Abstract
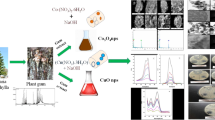
Co3O4 nanoparticles (NPs) were formed using hydrothermal synthesis method and various surfactants to study the effect of changing surface morphology on catalytic and antibacterial activities. FT-IR, TEM, SEM, BET, XRD, and XPS analyses were performed to characterize the NPs. It was observed that as the morphology of Co3O4 changes, it creates differences in the reduction efficiency of organic dyes and p-nitrophenol (p-NP), which are toxic to living organisms and widely used in industry. The reaction rate constants (Kapp) for Co3O4-urea, Co3O4-ed, and Co3O4-NaOH in the reduction of p-NP were found to be 1.86 × 10−2 s−1, 1.83 × 10−2 s−1, and 2.4 × 10−3 s−1, respectively. In the presence of Co3O4-urea catalyst from the prepared nanoparticles, 99.29% conversion to p-aminophenol (p-AP) was observed, while in the presence of the same catalyst, 98.06% of methylene blue (MB) was removed within 1 h. The antibacterial activity of Co3O4 particles was compared with five standard antibiotics for both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The results obtained indicate that the antimicrobial activity of the synthesized Co3O4 particles has a remarkable inhibitory effect on the growth of various pathogenic microorganisms. The current work could be an innovative and beneficial search for both biomedical and wastewater treatment applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Abdulhameed AS, Jawad AH, Kashi E, Radzun KA, Al Othman ZA, Wilson LD (2022) Insight into adsorption mechanism, modeling, and desirability function of crystal violet and methylene blue dyes by microalgae: Box-Behnken design application. Algal Res 67:102864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2022.102864
Ambika S, Gopinath S, Saravanan K, Sivakumar K, Ragupathi C, Sukantha TA (2019) Structural, morphological and optical properties and solar cell applications of thioglycolic routed nano cobalt oxide material. Energy Rep 5:305–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2019.02.005
Anar M, Hasanoğlu Özkan E, Ogutcu H, Ağar G, Şakıyan I, Sarı N (2016) Useful agents against Aflatoxin B1-antibacterial azomethine and Mn(III) complexes involving L-threonine, L-serine, and L-tyrosine. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 44:853–858. https://doi.org/10.3109/21691401.2014.991792
Anuma S, Mishra P, Bhat BR (2021) Polypyrrole functionalized cobalt oxide graphene (COPYGO) nanocomposite for the efficient removal of dyes and heavy metal pollutants from aqueous effluents. J. Hazard. Mater 416:125929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125929
Badruzzaman A, Yuda A, Ashok A, Kumar A (2020) Recent advances in cobalt based heterogeneous catalysts for oxygen evolution reaction. Inorg Chim Acta 511:119854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2020.119854
Chen H, Yang M, Tao S, Chen G (2017) Oxygen vacancy enhanced catalytic activity of reduced Co3O4 towards p-nitrophenol reduction. Appl Catal B 209:648–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.03.038
Cheng L, He Y, Gong M, He X, Ning Z, Yu H, Jiao Z (2021) MOF-derived synthesis of Co3O4 nanospheres with rich oxygen vacancies for long-term stable and highly selective n-butanol sensing performance. J Alloys Compd 857:158205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.158205
Chiu HY, Wi-Afedzi T, Liu YT, Ghanbari F, Kun-Yi AL (2020) Cobalt oxides with various 3D nanostructured morphologies forc reduction of 4-Nitrophenol: a comparative study. J Water Process Eng 37:101379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101379
Danish MSS, Bhattacharya A, Stepanova D, Mikhaylov A, Grilli ML, Khosravy M, Senjyu TA (2020) Systematic review of metal oxide applications for energy and environmental sustainability. Metals 10:1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10121604
Din MI, Rizwan R, Hussain Z, Khalid R (2021) Biogenic synthesis of mono dispersed Co/CoO nanoparticles using syzygium cumini leaves for catalytic application. Inorg Nano-Met Chem 51(6):773–779. https://doi.org/10.1080/24701556.2020.1808993
Erdogan H (2020) Catalytic degradation of 4-nitrophenol and methylene blue by bioinspired polydopamine coated dipeptide structures. Colloids Interface Sci Commun 39:100331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2020.100331
Fast SA, Gude VG, Truax DD, Martin J, Magbanua BS (2017) A critical evaluation of advanced oxidation processes for emerging contaminants removal. Environ Process 4:283–302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-017-0207-1
Gebre SH, Sendeku MG (2019) New frontiers in the biosynthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles and their environmental applications: an overview. SN Appl Sci 1:928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0931-4
