Abstract
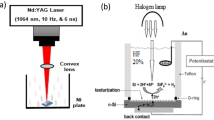
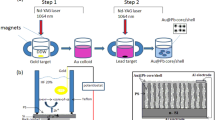
Gold-titanium dioxide nanoparticles (Au-TiO2 NPs) were synthesized via pulsed Nd:YAG laser ablation in the CTAB under the influence of an external magnetic field produced. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV–Vis spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) have been utilized in order to analyze Au-TiO2 NPs. The XRD pattern related to Au-TiO2 NPs indicated that they have been polycrystalline and the specimens Au-TiO2 were nanocrystalline. In the case when applying a magnetic field, spherical NPs are generated, particle agglomeration is reduced, and particle size declines from 31 to 25 nm, according to SEM. Following ablation with a magnetic field, the optical energy gap of Au-TiO2 NPs increased from 3.5 to 3.7 eV. With current density–voltage (J-V) measurements, the electrical parameters of Al/Au-TiO2/PS/Si/Al heterojunction, including the barrier height (ΦB) and ideal factor (n), were indicated. The efficiency regarding Au-TiO2/PS photodetectors has been enhanced over various wavelengths, quantum efficiency (QE) of Au-TiO2/PS photodetectors has been reduced after adding a magnetic field during the process of ablation.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Nayef UM, Kamel RI (2020) Bi2O3 nanoparticles ablated on porous silicon for sensing NO2 gas. Optik 208:164146
Mutlak Falah A-H, Ahmed AF, Nayef UM, Al-zaidi Q, Abdulridha SK (2021) Improvement of absorption light of laser texturing on silicon surface for optoelectronic application. Optik 237:166755
Jwied DH, Nayef UM, Mutlak FAH (2021) Synthesis of C: Se nanoparticles ablated on porous silicon for sensing NO2 and NH3 gases. Optik 241:167013
Khudiar SS, Mutlak FA-H, Nayef UM (2021) Synthesis of ZnO nanostructures by hydrothermal method deposited on porous silicon for photo-conversion application. Optik 247:167903
Ahmed AF, Yaseen WI, Abbas QA, Mutlak FA (2021) Plasma treatment effect on SnO2–GO nano-heterojunction: fabrication, characterization and optoelectronic applications. Appl Phys A 127:746
Nayef UM, Muayad MW, Khalaf HA (2014) Eur Phys J Appl Phys 66:20104
Abood HK, Mutlak FA-H (2020) Structural, morphological and optical properties of n-type porous silicon-effect of etching current density. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng 757:012065
Canham LT (1990) Appl Phys Lett 57(10):159–164
Nayef UM, Hussein HT, Hussien AMA (2018) Optik - Int J Light Electron Optics 172:1134–1139
Kamel RI, Ahmed DS, Nayef UM (2019) Synthesis of Bi2O3 nanoparticles by laser ablation on porous silicon for photoconversion application. Optik 193:163013
Nayef UM, Hubeatir KA, Abdulkareem ZJ (2016) Characterisation of TiO2 nanoparticles on porous silicon for optoelectronics application. Mater Technol Adv Funct Mater Vol. 31 No. 14
Abdulkhaleqa NA, Hasanb AK, Nayef UM (2020) Enhancement of photodetectors devices for silicon nanostructure from study effect of etching time by photoelectrochemical etching Technique. Optik 206:164325
Falah A-H (2014) Mutlak, Photovoltaic enhancement of Si micro- and nanostructure solar cells via ultrafast laser texturing. Turk J Phys 38:130–135
Mital G, Manoj T (2011) Phys Chem 56(16):1639–1657
Noothongkaew S, Han JK, Lee YB, Thumthan O, An K-S (2017) Au NPs decorated TiO2 nanotubes array candidate for UV photodetectors. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int 27:641–646
Abdulkhaleq NA, Nayef UM, Albarazanchi AKH (2020) MgO nanoparticles synthesis via laser ablation stationed on porous silicon for photoconversion application. Optik 212:164793
Jwied DH, Nayef UM, Mutlak FAH (2021) Preparation and characterization of C: Se nano-rods ablated on porous silicon. Optik 239:166811
Lin J, Guo M, Yip CT (2013) High temperature crystallization of free-standing anatasenTiO2 nanotube membranes for high efficiency dye sensitized solar cells. Adv Funct Matter 23:5952–5960
Anitha VC, Arghya BN, Joo SW, Ki B (2015) Min, Barrier oxide layer engineering of TiO2 nanotube arrays to get single and multistage Y-branched nanotubes: effect of voltage ramping and electrolyte conductivity. Mater Sci Eng B 195:1–11
Yang M, Zhu JL, Liu W, Sun JL (2011) Novel photodetectors based on double-walled carbon nanotube Film/TiO2 nanotube array heterodimensional contacts. Nano Res 4:901–907
Hong SM, Lee S, Jung HJ (2013) Bull Korean Chem Soc 34(1):279–282
Barreca F, Acacia N, Barletta E, Spadaro D, Curro G, Neri F (2010) Appl urf Sci 256:6408–6412
Hussein HT, Nayef UM, Hussien AMA (2019) Synthesis of graphene on porous silicon for vapor organic sensor by using photoluminescence. Optik 180:61–70
