Abstract
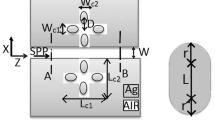
In this study, we designed and evaluated a sensing architecture using a metal–insulator-metal waveguide connected to an H-shape resonator for refractive index change measurement in two unique bands of refractive index: n = 1.8–1.95 and n = 2.1–2.3. A 3-D finite element approach is used to investigate the device sensing characteristics. For the waveguide, the H-shape resonator offers a cavity resonance zone where the substance to be detected is filled. The transmission curve plot revealed that the suggested arrangement generates two resonant dips. The resonant wavelength was found to have a direct and linear relationship with the refractive index of the material being sensed, the length of vertical height, and the width of the cavity’s mid-arm. Sensitivity and figure of merit have the highest values of 1007.78 nm/RIU and 29 \({\mathrm{RIU}}^{-1},\) respectively. The highest quality-factor obtained was 60. The proposed structure can be employed for refractive index sensing at the nanometer scale and increasing spectroscopy applications since it has features like nano size, high sensitivity, a linear relationship between tuning parameters, and a larger sensing span.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
All the references cited are available.
References
Dragoman M, Dragoman D (2008) Plasmonics : applications to nanoscale terahertz and optical devices 32:1–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pquantelec.2007.11.001
Zhang J, Zhang L, Xu W (2012) Surface plasmon polaritons: physics and applications. J Phys D Appl Phys. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/45/11/113001
Maier SA (2007) Chapter 2 surface plasmon polaritons at metal. Plasmon Fundam Appl 0:1–2
Lin X-S, Huang X-G (2008) Tooth-shaped plasmonic waveguide filters with nanometeric sizes. Opt Lett 33:2874. https://doi.org/10.1364/ol.33.002874
Zhang Q, Huang X-G, Lin X-S, Tao J, Jin X-P (2009) A subwavelength coupler-type MIM optical filter. Opt Express 17:7549. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.17.007549
Jin XP, Huang XG, Tao J, Lin XS, Zhang Q (2010) A novel nanometeric plasmonic refractive index sensor. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 9:134–137. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2009.2038909
Tao J, Wang QJ, Huang XG (2011) All-optical plasmonic switches based on coupled nano-disk cavity structures containing nonlinear material. Plasmonics 6:753–759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-011-9260-1
Yang R, Lu Z (2012) Subwavelength plasmonic waveguides and plasmonic materials. Int J Opt. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/258013
Onbasli MC, Okyay AK (2010) Nanoantenna couplers for metal-insulator-metal waveguide interconnects. Plasmon Met Nanostructures Their Opt Prop VIII 7757:77573R. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.876177
Rahman ZU, Krishna KM, Reddy KK, Babu MV, Mirza S, Fathima SY (2018) Ultra wide band band-pass filters using plasmonic MIM waveguide based ring resonators, IEEE Photonics Technol Lett PP (2018) 1. https://doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2018.2866966
Ebadi SM, Member S, Ebadi SM, Member S, Örtegren J (2020) A multipurpose and highly-compact plasmonic filter based on metal-insulator-metal a multipurpose and highly-compact plasmonic filter based on 12. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOT.2020.2974959
Chauhan D, Kumar A, Adhikari R, Saini RK, Chang SH, Dwivedi RP (2021) High performance vanadium dioxide based active nano plasmonic filter and switch. Optik (Stuttg) 225:165672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.165672
Taheri AN, Kaatuzian H (2015) Numerical investigation of a nano-scale electro-plasmonic switch based on metal-insulator-metal stub filter. Opt Quantum Electron 47:159–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-014-9895-1
Wen K, Yan L, Pan W, Luo B, Guo Z, Guo Y (2012) Wavelength demultiplexing structure based on a plasmonic metal-insulator-metal waveguide. J Opt (United Kingdom) 14. https://doi.org/10.1088/2040-8978/14/7/075001