Graham CLB, Newman H, Gillett FN, Smart K, Briggs N, Banzhaf M, Roper DIA (2021) Dynamic network of proteins facilitate cell envelope biogenesis in gram-negative bacteria. Int J Mol Sci 22(23):12831. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312831
Hasanoğlu Ozkan E, Aslan N, Koç MM, Kurnaz Yetim N, Sarı N (2022) Fe3O4 nanoparticle decorated novel magnetic metal oxide microcomposites for the catalytic degradation of 4-nitrophenol for wastewater cleaning applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33:1039–1053. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07376-2
He J, Song G, Wang X, Zhou L, Li J (2022) Multifunctional magnetic Fe3O4/GO/Ag composite microspheres for SERS detection and catalytic degradation of methylene blue and ciprofloxacin. J Alloys Compd 893:162226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162226
Jasri K, Abdulhameed AS, Jawad AH, Al Othman ZA, Yousef TA, Al Duaij OK (2023) Mesoporous activated carbon produced from mixed wastes of oil palm frond and palm kernel shell using microwave radiation-assisted K2CO3 activation for methylene blue dye removal: Optimization by response surface methodology. Diamond Relat Mater 131:109581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2022.109581
Jeevanandam J, Barhoum A, Chan YS, Dufresne A, Danquah MK (2018) Review on nanoparticles and nanostructured materials: history, sources, toxicity and regulations. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 9:1050–1074. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.9.98
Khan I, Saeed K, Khan I (2019) Nanoparticles: properties, applications and toxicities. Arab J Chem 12(7):908–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011
Karimi S, Bibak F, Meshkani F, Rastegarpanah A, Deng J, Liu Y, Dai H (2021) Promotional roles of second metals in catalyzing methane decomposition over the Ni-based catalysts for hydrogen production: a critical review. Int J Hydrog Energy 46(39):20435–20480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.03.160
Kavitha T, Haider S, Kamal T, Ul-Islam M (2017) Thermal decomposition of metal complex precursor as route to the synthesis of Co3O4 nanoparticles: antibacterial activity and mechanism. J Alloys Compd 704:296–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.01.306
Kim HS, Kim HJ, Kim JH, Kim JH, Kang SH, Ryu JH, Park NK, Yun DS, Bae JW (2022) Noble-metal-based catalytic oxidation technology trends for volatile organic compound (VOC) removal. Catalysts 12(63):1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12010063
Koçoğlu S, Hayvalı Z, Ogutcu H (2021) A polydentate ligand based on 2,2’-dipyridylamine unit linked benzo-15-crown-5; alkali and transition metal complexes; photoresponsive ligand; antimicrobial evaluation against pathogenic microorganisms. Transit Met Chem 46:509–522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-021-00469-1
KurnazYetim N (2021) Hydrothermal synthesis of Co3O4 with different morphology: investigation of magnetic and electrochemical properties. J Mol Struct 1226:129414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129414
Kurnaz Yetim N, Hasanoğlu Özkan E, Akkurt N, Koç MM (2022) Catalytic performance of Fe3O4@G2-PAMAM/MoO3 magnetic nanocomposites for degradation of 4-NP to 4-AP. J Mater Electronic Devices 3(1):1–6
Kurnaz Yetim N, Hasanoğlu Ozkan E (2021) Synthesis of Au-doped magnetic nanocomposites: structural, magnetic, and catalytic properties. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32:24766–24774. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06922-2
Li Q, Chen Z, Wang H, Yang H, Wen T, Wang S, Hu B, Wang X (2021) Removal of organic compounds by nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites. Sci Total Environ 792:148546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148546
Li Y, Fu Y, Lai C, Qin L, Li B, Liu S, Yi H, Xu F, Li L, Zhang M, Xu M, Duc C, Chen W (2021) Porous materials confining noble metals for the catalytic reduction of nitroaromatics: controllable synthesis and enhanced mechanism. Environ Sci: Nano 8:3067–3097. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00628B
Liu WJ, Wang H, Lee J, Kwon EE, Bui WT, You S, Young-Kwon P, Tong S, Kun-Yi AL (2021) Investigating crystal plane effect of Co3O4 with various morphologies on catalytic activation of monopersulfate for degradation of phenol in water. Sep Purif Technol 276:119368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119368
Liu Z, Wang R, Li S, Gu Y, Lan J, Zhou Q, Xu W (2022) Oxygen vacancy-rich ultrafine CoP/Co3O4 nanoparticles as high-efficiency trifunctional electrocatalyst. Electrochim Acta 412:140134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2022.140134
Mogudi BM, Ncube P, Meijboom R (2016) Catalytic activity of mesoporous cobalt oxides with controlled porosity and crystallite sizes: evaluation using the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Appl Catal B 198:74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.05.051
