Abstract
Purpose
This research presents experimental investigation into the performance improvement of dredged sediment (DS) stabilization with ternary alkali-activated materials (AAMs) based on fly ash (FA), ground granulated blast-furnace slag (GGBS), and desulfurization gypsum (DG) for use as embankment fill materials.
Methods
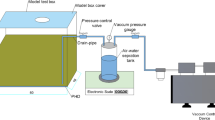
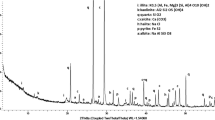
The performance of stabilized DS was assessed through a series of pH, electrical conductivity (EC), and unconfined compressive strength (UCS) tests. Microstructure characterization was also conducted to reveal the performance improvement mechanism of stabilized DS.
Results
The pH value of the stabilized DS exhibited a significant increase, reaching its peak at a DG content of 8%. This increase was attributed to the consumption of free water and the priority reaction of C-(A)-S–H. Subsequently, the pH value gradually decreased, primarily due to the consumption of OH− through Ca(OH)2 precipitation. Concurrently, the EC value steadily increased due to the rising Ca2+ concentration. Additionally, the UCS of the stabilized DS exhibited a noteworthy increase at a DG content of 8% and then showed a tendency to increase or decrease slightly with varying DG content, in line with the changes in pH value.
Conclusions
The performance improvement of the stabilized DS was attributable to the cementation provided gels (i.e., geopolymer gel and C-(A)-S–H gel), along with the pore-filling of ettringite (AFt) in the alkaline environment. Conversely, the performance of stabilized DS deteriorated due to the presence of microcracks resulting from excessive AFt expansion.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data, models, and code generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
References
ASTM (2003) ASTM D 2166: standard test method for unconfined compressive strength of cohesive soil. ASTM Int., West Conshohocken, PA, USA
ASTM (2011) ASTM D2487: standard practice for classification of soils for engineering purposes (Unified Soil Classification System). ASTM Int., West Conshohocken, PA, USA
Bian X, Zeng LL, Ji F, Xie M (2022) Plasticity role in strength behaviour of cement-phosphogypsum stabilized soils. J Rock Mech Geotech 14:1977–1988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.01.003
Borges PHR, Banthia N, Alcamand HA, Vasconcelos WL, Nunes EHM (2016) Performance of blended metakaolin/blastfurnace slag alkali-activated mortars. Cement Concrete Comp 71:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2016.04.008
Brils J, de Boer P, Mulder J, de Boer E (2014) Reuse of dredged material as a way to tackle societal challenges. J Soils Sediments 14(9):1638–1641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-014-0918-0
Chompoorat T, Thepumong T, Taesinlapachai S, Likitlersuang S (2021) Repurposing of stabilised dredged lakebed sediment in road base construction. J Soils Sediments 21(7):2719–2730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02974-3
Chrysochoou M, Grubb DG, Drengler KL, Malasavage NE (2010) Stabilized dredged material. III: mineralogical perspective. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 136(8):1037–1050. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000292
Chuah S, Duan WH, Pan Z, Hunter E, Korayem AH, Zhao XL, Collins F, Sanjayan JG (2016) The properties of fly ash based geopolymer mortars made with dune sand. Mater Design 92:571–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.12.070
Davidovits J (1991) Geopolymers - inorganic polymeric new materials. J Therm Anal Calorim 37(8):633–656. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01912193
Hassan A, Arif M, Shariq M (2019) Use of geopolymer concrete for a cleaner and sustainable environment-a review of mechanical properties and microstructure. J Clean Prod 223:704–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.051
He J, Shi XK, Li ZX, Zhang L, Feng XY, Zhou LR (2020) Strength properties of dredged soil at high water content treated with soda residue, carbide slag, and ground granulated blast furnace slag. Constr Build Mater 242:118126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118126
Hong SH, Hwang S, Lee CG, Park SJ (2023) Stabilization of As-contaminated dredged sediment using Al- and Fe- impregnated food waste biochar. J Soils Sediments. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03520-z
Hoy M, Horpibulsuk S, Rachan R, Chinkulkijniwat A, Arulrajah A (2017) Recycled asphalt pavement – fly ash geopolymers as a sustainable pavement base material: strength and toxic leaching investigations. Sci Total Environ 573:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.078
Huang YH, Dong C, Zhang CL, Xu K (2017) A dredged material stabilization treatment for fill soils in East China: a case history. Mar Georesour Geotec 35(6):865–872. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2016.1257669
Lehne J, Preston F (2018) Making concrete change. London, UK: The Royal Institute of International Affairs
Li Y, Liu XM, Li ZP, Ren YY, Wang YG, Zhang W (2021) Preparation, characterization and application of red mud, fly ash and desulfurized gypsum based eco-friendly road base materials. J Clean Prod 284:124777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124777
Meskini S, Samdi A, Ejjaouani H, Remmal T (2021) Valorization of phosphogypsum as a road material: Stabilizing effect of fly ash and lime additives on strength and durability. J Clean Prod 323:129161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129161
Miraki H, Shariatmadari N, Ghadir P, Jahandari S, Tao Z, Siddique R (2022) Clayey soil stabilization using alkali-activated volcanic ash and slag. J Rock Mech Geotech 14(2):576–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.08.012
Provis JL, Palomo A, Shi CJ (2015) Advances in understanding alkali-activated materials. Cement Concrete Res 78:110–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2015.04.013