Chauhan D, Mola GT, Dwivedi RP (2020) An ultra-compact plasmonic modulator/switch using VO2 and elasto-optic effect. Optik (Stuttg) 201:163531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.163531
Dwivedi RP, Lee HS, Song JH, An S, Lee EH (2011) Plasmonic modulator utilizing three parallel metal-dielectric-metal waveguide directional coupler and elasto-optic effects. Opt Commun 284:1418–1423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2010.10.038
Wahsheh RA, Lu Z, Abushagur MAG (2009) Nanoplasmonic couplers and splitters. Opt Express 17:19033. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.17.019033
Guo Y, Yan L, Pan W, Luo B, Wen K, Guo Z, Li H, Luo X (2011) A plasmonic splitter based on slot cavity. Opt Express 19:13831. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.19.013831
Wu T, Liu Y, Yu Z, Peng Y, Shu C, Ye H (2014) The sensing characteristics of plasmonic waveguide with a ring resonator. Opt Express 22:7669. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.22.007669
Binfeng Y, Guohua H, Ruohu Z, Yiping C (2014) Design of a compact and high sensitive refractive index sensor base on metal-insulator-metal plasmonic Bragg grating. Opt Express 22:28662. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.22.028662
Rakhshani MR, Mansouri-Birjandi MA (2017) High sensitivity plasmonic refractive index sensing and its application for human blood group identification. Sens Actuators B Chem 249:168–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.04.064
Butt MA, Khonina SN, Kazanskiy NL (2021) Metal-insulator-metal nano square ring resonator for gas sensing applications. Waves Random Complex Media 31:146–156. https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2019.1568609
Butt MA, Kazanskiy NL, Khonina SN (2020) Highly sensitive refractive index sensor based on plasmonic bow tie configuration. Photonic Sens 10:223–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13320-020-0588-z
Chen Z, Yu L (2014) Multiple Fano resonances based on different waveguide modes in a symmetry breaking plasmonic system. IEEE Photonics J. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOT.2014.2368779
Chen Z, Cao X, Song X (2015) Side-coupled cavity-induced Fano resonance and its application in nanosensor. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0035-y
Zhang Y, Li S, Zhang X, Chen Y, Wang L, Zhang Y, Yu L (2016) Evolution of Fano resonance based on symmetric/asymmetric plasmonic waveguide system and its application in nanosensor. Opt Commun 370:203–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2016.03.001
Tang Y, Zhang Z, Wang R, Hai Z, Xue C, Zhang W, Yan S (2017) Refractive index sensor based on fano resonances in metal-insulator-metal waveguides coupled with resonators. Sensors (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040784
Deng Y, Cao G, Yang H, Li G, Chen X, Lu W (2017) Tunable and high-sensitivity sensing based on Fano resonance with coupled plasmonic cavities. Sci Rep 7:2–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10626-1
Zhang Y, Kuang Y, Zhang Z, Tang Y, Han J, Wang R, Cui J, Hou Y, Liu W (2019) High-sensitivity refractive index sensors based on Fano resonance in the plasmonic system of splitting ring cavity-coupled MIM waveguide with tooth cavity. Appl Phys A. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2283-0
Wang S, Zhao T, Yu S, Ma W (2020) High-performance nano-sensing and slow-light applications based on tunable multiple Fano resonances and EIT-like effects in coupled plasmonic resonator system. IEEE Access 8:40599–40611. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2974491
Xiao G, Xu Y, Yang H, Ou Z, Chen J, Li H, Liu X, Zeng L, Li J (2021) High sensitivity plasmonic sensor based on fano resonance with inverted u-shaped resonator. Sensors (Switzerland) 21:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041164
Chauhan D, Adhikari R, Saini RK, Chang SH, Dwivedi RP (2020) Subwavelength plasmonic liquid sensor using Fano resonance in a ring resonator structure. Optik (Stuttg) 223:165545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.165545
Baqir MA, Farmani A, Fatima T, Raza MR, Shaukat SF, Mir A (2018) Nanoscale, tunable, and highly sensitive biosensor utilizing hyperbolic metamaterials in the near-infrared range. Appl Opt 57:9447. https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.57.009447