Mohanty A, Garg N, Jin RA (2010) Universal approach to the synthesis of noble metal nanodendrites and their catalytic properties. Angew Chem Int Ed 49(29):4962–4966. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201000902
Mohd Hanafi NA, Abdulhameed AS, Jawad AH, AL Othman ZA, Yousef TA, Al Duaij OK, Alsaiari NS (2022) Optimized removal process and tailored adsorption mechanism of crystal violet and methylene blue dyes by activated carbon derived from mixed orange peel and watermelon rind using microwave-induced ZnCl2 activation. Biomass Conv. Biorefhttps://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03646-z
Muhammad I, Kalsoom A, Khan MI, Tahseen K, Khan MA, Asiri AM, Seo J, Khan SB (2019) Pollution, toxicity and carcinogenicity of organic dyes and their catalytic bio- remediation. Curr Pharm Des 25:3653–3671. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612825666191021142026
Nadhirah Long Tamjid Farki NNA, Abdulhameed AS, Surip SN, Al Othman ZA, Jawad AH (2023) Tropical fruit wastes including durian seeds and rambutan peels as a precursor for producing activated carbon using H3PO4-assisted microwave method: RSM-BBD optimization and mechanism for methylene blue dye adsorption. International Journal of Phytoremediationhttps://doi.org/10.1080/152265142175780
Nafiey AA, Addad A, Sieber B, Chastanet G, Barras A, Szunerits S, Boukherroub R (2017) Reduced graphene oxide decorated with Co3O4 nanoparticles (rGO-Co3O4) nanocomposite: a reusable catalyst for highly efficient reduction of 4-Nitrophenol, and Cr(VI) and dye Removal from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 322:375–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.039
Najafabadi AH, Mansoorianfar M, Liang T, Shahin K, Karimi-Maleh H (2022) A review on magnetic sensors for monitoring of hazardous pollutants in water resources. Sci. Total Environ. 824:153844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153844
Najafi M, Azizian S (2020) Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol on the surface of copper/copper oxide nanoparticles: a kinetics study. Appl Nanosci 10:3827–3837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01485-w
Nartop D, Demirel B, Güleç M, HasanogluOzkan E, KurnazYetim N, Sarı N, Ceker S, Ogutcu H, Agar G (2020) Novel polymeric microspheres: synthesis, enzyme immobilization, antimutagenic activity, and antimicrobial evaluation against pathogenic microorganisms. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 34(2):e22432. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22432
Nartop D, Hasanoglu Ozkan E, Gündem M, Ceker S, Agar G, Ogutcu H, Sarı N (2019) Synthesis, antimicrobial and antimutagenic effects of novel polymeric-schiff bases including indol. J Mol Struct 1195:877–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.06.042
Nartop D, Tokmak E, HasanogluOzkan E, Kızıl HE, Ogutcu H, Agar G, Allı S (2020) Synthesis of novel polymers containing schiff base as potential antimutagenic and antimicrobial agents. J Med Chem Sci 4(3):363–372. https://doi.org/10.26655/jmchemsci.2020.4.6
Naseem T, Durrani T (2021) The role of some important metal oxide nanoparticles for wastewater and antibacterial applications: a review. J Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 3:59–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enceco.2020.12.001
Nava MR, AlvesPereira CA, Brackmann R, Lenzi GG, Dias DT, Ferreirade Souza ÉC, Marcelino Borges JF, Marimonda-Cunha JB, Barreto-Rodrigues M (2022) CeO2-Fe2O3 mixed oxides: Synthesis, characterization and evaluation in the photocatalytic degradation of nitroaromatic compounds from wastewater of the explosives industry. J. Photochem Photobiol A: Chem 428:113839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2022.113839
Ogutcu H, Kurnaz Yetim N, Hasanoglu Ozkan E, Eren O, Kaya G, Sarı N, Dıslı A (2017) Nanospheres caped Pt(II) and Pt (IV): synthesis and evaluation as antimicrobial and antifungal Agent. Pol J Chem Technol 19(1):74–80. https://doi.org/10.1515/pjct-2017-0011
Ozkan EH (2023) Detection of 4-nitrophenol in wastewater using microstructures of various morphologies. J Mol Struct 1274(2):134564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134564
Prakash S, Kumar R, Kumar P, Rani S, Kumari K, Kumari S, Dhakate SR (2022) Reticulated porous carbon foam with cobalt oxide nanoparticles for excellent oxygen evolution reaction. Mater Chem Phys. 275:125131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125131
Pugazhendhi A, Vasantharaj S, Sathiyavimal S, Raja RK, Karuppusamy I, Narayanan M, Kandasamy S, Brindhadevi K (2021) Organic and inorganic nanomaterial coatings for the prevention of microbial growth and infections on biotic and abiotic surfaces. Surf Coat Technol 425:127739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127739
Rahman A, Jonnalagadda SB (2008) Swift and selective reduction of nitroaromatics to aromatic amines with Ni-boride-silica catalysts system at low temperature. Catal Lett 123:264–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-008-9417-5