Puligilla S, Mondal P (2013) Role of slag in microstructural development and hardening of fly ash-slag geopolymer. Cement Concrete Res 43(1):70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2012.10.004
Shen W, Zhou M, Zhao Q (2007) Study on lime-fly ash-phosphogypsum binder. Construct Build Mater 21:1480–1485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2006.07.010
Shi C, Jimenez AF, Palomo A (2011) New cements for the 21st century: the pursuit of an alternative to Portland cement. Cement Concrete Res 41(7):750–763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2011.03.016
Singh M, Garg M (1995) Phosphogypsum-fly ash cementitious binder - its hydration and strength development. Cement Concrete Res 25:752–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-8846(95)00065-K
Singh NB, Middendorf B (2020) Geopolymers as an alternative to Portland cement: an overview. Construct Build Mater 237:117455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117455
Song WL, Zhu ZD, Pu SY, Wan Y, Xu XY, Song SG, Zhang J, Yao K, Hu LL (2020) Multi-technical characterization and correlations between properties of standard cured alkali-activated high-calcium FA binders with GGBS as additive. Construct Build Mater 241:117996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.117996
Spagnoli G, Romero E, Fraccica A, Arroyo M, Gomez R (2022) The effect of curing conditions on the hydromechanical properties of a metakaolin-based soilcrete. Geotechnique 72(5):455–469. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.20.P.259
Standardization Administration of China (SAC), Ministry of Water Resources (1999) China National Standards GB/T50123–1999: standard for soil test method. China Planning Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Tenn N, Allou F, Petit C, Absi J, Rossignol S (2015) Formulation of new materials based on geopolymer binders and different road aggregates. Ceram Int 41:5812–5820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.01.010
Wan X, Ding JW, Jiao N, Mou C, Gao MY (2022) Mechanical and microstructural properties of cement-treated marine dredged clay with red mud and phosphogypsum. B Eng Geol Environ 81(7):266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02753-5
Wang DX, Abriak NE, Zentar R (2017) Dredged marine sediments used as novel supply of filling materials for road construction. Mar Georesour Geotec 35(4):472–480. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2016.1198945
Wang JH, Luan YC, Ma T, Zhang WG, Xu GJ (2023b) Experimental investigation on the mechanical performance and microscopic characterization of desulfurization gypsum-reinforced ternary geopolymer. Construct Build Mater 392:131855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.131855
Wang JH, Ma T, Luan YC, Wang SQ, Zhang Y (2023a) Investigation on the effects of desulfurization gypsum on the engineering properties of ternary geopolymers: improving the utilization of industrial wastes. J Clean Prod 414:137638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137638
Wu J, Deng YF, Zhang GP, Zhou AN, Tan YZ, Xiao HL, Zheng QS (2022) A generic framework of unifying industrial by-products for soil stabilization. J Clean Prod 321:128920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128920
Wu YJ, Xu JL, Lu YT, Zhang XD, Tran QC (2023) Geotechnical properties of marine dredged fill with different particle size. Mar Georesour Geotec 41(1):24–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2021.2009070
Yao X, Zhang Z, Zhu H, Chen Y (2009) Geopolymerization process of alkali-metakaolinite characterized by isothermal calorimetry. Thermochim Acta 493(1):49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2009.04.002
Yazdi MA, Liebscher M, Hempel S, Yang J, Mechtcherine V (2018) Correlation of microstructural and mechanical properties of geopolymers produced from fly ash and slag at room temperature. Construct Build Mater 191:330–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.10.037
Yin J, Hu MM, Xu GZ, Han WX, Miao YH (2020) Effect of salinity on rheological and strength properties of cement-stabilized clay minerals. Mar Georesour Geotec 38(5):611–620. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2019.1608484
Yoobanpot N, Jamsawang P, Simarat P, Jongpradist P, Likitlersuang S (2020) Sustainable reuse of dredged sediments as pavement materials by cement and fly ash stabilization. J Soils Sediments 20(10):3807–3823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02635-xx
Zeng LL, Bian X, Zhao L, Wang YJ, Hong ZS (2021) Effect of phosphogypsum on physiochemical and mechanical behaviour of cement stabilized dredged soil from Fuzhou. China Geomech Energy Envir 25:100195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gete.2020.100195
Zeng LL, Hong ZS, Tian WB, Shi JW (2018) Settling behavior of clay suspensions produced by dredging activities in China. Mar Georesour Geotec 36(1):30–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2016.1274808
Zhang XW, Liu XY, Zhang W, Yang AW, Xu YQ (2022) Sedimentation of the fine-grained dredged slurry in the marine environment. B Eng Geol Environ 81(5):173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-022-02680-5
Funding
This study is supported by the Open Foundation of Key Laboratory of Underground Engineering, Fujian Province University (Fujian University of Technology) (KF–06–22006), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 51978159, 52308342), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (Grant number 2022J05186), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (RF1028623071), and the funding from the State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Building Science in South China University of Technology (2022ZC01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Victor Magar
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Wang, H., Ding, J. et al. Investigation on performance improvement of dredged sediment with high water content stabilized with alkali-activated materials. J Soils Sediments 24, 1464–1473 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03680-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03680-y