Baqir MA (2019) Wide-band and wide-angle, visible- and near-infrared metamaterial-based absorber made of nanoholed tungsten thin film. Opt Mater Express 9:29–31. https://doi.org/10.1364/OME.9.002358
Naveed MA, Bilal RMH, Baqir MA, Bashir MM, Ali MM, Rahim AA (2021) Ultrawideband fractal metamaterial absorber made of nickel operating in the UV to IR spectrum. Opt Express 29:42911. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.446423
Bilal RMH, Baqir MA, Iftikhar A, Naqvi SA, Mughal MJ, Ali MM (2022) Polarization-controllable and angle-insensitive multiband Yagi-Uda-shaped metamaterial absorber in the microwave regime. Opt Mater Express 12:798. https://doi.org/10.1364/ome.451073
Adhikari R, Chauhan D, Mola GT, Dwivedi RP (2021) A review of the current state-of-the-art in Fano resonance-based plasmonic metal-insulator-metal waveguides for sensing applications. Opto-Electronics Rev 29:148–166. https://doi.org/10.24425/opelre.2021.139601
Adhikari R, Sbeah Z, Chauhan D, Chang SH, Dwivedi RP (2022) A voyage from plasmonic to hybrid waveguide refractive index sensors based on wavelength interrogation Technique: a Review. Brazilian J Phys 52:61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-022-01064-0
Xie YY, Huang YX, Zhao WL, Xu WH, He C (2015) A novel plasmonic sensor based on metal-insulator-metal waveguide with side-coupled hexagonal cavity. IEEE Photonics J 7(2):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOT.2015.2419635
Chen L, Liu Y, Yu Z, Wu D, Ma R, Zhang Y, Ye H (2016) Numerical analysis of a near-infrared plasmonic refractive index sensor with high figure of merit based on a fillet cavity. Opt Express 24:9975. https://doi.org/10.1364/oe.24.009975
Rakhshani MR, Mansouri-Birjandi MA (2016) High-sensitivity plasmonic sensor based on metal-insulator-metal waveguide and hexagonal-ring cavity. IEEE Sens J 16:3041–3046. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2016.2522560
Butt MA, Khonina SN, Kazanskiy NL (2019) Plasmonic refractive index sensor based on metal–insulator-metal waveguides with high sensitivity. J Mod Opt 66:1038–1043. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500340.2019.1601272
Butt MA, Khonina SN, Kazanskiy NL (2019) Plasmonic refractive index sensor based on M-I-M square ring resonator. Int Conf Comput Electron Electr Eng ICE Cube 2018:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICECUBE.2018.8610998
Danaie M, Shahzadi A (2019) Design of a high-resolution metal–insulator–metal plasmonic refractive index sensor based on a ring-shaped si resonator. Plasmonics 14:1453–1465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-00926-9
Li X, Zhang Z, Guo F, Huang Y, Zhang B, Zhang L, Yang Q, Tan Y, Liu X, Bai H, Song Y (2019) Tunable plasmonically induced reflection in HRR-coupled MIM waveguide structure. Optik (Stuttg) 199:163353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.163353
Al Mahmud R, Faruque MO, Sagor RH (2021) A highly sensitive plasmonic refractive index sensor based on triangular resonator. Opt Commun 483:126634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2020.126634
Kazanskiy NL, Khonina SN, Butt MA (2020) Plasmonic sensors based on metal-insulator-metal waveguides for refractive index sensing applications: a brief review. Phys E Low-Dimens Syst Nanostructures 113798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2019.113798
Zafar R, Salim M (2015) Enhanced figure of merit in Fano resonance-based plasmonic refractive index sensor. IEEE Sens J 15:6313–6317. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2015.2455534
Chou Chau YF, Chou Chao CT, Huang HJ, Kumara NT, Lim CM CM, Chiang HP (2019) Ultra-high refractive index sensing structure based on a metal-insulator-metal waveguide-coupled T-shape cavity with metal nanorod defects. Nanomaterials. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101433
Butt MA, Khonina SN, Kazanskiy NL (2019) A multichannel metallic dual nano-wall square split-ring resonator: design analysis and applications. Laser Phys Lett. https://doi.org/10.1088/1612-202X/ab5574
