Abstract
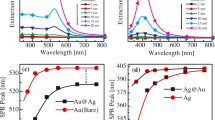
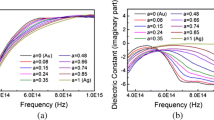
The local surface plasmon resonances (LSPR) of bimetallic Au-Ag core-shell nanostructure particles are studied using discrete-dipole approximation (DDA) method and plasmon hybridization theory. It is found that LSPR is sensitive to the surrounding medium refractive index, showing a distinct redshift with increasing the surrounding medium refractive index. Au-Ag core-shell nanostructure exhibits a strong coupling between the core and shell plasmon resonance modes. The coupled resonance mode wavelengths show dependence on the layer thickness and the composition of core and shell metal. LSPR can be tuned over an extended wavelength range by adjusting the ratio of core to shell. The lower energy mode ω − of Au-Ag core-shell nanoparticle shows a redshift with increasing Ag shell thickness or Au core radius, while the higher energy mode ω + shows the opposite behaviors. In addition, Ag-Au core-shell nanostructure compound particles are also studied with the same method, whose properties are different from that of Au-Ag core-shells. For the sake of clarity, the wavelength shifts of LSPR are plotted as functions of surrounding media refractive index, core radius, shell thickness, and core-shell ratio with figures of merits (FOM). The underlying mechanisms are analyzed with the plasmon hybridization theory and phase retardation effect.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nie S, Enmory SR (1997) Probing single molecules and single nanoparticles by surface-enhanced. Science 275:1102
Warnes WL, Dereux A, Bobesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424:824
Murray WA, Barnes WL (2007) Plasmonic materials. Adv Mater 19:3771
Maier SA (2007) Plasmonics: fundamentals and application. Springer
Novotny L, Hecht B (2006) Principle of nano-optics. Cambridge University Press
Shuford KL, Ratner MA, Schatz GC (2005) Multipolar excitation in triangular nanoprisms. J Chem Phys 123:114713
Kelly KL, Coronado E, Zhao LL, Schatz GC (2003) The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: the influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J Phys Chem B 107:668
Ma YW, Zh WW, Zhang LH, Zhang J, Jian GS, Pan Sh (2013) Theoretical study of the local surface plasmon resonance properties of silver nanosphere clusters. Plasmonics 8:1351
Aubry A, Lei DY, Maier SA, Pendry JB (2010) Interaction between plasmonic nanoparticles revisited with transformation optics. Phys Rev Lett 105:233901
Alaverdyan Y, Seplveda B, Eurenius L, Olsson E, Kall M (2007) Optical antennas based on coupled nanoholes in thin metal films. Nature Phys 3:884
Bruzzzone S, Arrighini GP, Guidotti c (2003) Theoretical study of the optical absorption behavior of Au-Ag core-shell nanoparticles. Master Sci Eng C 23:965
Moskovits M, Srnova-Sloufova I, Vlckova B (2002) Bimetallic Ag-Au nanoparticles: extracting meaningful optical constants from the surface-plasmon extinction spectrum. J Chem Phys 116:10435
Chaudhuri RG, Paria S (2011) Core/shell nanoparticles: classes, properties, synthesis mechanisms, characterization, and applications. Chem Rev 112:2373
Wu DJ, Liu XJ (2010) Optimization of bimetallic gold and silver alloy nanoshell for bimedical applications in vivo. App Phys Lett 97:061904
Wang C, Peng S, Chan R, Sun SH (2009) Synthesis of AuAg alloy nanoparticles from core/shell structured Ag/Au. Small 5:567
Bachelier G, Russier-Antoine I, Benichou E, Jonin C (2008) Fano profiles induced by near-field coupling in heterogeneous dimers of gold and silver nanoparticles. Phys Rev Lett 110:19740
Zhu J, Zhao JW, Li JJ (2010) Location-depeendent local field enhancement along the surface of metal-dielectric core-shell nanostructure. Plasmonics 311:5
Draine BT, Flatau PJ (1994) Discrete-dipole approximation for scattering calculations. J Opt Soc Am A 11:1491
Gresho PM, Sani RL (2000) Incompressible flow and finite element method. Wiley, New York
Taflove A (2000) Computational electrodynamics: the finite difference time domain method. Artech House, Norwood
DDSCAT7.2 arXiv:1202.3424
Purcell EM, Pennypacker CR (1973) The discrete-dipole approximation and its application to inerstellar graphite grains. Astrophys 186:705
Bohren CF, Huffman DR (2000) Absorption and scattering of light by small particles. Wiley, New York
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 12:4370
Kreibig U., Vollmer M (1995) Optical properties of metal clusters. Springer Ser.Mater.Sci, vol 25. Springer, Berlin
Prodan E, Radbloff C, Halas NJ, Nordander P (2003) A hybridization model for the plasmon reponse of complex nanostructures. Science 302:419
Prodan E, Nordander P (2004) Plamon hybridization in spherical nanoparticels. J Chem Phys 120:5444
Pea-Rodrłguez O, Pal U, Rodrłguez-Iglesias V, et al. (2011) Configuring Au and Ag nanorods for sensing applications. J Opt Soc Am B 4:714–720
Pea-Rodrłguez O, Rodrłguez-Iglesias V, Pal U (2011) Au@Ag core-shell nanoparticles: efficient all-plasmonics Fano-resonance generators. Nanosclae 3:3609
Mulvaney P, Giersig M, Henglein A (1993) Electrochemistry of multilayer colloids: preparation and absorption spectrum of gold-coated silver particles. J Phys Chem 97:7061
Acknowledgments
We thank the financial support from the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (1308085QA19, 1408085QA15), the Key Scientific Research Foundation of Anhui Provincial Education Department under grant nos. (KJ2013A180, KJ2012B087, and KJ2011Z234), and the Young Foundation of AnQing Normal University (KJ201313 and KJ201008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, YW., Zhang, LH., Wu, ZW. et al. The Study of Tunable Local Surface Plasmon Resonances on Au-Ag and Ag-Au Core-Shell Alloy Nanostructure Particles With DDA Method. Plasmonics 10, 1791–1800 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9997-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9997-z