Rajasekar R, Samuel M, Immanuel-Edison TNJ, Raman N (2021) Sustainable synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Alstonia scholaris for enhanced catalytic degradation of methylene blue. J Mol Struct 1246:131208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.131208
Razali NS, Abdulhameed AS, Jawad AH, AlOthman ZA, Yousef TA, Al-Duaij OK, Alsaiari NS (2022) High-surface-area-activated carbon derived from mango peels and seeds wastes via microwave-induced ZnCl2 activation for adsorption of methylene blue dye molecules: statistical optimization and mechanism. Molecules 27:6947. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27206947
Ryabchuk P, Agostini G, Pohl MM, Lund H, Agapova A, Junge H, Junge K, Beller M (2018) Intermetallic nickel silicide nanocatalyst-A non-noblemetal-based general hydrogenation catalyst. Sci Adv 4:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aat0761
Seitkalieva MM, Samoylenko DE, Lotsman KA, Rodygin KS, Ananikov VP (2021) Metal nanoparticles in ionic liquids: synthesis and catalytic applications. Coord Chem Rev 445:213982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2021.213982
Singh S, Kumar N, Kumar M, Agarwal JA, Mizaikoff B (2017) Electrochemical sensing and remediation of 4-nitrophenol using bio-synthesized copper oxide nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 313:283–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.049
Sun H, Ahmad M, Zhu J (2013) Morphology-controlled synthesis of Co3O4 porous nanostructures for the application as lithium-ion battery electrode. Electrochim Acta 89:199–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.10.116
Wang Z, Zhai S, Lv J, Qi H, Zheng W, Zhai B, An Q (2015) Versatile hierarchical Cu/Fe3O4 nanocatalysts for efficient degradation of organic dyes prepared by a facile, controllable hydrothermal method. RSC Adv 5:74575–74584. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra16027h
Wen Y, Zhang J, Xu Q, Wu XT, Zhu QL (2018) Pore surface engineering of metal-organic frameworks for heterogeneous catalysis. Coord Chem Rev 376:248–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2018.08.012
Xu X, Zhang W, Li Y, Wang P, Zhang Y (2022) Synthesis of Co3O4@TiO2 catalysts for oxygen evolution and oxygen reduction reactions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 335:111844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2022.111844
Ye J, Wang S, Li G, He B, Chen X, Cui Y, Zhao W, Sun J (2021) Insight into the morphology-dependent catalytic performance of CuO/CeO2 produced by tannic acid for efficient hydrogenation of 4-Nitrophenol. Chem Asian J 16(21):3371–3384. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.202100696
Zaera F (2017) The surface chemistry of metal-based hydrogenation catalysis. ACS Catal 7(8):4947–4967. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.7b01368
Zhang M, Su X, Ma L, Khan A, Wang L, Wang J, Maloletnev AS, Yang C (2021) Promotion effects of halloysite nanotubes on catalytic activity of Co3O4 nanoparticles toward reduction of 4-nitrophenol and organic dyes. J Hazard Mater 403:123870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123870
Zhang T, He C, Sun F, Ding Y, Wang M, Peng L, Wang J, Lin Y (2017) Co3O4 nanoparticles anchored on nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide as a multifunctional catalyst for H2O2 reduction, oxygen reduction and evolution reaction. Sci Rep 7:43638. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43638
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Wang T, Zhou J, Zhao Y (2008) Synthesis and magnetic properties of nanoporous Co3O4 nanoflowers. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 114:257–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.01.011
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N. Kurnaz Yetim carried out the experiments depending on synthesis and characterization of nanoparticles. E. Hasanoğlu Özkan studied the catalytic activities of nanoparticles and wrote the main manuscript text. H. Öğütçü carried out the antimicrobial assessment. Each author contributed to the final manuscript and discussed the findings.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
No ethical issues were violated in this study.
Consent to participate
All authors agree to participate.
Consent for publication
All authors agree for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme Luiz Dotto.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kurnaz Yetim, N., Hasanoğlu Özkan, E. & Öğütçü, H. Use of Co3O4 nanoparticles with different surface morphologies for removal of toxic substances and investigation of antimicrobial activities via in vivo studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 106585–106597 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29879-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29879-7