Hartland GV (2011) Optical studies of dynamics in noble metal nanostructures. Che Rev 111:3858–3887
Garcia M (2011) Surface plasmons in metallic nanoparticles: fundamentals and applications. J Appl Phys 44:283001–19
Hammad QK, Ayyash AN, Mutlak FAH (2012) Improving SERS substrates with Au/Ag-coated Si nanostructures generated by laser ablation synthesis in PVA. J Opt
Zhu J, Du HF, Zhang Q et al (2019) SERS detection of glucose using graphene-oxide-wrapped gold nanobones with silver coating. J Mater Chem C 7:3322–3334
Sau TK, Rogach AL, Jackel F, Klar TA, Feldmann J (2010) Properties and applications of colloidal nonspherical noble metal nanoparticles. Adv Mater 22:1805–1825
Abid HN, Nayef UM, Mutlak FA (2019) Preparation and characterization Co3O4 nanoparticles on porous silicon for humidity sensor by photoluminescence. Optik 178:379–383
Nguyen NT, Altomare M, Yoo J, Schmuki P (2015) Efficient photocatalytic H-2 evolution: controlled dewetting-dealloying to fabricate site-selective high-activity nanoporous Au particles on highly ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays. Adv Mater 27:3208–3215
Liu GQ, Liu Y, Tang L, Liu XS, Fu GL, Liu ZQ (2019) Semiconductorenhanced Raman scattering sensors via quasi-three-dimensional Au/Si/Au structures. Nanophotonics 8:1095–1107
Murawska M, Skrzypczak A, Kozak M (2012) Structure and morphology of gold nanoparticles in solution studied by TEM,SAXS and UV-Vis. ACTA Phys Polonica A
Abed MA, Mutlak FA, Ahmed, AF, Nayef UM, Abdulridha SK, Jabir MS (2021) Synthesis of Ag/Au (core/shell) nanoparticles by laser ablation in liquid and study of their toxicity on blood human components. J Phys: Conf Ser 1795:012013
Albornoz C, Jacobo SE (2006) J Magn Magn Mater 12:305
Wan J et al (2005) Cryst Growth 276:571
Martinez-Mera I et al (2007) Mater Lett 61:4447
Rashid TM, Nayef UM, Jabir MS, Mutlak FA-H (2021) Study of optical and morphological properties for Au-ZnO nanocomposite prepared by Laser ablation in liquid. J Phys: Conf Ser 1795(1):012041
Hahn A, Barcikowski S, Chichkov BN (2008) J Laser Micro/Nano Eng 3:2
Sasaki K, Takada N (2010) Pure Appl Chem 82:1317
Nayef UM, Khudhair IM, Kayahan E (2017) Optik 144:546–552
Jamal RK, Mutlak FA-H, Ibrahim FT, Nayef UM (2020) Optik 218:164971
Nayef UM, Khudhair IM (2017) Optik 135:169–173
Rashid TM, Nayef UM, Jabir MS, Mutlak FA (2021) Synthesis and characterization of Au:ZnO (core:shell) nanoparticles via laser ablation. Optik 244:167569
Bisi O, Ossicini S, Pavesi L (2000) Porous silicon: a quantum sponge structure for silicon based optoelectronics. Surf Sci Rep 38:1–126
Nayef UM, Kamel RI (2020) Enhancement the electrical properties of porous silicon for photodetectors applications by depositing Bi2O3 nanoparticles. Optik 207:163847
Sailor MJ, Heinrich JL, Lauerhaas JM (1997) Stud Surf Sci Catal 103:209–235. Elsevier
Azim AM, Ashrafabadi S, Kanjuri F (2012) Electrical behavior of nanostructured porous silicon. Acta Phys Pol A 122(1)
Jwied DH, Nayef UM, Mutlak FAH (2021) Synthesis of C: Se (core:shell) nanoparticles via laser ablation on porous silicon for photodetector application. Optik 231:166493
Nayef UM (2017) Optik 130:441–447
Mutlak FA, Taha AB, Nayef UM (2018) Silicon 10:967–974
Jwied D, Nayef U, Mutlak F (2021) Improvement of responsivity of C:Se nanoparticles ablated on porous silicon. Optik 241
Sulaiman EM, Mutlak FAH, Nayef UM (2022) High-performance photodetector of Au–MgO/PS nanostructure manufactured via pulsed laser ablation technique. Opt Quant Electron 54:744
Alber AS, Mutlak FAH (2022) A novel laser-assisted approach for synthesis of AuNPs/PS nanostructures as photodetector. J Opt
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the University of Technology-Iraq for the logistic support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Uday Nayef and Falah Mutlak conceived and supervised the study and designed the experiments. Ahmad Jwar carried out the XRD, SEM, and the absorption measurements. Uday Nayef fabricated the PS and hybrid Au-TiO2 NPs/PS layers acquired the electrical characterization and spectral responsivity. Uday Nayef drafted the initial version of the manuscript. All the authors commented on the results, provided ideas for the study, and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jwar, A.J., Nayef, U.M. & Mutlak, F.AH. Study Effect of Magnetic Field on Au-TiO2 Core–Shell Nanoparticles via Laser Ablation Deposited on Porous Silicon for Photodetector. Plasmonics 18, 595–605 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01791-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01791-3