Abstract
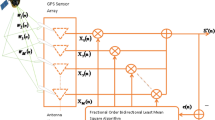
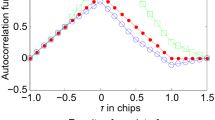
In this paper, a novel adaptive interference suppression algorithm is proposed for high dynamic GPS (global positioning system) receiver. The new method incorporates derivative constraints on the interference DOA (direction of arrival) into power minimization approach, which could broaden the width of nulls in the interferences directions and adapt to the rapid change of the interference directions. Compared with the traditional wide nulling algorithm based on the derivative constraints, the new method does not have to know or estimate the DOAs of the desired signal and the interference. The new method is firstly discussed in the context of spatial processing, and then extended to space-time adaptive processing to mitigate wideband diffusive multipath interference. Effectiveness of the new method is verified via simulation examples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fang Y P, Dong E L. The analysis to effective interfering GPS guided missile (in Chinese). Aerospace Electron Warfare, 2001, 2: 35–39
Jay R S. Interference mitigation approaches for the global positioning system. Lincoln Lab J, 2003, 14: 168–180
Malmström J. Robust navigation with GPS/INS and adaptive beamforming. Swedish Defence Research Agency System Technology Division, FOI-R-0848-SE, 2003
Zoltowski M D, Gecan A S. Advanced adaptive null steering concepts for GPS. In: Military Communications Conference. California: IEEE Press, 1995. 1214–1218
Sun W, Amin M G. A self-coherence anti-jamming GPS receiver. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2005, 53: 3910–3915
Huang W, Lu D, Wu R B, et al. A novel blind GPS anti-jamming algorithm based on subspace technique. In: International Conference of Signal Processing. Guilin, China: IEEE Press, 2006. 448–450
Li P, Lu D, Wu R B, et al. Adaptive anti-jamming algorithm based on the characteristics of the GPS signal. In: Proceedings of 2008 International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communication Systems. Xiamen, China: IEEE Press, 2008. 181–184
Ziedan N I, Garrison J L. Extended Kalman filter-based tracking of weak GPS signals under high dynamic conditions. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation. California: ION, 2004. 20–31
Chen K. Real-time precise point positioning and its potential applications. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation. California: ION, 2004, 1844–1854
Hurd W J, Statman J J, Vilnrotter V A. High dynamic GPS receiver using maximum likelihood estimation and frequency tracking. IEEE Trans Aerospace Electron Syst, 1988, 23: 425–436
Gershman A B, Serebryakov G V, Bohme J F. Constrained Hung-Turner adaptive beam-forming algorithm with additional robustness to wideband and moving jammers. IEEE Trans Antennas Propagate, 1996, 44: 361–366
Gershman A B, Nickel U, Bohme J F. Adaptive beamforming algorithms with robustness against jammer motion. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 1997, 45: 1878–1885
Hinedi S, Statman J I. High-Dynamic GPS Trackings Final Report. JPL Publication 88-35, 1988. 9–11
Wu R B. The theory and realisation of the space-time adaptive filtering on airborne early warning radar (in Chinses). Dissertation for the Doctoral Degree. Xi’an: Xidian University, 1994
Bao Z, Liao G S, Wu R B. Space-time adaptive filtering for clutter suppression on airborne phased array radar (in Chinses). J Electron, 1993, 21: 1–8
Fante R L, Vaccaro J J. Wideband cancellation of interference in a GPS receiver array. IEEE Trans AES, 2000, 36: 549–564
Fante R L, Torres J A. Cancellation of diffuse jammer multipath by an airborne adaptive radar. IEEE Trans AES, 1995, 31: 805–820
Hatke G F. Adaptive array processing for wideband nulling in GPS system. In: Conference Record of the Thirty-Second Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers. Grove: Omnipress, 1998. 1332–1336
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, R., Li, C. & Lu, D. Power minimization with derivative constraints for high dynamic GPS interference suppression. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 55, 857–866 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-011-4309-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-011-4309-5