2019: leaving no one behind. UNESCO, Paris. https://en.unesco.org/themes/water-security/wwap/wwdr/2019. Accessed 10 Aug 2021
Wan R, Ni M (2021) Sustainable water–energy–environment nexus. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:40049–40052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14242-5
Wicaksono A, Jeong G, Kang D (2019) Water-energy-food nexus simulation: An optimization approach for resource security. Water (Switzerland) 11(4):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040667
Wicaksono A, Jeong G, Kang D (2020) WEFSiM: a model for water–energy–food nexus simulation and optimization. In: Naddeo V, Balakrishnan M, Choo K-H (eds) Frontiers in water-energy-nexus—nature-based solutions, advanced technologies and best practices for environmental sustainability. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 55–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-13068-8_13
Xue J, Liu G, Cristiano S, et al (2021) Development of an urban household food-energy-water policy nexus dynamic simulator. J Clean Prod 328:129521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129521
Yavari F, Salehi Neyshabouri SA, Yazdi J, Molajou A, Brysiewicz A (2022) A novel framework for urban flood damage assessment. Water Resour Manag 36(6):1991–2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03122-3
Yu X, Shan L, Wu Y (2021) Land use optimization in a resource-exhausted city based on simulation of the f-e-w nexus. Land (Basel) 10(10):1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10101013
Yuxi Z, Jingke H, Changlin X, Zhangmiao L (2021) Unfolding the synergy and interaction of water-land-food nexus for sustainable resource management: a super network analysis. Sci Total Environ 784:147085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147085
Zeng XT, Zhang JL, Yu L et al (2019) A sustainable water-food-energy plan to confront climatic and socio-economic changes using simulation-optimization approach. Appl Energy 236:743–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.11.086
Zhai M, Huang G, Liu L et al (2021) Economic modeling of national energy, water and air pollution nexus in China under changing climate conditions. Renew Energy 170:375–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.01.011
Zhai M, Huang G, Liu L, et al (2020) Inter-regional carbon flows embodied in electricity transmission: network simulation for energy-carbon nexus. Renew Sust Energ Rev 118:109511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109511
Zhang C, Chen X, Li Y et al (2018) Water-energy-food nexus: concepts, questions and methodologies. J Clean Prod 195:625–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2018.05.194
Zhang Y, Fu Z, Xie Y et al (2021) Dynamic metabolism network simulation for energy-water nexus analysis: a case study of Liaoning Province, China. Sci Total Environ 779:146440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146440
Zhang X, Ren L (2021) Simulating and assessing the effects of seasonal fallow schemes on the water-food-energy nexus in a shallow groundwater-fed plain of the Haihe River basin of China. J Hydrol (Amst) 595:125992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.125992
Zhou Y, Chang L-C, Uen T-S et al (2019) Prospect for small-hydropower installation settled upon optimal water allocation: an action to stimulate synergies of water-food-energy nexus. Appl Energy 238:668–682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.01.069
Zhuge C, Yu M, Wang C, et al (2020) An agent-based spatiotemporal integrated approach to simulating in-home water and related energy use behaviour: A test case of Beijing, China. Sci Total Environ 708:135086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135086
Zimoch I, Bartkiewicz E, Machnik-Slomka J, et al (2021) Sustainable water supply systems management for energy efficiency: A case study. Energies (Basel) 14:5101. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14165101
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MV: conceptualization, original draft, visualization, writing, and editing. AA: supervision, conceptualization, review, and editing. AM: conceptualization, original draft, and visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Consent to participate
The authors declare that they agree with the participation of the journal.
Consent for publication
The authors declare that they agree with the publication of this paper in this journal.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Marcus Schulz
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vahabzadeh, M., Afshar, A. & Molajou, A. Energy simulation modeling for water-energy-food nexus system: a systematic review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 5487–5501 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24300-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24300-1