Rahmatiyar M, Danaie M, Afsahi M (2020) Employment of cascaded coupled resonators for resolution enhancement in plasmonic refractive index sensors. Opt Quantum Electron. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02266-z
Kazanskiy NL, Butt MA, Khonina SN (2020) Nanodots decorated MIM semi-ring resonator cavity for biochemical sensing applications. Photonics Nanostructures - Fundam Appl 42:100836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.photonics.2020.100836
Laskar JM, Kumar PS, Herminghaus S, Daniels KE, Schröter M (2016) High refractive index immersion liquid for superresolution 3D imaging using sapphire-based aplanatic numerical aperture increasing lens optics. 55(12):3165–3169
Kang S, Nakajima S, Arakawa Y, Konishi G, Watanabe J (2013) Large extraordinary refractive index in highly birefringent nematic liquid crystals of dinaphthyldiacetylene-based materials. J Materials Chem. 27:4222-4226. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tc30640b
Wypych G (2016) Physical properties of fillers and filled materials. In: Wypych G (ed) Handb Fill, Fourth Ed. ChemTec Publishing p 373–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-895198-91-1.50007-5
Xiang L, Huang L (2020) High-sensitivity complex refractive index sensor by designing a slot-waveguide side-coupled Fano resonant cavity. Opt Commun 475:126298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2020.126298
Zhang Z, Luo L, Xue C, Zhang W, Yan S (2016) Fano resonance based on metal-insulator-metal waveguide-coupled double rectangular cavities for plasmonic nanosensors. Sensors (Switzerland) 16:22–24. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050642
Wang Q, Ouyang Z, Sun Y, Lin M, Liu Q, Zheng G, Fan J (2018). Tunable nanosensor based on Fano resonances created by changing the deviation angle of the metal core in a plasmonic cavity. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041026
Zhao X, Zhang Z, Yan S (2017) Tunable Fano resonance in asymmetric MIM waveguide structure. Sensors (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/s17071494
Liu G, Liu Z, Liu G, Fu X (2020) Plasmonic sensors with an ultra-high figure of merit. Nanotechnology 31:11. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab5a00
Shi X, Ma L, Zhang Z, Tang Y, Zhang Y, Han J, Sun Y (2018) Dual Fano resonance control and refractive index sensors based on a plasmonic waveguide-coupled resonator system. Opt Commun 427:326–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2018.06.042
Jina L, Chen J, Liu X, Tian H, Wang J, Cui J, Rohimah S (2021) Optical sensing based on multimode Fano resonances in metal-insulator-metal waveguide systems with X-shaped resonant cavities. 60:5312–5319
Zubaidah binti Haji Juma S, Chao CT, Chau YF, Mahadi AH, Kooh MR, Kumara NT, Chiang HP (2021) Plasmonic refractive index sensor based on the combination of rectangular and circular resonators including baffles. Chinese J Phys 71:286–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2021.02.006
Zhang Z, Yang J, He X, Zhang J, Huang J, Chen D, Han Y (2018) Plasmonic refractive index sensor with high figure of merit based on concentric-rings resonator. Sensors (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010116
Amoosoltani N, Mehrabi K, Zarifkar A, Farmani A, Yasrebi N (2021) Double-ring resonator plasmonic refractive index sensor utilizing dual-band unidirectional reflectionless propagation effect. Plasmonics 16:1277–1285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-021-01395-9
Rakhshani MR (2020) Tunable and sensitive refractive index sensors by plasmonic absorbers with circular arrays of nanorods and nanotubes for detecting cancerous cells. Plasmonics 15:2071–2080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01237-0
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Shoolini University, India.
Funding
The research was not financially supported by any institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have the same contributions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adhikari, R., Sbeah, Z., Gupta, R. et al. Compact and Sensitive H-Shaped Metal–Dielectric–Metal Waveguide Plasmonic Sensor. Plasmonics 17, 1593–1606 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-022-01646-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-022-01646-3